Clinical significance
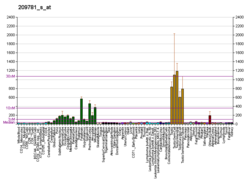
KHDRBS3 (T-STAR) expression has been shown to be increased in prostate cancer tissue compared to the surrounding benign tissue. [9] Expression of KHDRBS3 correlates with mpMRI signal measured through Likert score a system similar to PI-RADS. [9] While still under debate, mpMRI signal correlates with higher Gleason grade and tumour size, in addition to histopathological features associated with clinically aggressive prostate cancer. [10] [11] Expression of KHDRBS3 was increased in the failing human myocardium of heart failure patients, here KHDRBS3 protein interacted with several important mRNAs coding for sarcomere components, such as actin gamma 1 ( ACTG1 ), myosin light chain 2 ( MYL2 ), ryanodine receptor 2 ( RYR2 ), troponin I3 ( TNNI3 ), troponin T2 ( TNNT2 ), tropomyosin 1 ( TPM1 ), tropomyosin 2 ( TPM2 ), and titin ( TTN). [12]
In prostate cancer cell lines KHDRBS3 appears to be androgen regulated, with a reduction in mRNA expression occurring following addition of synthetic androgen R1881 to cells. [9]
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.