
Methyl jasmonate is a volatile organic compound used in plant defense and many diverse developmental pathways such as seed germination, root growth, flowering, fruit ripening, and senescence. Methyl jasmonate is derived from jasmonic acid and the reaction is catalyzed by S-adenosyl-L-methionine:jasmonic acid carboxyl methyltransferase.
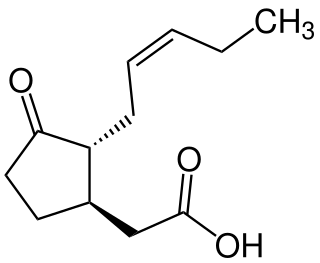
Jasmonic acid (JA) is an organic compound found in several plants including jasmine. The molecule is a member of the jasmonate class of plant hormones. It is biosynthesized from linolenic acid by the octadecanoid pathway. It was first isolated in 1957 as the methyl ester of jasmonic acid by the Swiss chemist Édouard Demole and his colleagues.

Methyltransferases are a large group of enzymes that all methylate their substrates but can be split into several subclasses based on their structural features. The most common class of methyltransferases is class I, all of which contain a Rossmann fold for binding S-Adenosyl methionine (SAM). Class II methyltransferases contain a SET domain, which are exemplified by SET domain histone methyltransferases, and class III methyltransferases, which are membrane associated. Methyltransferases can also be grouped as different types utilizing different substrates in methyl transfer reactions. These types include protein methyltransferases, DNA/RNA methyltransferases, natural product methyltransferases, and non-SAM dependent methyltransferases. SAM is the classical methyl donor for methyltransferases, however, examples of other methyl donors are seen in nature. The general mechanism for methyl transfer is a SN2-like nucleophilic attack where the methionine sulfur serves as the leaving group and the methyl group attached to it acts as the electrophile that transfers the methyl group to the enzyme substrate. SAM is converted to S-Adenosyl homocysteine (SAH) during this process. The breaking of the SAM-methyl bond and the formation of the substrate-methyl bond happen nearly simultaneously. These enzymatic reactions are found in many pathways and are implicated in genetic diseases, cancer, and metabolic diseases. Another type of methyl transfer is the radical S-Adenosyl methionine (SAM) which is the methylation of unactivated carbon atoms in primary metabolites, proteins, lipids, and RNA.
Protein L-isoaspartyl methyltransferase , also called S-adenosyl-L-methionine:protein-L-isoaspartate O-methyltransferase, is an enzyme which recognizes and catalyzes the repair of damaged L-isoaspartyl and D-aspartyl groups in proteins. It is a highly conserved enzyme which is present in nearly all eukaryotes, archaebacteria, and Gram-negative eubacteria.
In enzymology, a 3-demethylubiquinone-9 3-O-methyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 3'-hydroxy-N-methyl-(S)-coclaurine 4'-O-methyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a fatty-acid O-methyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an inositol 1-methyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an inositol 3-methyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an inositol 4-methyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an iodophenol O-methyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a loganate O-methyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a methionine S-methyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a polysaccharide O-methyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a protein-glutamate O-methyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
The isoprenylcysteine o-methyltransferase carries out carboxyl methylation of cleaved eukaryotic proteins that terminate in a CaaX motif. In Saccharomyces cerevisiae this methylation is carried out by Ste14p, an integral endoplasmic reticulum membrane protein. Ste14p is the founding member of the isoprenylcysteine carboxyl methyltransferase (ICMT) family, whose members share significant sequence homology.
8-hydroxyfuranocoumarin 8-O-methyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name S-adenosyl-L-methionine:8-hydroxyfurocoumarin 8-O-methyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
16S rRNA (cytidine1402-2'-O)-methyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name S-adenosyl-L-methionine:16S rRNA (cytidine1402-2'-O)-methyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Naringenin 7-O-methyltransferase is a methyltransferase isolated from rice, which catalyzes the biosynthesis of sakuranetin.
(phosphatase 2A protein)-leucine-carboxy methyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name S-adenosyl-L-methionine:(phosphatase 2A protein)-leucine O-methyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction





