
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, and is bounded by the continents of Asia and Oceania in the west and the Americas in the east.
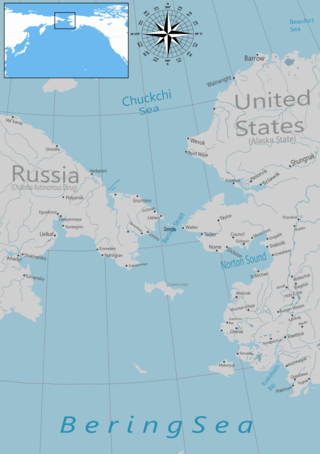
The Bering Strait is a strait between the Pacific and Arctic oceans, separating the Chukchi Peninsula of the Russian Far East from the Seward Peninsula of Alaska. The present Russia-United States maritime boundary is at 168° 58' 37" W longitude, slightly south of the Arctic Circle at about 65° 40' N latitude. The Strait is named after Vitus Bering, a Danish explorer in the service of the Russian Empire.

The Sea of Okhotsk is a marginal sea of the western Pacific Ocean. It is located between Russia's Kamchatka Peninsula on the east, the Kuril Islands on the southeast, Japan's island of Hokkaido on the south, the island of Sakhalin along the west, and a stretch of eastern Siberian coast along the west and north. The northeast corner is the Shelikhov Gulf. The sea is named for the port of Okhotsk, itself named for the Okhota River.

The Bering Sea is a marginal sea of the Northern Pacific Ocean. It forms, along with the Bering Strait, the divide between the two largest landmasses on Earth: Eurasia and the Americas. It comprises a deep water basin, which then rises through a narrow slope into the shallower water above the continental shelves. The Bering Sea is named after Vitus Bering, a Danish navigator in Russian service, who, in 1728, was the first European to systematically explore it, sailing from the Pacific Ocean northward to the Arctic Ocean.

Bering Island is located off the Kamchatka Peninsula in the Bering Sea.

Georg Wilhelm Steller was a German botanist, zoologist, physician and explorer, who worked in Russia and is considered a pioneer of Alaskan natural history.
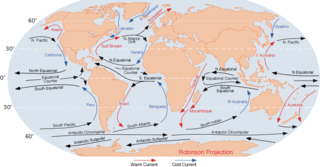
An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of seawater generated by a number of forces acting upon the water, including wind, the Coriolis effect, breaking waves, cabbeling, and temperature and salinity differences. Depth contours, shoreline configurations, and interactions with other currents influence a current's direction and strength. Ocean currents are primarily horizontal water movements.
Physical oceanography is the study of physical conditions and physical processes within the ocean, especially the motions and physical properties of ocean waters.
Ivan Fyodorov was a Russian navigator and commanding officer of the expedition to northern Alaska in 1732.
Dmitry Yakovlevich Laptev was a Russian Arctic explorer and Vice Admiral (1762). The Dmitry Laptev Strait is named in his honor and the Laptev Sea is named in honor of him and his cousin, and fellow Arctic explorer, Khariton Laptev.

Chionoecetes is a genus of crabs that live in the northern Pacific and Atlantic Oceans.

Oyashio, also known as Oya Siwo, Okhotsk or the Kurile current, is a cold subarctic ocean current that flows south and circulates counterclockwise in the western North Pacific Ocean. The waters of the Oyashio Current originate in the Arctic Ocean and flow southward via the Bering Sea, passing through the Bering Strait and transporting cold water from the Arctic Sea into the Pacific Ocean and the Sea of Okhotsk. It collides with the Kuroshio Current off the eastern shore of Japan to form the North Pacific Current . The nutrient-rich Oyashio is named for its metaphorical role as the parent that provides for and nurtures marine organisms.

A survey vessel is any type of ship or boat that is used for underwater surveys, usually to collect data for mapping or planning underwater construction or mineral extraction. It is a type of research vessel, and may be designed for the purpose, modified for the purpose or temporarily put into the service as a vessel of opportunity, and may be crewed, remotely operated, or autonomous. The size and equipment vary to suit the task and availability.

The Alaska Current is a southwestern shallow warm-water current alongside the west coast of the North American continent beginning at about 48-50°N. The Alaska Current produces large clockwise eddies at two sites: west of the Haida Gwaii and west of Sitka, Alaska.

The Great Northern Expedition or Second Kamchatka Expedition was one of the largest exploration enterprises in history, mapping most of the Arctic coast of Siberia and some parts of the North American coastline, greatly reducing "white areas" on maps. It was conceived by Russian Emperor Peter the Great, but implemented by Russian Empresses Anna and Elizabeth. The main organiser and leader of the expedition was Vitus Bering, who earlier had been commissioned by Peter I to lead the First Kamchatka Expedition. The Second Kamchatka Expedition lasted roughly from 1733 to 1743 and later was called the Great Northern Expedition due to the immense scale of its achievements.
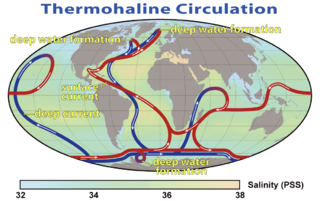
The following outline is provided as an overview of and introduction to Oceanography.

The Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceans. It spans an area of approximately 14,060,000 km2 (5,430,000 sq mi) and is known as one of the coldest of oceans. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, although some oceanographers call it the Arctic Mediterranean Sea. It has also been described as an estuary of the Atlantic Ocean. It is also seen as the northernmost part of the all-encompassing World Ocean.

The Aleutian Islands, also called the Aleut Islands or Aleutic Islands and known before 1867 as the Catherine Archipelago, are a chain of 14 large volcanic islands and 55 smaller islands. Most of the Aleutian Islands belong to the U.S. state of Alaska, but some belong to the Russian federal subject of Kamchatka Krai. They form part of the Aleutian Arc in the Northern Pacific Ocean, occupying a land area of 6,821 sq mi (17,666 km2) and extending about 1,200 mi (1,900 km) westward from the Alaska Peninsula toward the Kamchatka Peninsula in Russia, and act as a border between the Bering Sea to the north and the Pacific Ocean to the south. Crossing longitude 180°, at which point east and west longitude end, the archipelago contains both the westernmost part of the United States by longitude and the easternmost by longitude. The westernmost U.S. island in real terms, however, is Attu Island, west of which runs the International Date Line. While nearly all the archipelago is part of Alaska and is usually considered as being in the "Alaskan Bush", at the extreme western end, the small, geologically related Commander Islands belong to Russia.

The Commander Basin is located between the Shirshov Ridge and the Kamchatka Peninsula. Its southern boundary is the Aleutian arc and occupies the western part of the Bering Sea. The Kamchatka Strait provides a deep water access to the basin from the southwest.

















