Related Research Articles

Antarctic Circumpolar Current (ACC) is an ocean current that flows clockwise from west to east around Antarctica. An alternative name for the ACC is the West Wind Drift. The ACC is the dominant circulation feature of the Southern Ocean and has a mean transport estimated at 100–150 Sverdrups, or possibly even higher, making it the largest ocean current. The current is circumpolar due to the lack of any landmass connecting with Antarctica and this keeps warm ocean waters away from Antarctica, enabling that continent to maintain its huge ice sheet.

In oceanography, the sverdrup is a non-SI metric unit of volumetric flow rate, with 1 Sv equal to 1 million cubic metres per second (264,172,052 US gal/s). It is equivalent to the SI derived unit cubic hectometer per second : 1 Sv is equal to 1 hm3/s. It is used almost exclusively in oceanography to measure the volumetric rate of transport of ocean currents. It is named after Harald Sverdrup.
The Antarctic Circumpolar Wave (ACW) is a coupled ocean/atmosphere wave that circles the Southern Ocean in approximately eight years at 6–8 cm/s (2.4–3.1 in/s). Since it is a wave-2 phenomenon at each fixed point in space a signal with a period of four years is seen. The wave moves eastward with the prevailing currents.

The Drake Passage is the body of water between South America's Cape Horn, Chile, Argentina, and the South Shetland Islands of Antarctica. It connects the southwestern part of the Atlantic Ocean with the southeastern part of the Pacific Ocean and extends into the Southern Ocean. The passage is named after the 16th-century English explorer and privateer Sir Francis Drake.
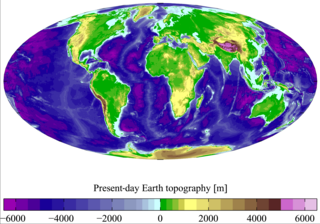
Physical oceanography is the study of physical conditions and physical processes within the ocean, especially the motions and physical properties of ocean waters.

The hourglass dolphin is a small dolphin in the family Delphinidae that inhabits offshore Antarctic and sub-Antarctic waters. It is commonly seen from ships crossing the Drake Passage but has a circumpolar distribution.

The Antarctic realm is one of eight terrestrial biogeographic realms. The ecosystem includes Antarctica and several island groups in the southern Atlantic and Indian oceans. The continent of Antarctica is so cold that it has supported only 2 vascular plants for millions of years, and its flora presently consists of around 250 lichens, 100 mosses, 25–30 liverworts, and around 700 terrestrial and aquatic algal species, which live on the areas of exposed rock and soil around the shore of the continent. Antarctica's two flowering plant species, the Antarctic hair grass and Antarctic pearlwort, are found on the northern and western parts of the Antarctic Peninsula. Antarctica is also home to a diversity of animal life, including penguins, seals, and whales.
Circumpolar may refer to:

In oceanography, a gyre is any large system of ocean surface currents moving in a circular fashion driven by wind movements. Gyres are caused by the Coriolis effect; planetary vorticity, horizontal friction and vertical friction determine the circulatory patterns from the wind stress curl (torque).

The fulmarine petrels or fulmar-petrels are a distinct group of petrels within the family Procellariidae. They are the most variable of the four groups within the Procellariidae, differing greatly in size and biology. They do, however, have a unifying feature, their skull, and in particular their nasal tubes. They are predominantly found in the Southern Ocean with one species, the northern fulmar, ranging in the North Pacific and Atlantic Oceans.

The subantarctic zone is a region in the Southern Hemisphere, located immediately north of the Antarctic region. This translates roughly to a latitude of between 46° and 60° south of the Equator. The subantarctic region includes many islands in the southern parts of the Atlantic, Indian, and Pacific oceans, especially those situated north of the Antarctic Convergence. Subantarctic glaciers are, by definition, located on islands within the subantarctic region. All glaciers located on the continent of Antarctica are by definition considered to be Antarctic glaciers.
The Tasman Outflow is a water pathway connecting water from the Pacific Ocean and the Indian Ocean. The existence of the outflow was published by scientists of the Australian CSIRO's Division of Marine and Atmospheric Research team in August 2007, interpreting salinity and temperature data captured from 1950 to 2002. The Tasman Outflow is seen as the missing link in the supergyre of the Southern Hemisphere and an important part of the thermohaline circulation.
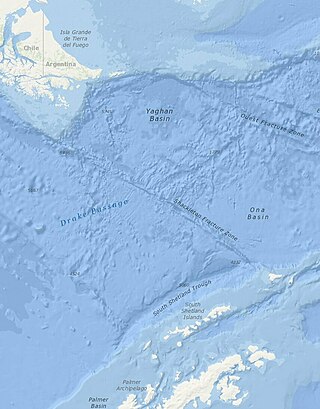
The Shackleton Fracture Zone (SFZ) is an undersea fracture zone, mid-oceanic ridge and fault located in the Drake Passage, at the separation between the Scotia plate from the Antarctic plate. It extends between 59° and 60°40' south latitude and between 56°30' and 61° west longitude and runs in a northwest to southeast direction from the South American continental shelf to the South Shetland Islands. Chile claims the area as part of its Outer Continental Shelf boundary.

The Weddell Gyre is one of the two gyres that exist within the Southern Ocean. The gyre is formed by interactions between the Antarctic Circumpolar Current (ACC) and the Antarctic Continental Shelf. The gyre is located in the Weddell Sea, and rotates clockwise. South of the ACC and spreading northeast from the Antarctic Peninsula, the gyre is an extended large cyclone. Where the northeastern end ends at 30°E, which is marked by the southward turn of the ACC, the northern part of the gyre spreads over the Southern Scotia Sea and goes northward to the South Sandwich Arc. Axis of the gyre is over the southern flanks of the South Scotia, America-Antarctic, and Southwest Indian Ridges. In the southern part of the gyre, the westward return flow is about 66 sverdrup (Sv), while in the northern rim current, there is an eastward flow of 61 Sv.
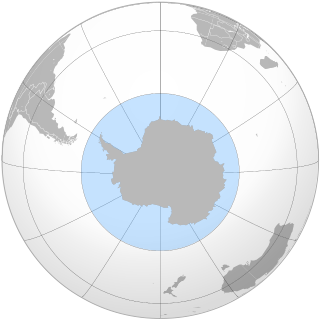
The Southern Ocean, also known as the Antarctic Ocean, comprises the southernmost waters of the world ocean, generally taken to be south of 60° S latitude and encircling Antarctica. With a size of 21,960,000 km2 (8,480,000 sq mi), it is the second-smallest of the five principal oceanic divisions, smaller than the Pacific, Atlantic and Indian oceans, and larger than the Arctic Ocean.
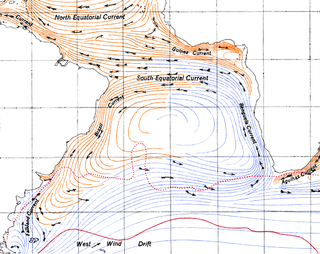
The South Atlantic Gyre is the subtropical gyre in the south Atlantic Ocean. In the southern portion of the gyre, northwesterly winds drive eastward-flowing currents that are difficult to distinguish from the northern boundary of the Antarctic Circumpolar Current. Like other oceanic gyres, it collects vast amounts of floating debris as a garbage patch.
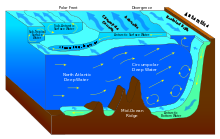
Circumpolar Deep Water (CDW) is a designation given to the water mass in the Pacific and Indian oceans that is a mixing of other water masses in the region. It is characteristically warmer and saltier than the surrounding water masses, causing CDW to contribute to the melting of ice shelves in the Antarctic region.

The Agulhas Basin is an oceanic basin located south of South Africa where the South Atlantic Ocean and south-western Indian Ocean meet. Part of the African plate, it is bounded by the Agulhas Ridge to the north and the Southwest Indian Ridge to the south; by the Meteor Rise to the west and the Agulhas Plateau to the east. Numerous bathymetric anomalies hint at the basin's dynamic tectonic history.

The Northeast Georgia Rise is an oceanic plateau located in the South Atlantic Ocean northeast of South Georgia Island and west of the Falkland Plateau.
The Brazil–Falkland Confluence Zone is a very energetic region of water just off the coast of Argentina and Uruguay where the warm poleward flowing Brazil Current and the cold equatorward flowing Falkland Current converge. The region oscillates latitudinally, but in general the region of confluence occurs between 35 and 45 degrees south latitude and 50 to 70 degrees west longitude. The confluence of these two currents causes a strong thermohaline to exist and causes numerous high energy eddies to form.
References
- Scott Guhin; Pallav Ray; Arthur J. Mariano; Edward H. Ryan (2003). "The South Atlantic Current". Ocean Surface Currents. University of Miami. Archived from the original on 2023-04-23. Retrieved 2007-08-19.