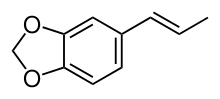
 trans-Isosafrole | |
 cis-Isosafrole | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name 5-(Prop-1-enyl)-2H-1,3-benzodioxole | |
| Other names 5-(1-Propenyl)-1,3-benzodioxole 3,4-Methylenedioxyphenyl-1-propene | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.010 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG |
|
PubChem CID | |
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII |
|
| UN number | 3082 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H10O2 | |
| Molar mass | 162.188 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.1206 g/cm3, trans 1.1182 g/cm3, cis |
| Melting point | 8.2 °C (46.8 °F; 281.3 K) trans −21.5 °C, cis |
| Boiling point | 255 °C (491 °F; 528 K) trans 243 °C, cis |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
  | |
| Danger | |
| H302, H315, H341, H350 | |
| P201, P202, P264, P270, P280, P281, P301+P312, P302+P352, P308+P313, P321, P330, P332+P313, P362, P405, P501 | |
| Legal status | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Isosafrole is an organic compound that is used in the fragrance industry. Structurally, the molecule is related to allylbenzene, a type of aromatic organic chemical. Its fragrance is reminiscent of anise or licorice. It is found in small amounts in various essential oils, but is most commonly obtained by isomerizing the plant oil safrole. It exists as two geometric isomers, cis-isosafrole and trans-isosafrole.
Isosafrole is a precursor to the important fragrance piperonal. [3] It can also be converted via the intermediate compound MDP2P into the psychoactive drug MDMA ('ecstasy'). As such it requires permits to purchase or sell in any significant quantity in the US.