
Papua is a province of Indonesia, comprising the northern coast of Western New Guinea together with island groups in Cenderawasih Bay to the west. It roughly follows the borders of Papuan customary region of Tabi Saireri. It is bordered by nation of Papua New Guinea to the east, the Pacific Ocean to the north, Cenderawasih Bay to the west, and the provinces of Central Papua and Highland Papua to the south. The province also shares maritime boundaries with Palau in the Pacific. Following the splitting off of twenty regencies to create the three new provinces of Central Papua, Highland Papua, and South Papua on 30 June 2022, the residual province is divided into eight regencies and one city (kota), the latter being the provincial capital of Jayapura. The province has a large potential in natural resources, such as gold, nickel, petroleum, etc. Papua, along with five other Papuan provinces, has a higher degree of autonomy level compared to other Indonesian provinces.

The Korowai, also called the Kolufo, live in southeastern Papua in the Indonesian provinces of South Papua and Highland Papua. Their tribal area is split by the borders of Boven Digoel Regency, Mappi Regency, Asmat Regency, and Yahukimo Regency. They number about 4000 to 4400 people.

West Papua, formerly Irian Jaya Barat, is an Indonesian province located in Indonesia Papua. It covers most of the two western peninsulas of the island of New Guinea: the eastern half of the Bird's Head Peninsula and the whole of the Bomberai Peninsula, along with nearby smaller islands. The province is bordered to the north by the Pacific Ocean, to the west by Southwest Papua Province, the Halmahera Sea and the Ceram Sea, to the south by the Banda Sea, and to the east by the province of Central Papua and the Cenderawasih Bay. Manokwari is the province's capital and largest city. With an estimated population of 569,570 in mid-2023, West Papua is the least populous province in Indonesia after South Papua, following the separation off in 2022 of the western half of the Bird's Head Peninsula to create the new province of Southwest Papua, containing 52% of what had been West Papua's population.Its population density is similar to Russia.

Western New Guinea, also known as Papua, Indonesian New Guinea, and Indonesian Papua, is the western half of the island of New Guinea, formerly Dutch and granted to Indonesia in 1962. Given the island is alternatively named Papua, the region is also called West Papua.

Merauke is a large town (kelurahan) and an administrative district (distrik) in Merauke Regency of South Papua Province, Indonesia. It is also the administrative centre of Merauke Regency, and is considered to be the easternmost city in Indonesia, although it currently lacks city status. The town was originally called Ermasoe. It is next to the Maro River where the Port of Merauke is located. Merauke District covers a land area of 500.41 km2, and had a population of 87,634 at the 2010 Census. which at the 2020 Census had increased to 102,351; the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 110,541.

Sorong is the largest city and the capital of the Indonesian province of Southwest Papua. The city is located on the western tip of the island of New Guinea with its only land borders being with Sorong Regency. It is the gateway to Indonesia's Raja Ampat Islands, species rich coral reef islands in an area considered the heart of the world's coral reef biodiversity. It also is the logistics hub for Indonesia's thriving eastern oil and gas frontier. Sorong experienced rapid growth during the decade from 2010, and further growth is anticipated as Sorong becomes linked by road to other frontier towns in Papua's Bird's Head Peninsula. The official estimate of population as at mid 2023 was 294,978 - comprising 154,543 males and 140,435 females. The suburban area of Sorong city contains tropical rainforest and mangrove forest that has increasingly become popular as ecotourism attractions especially for birdwatching or wildlife watching.

Frans Kaisiepo was a Papuan politician and Indonesian nationalist. He served as the fourth Governor of Papua Province. In 1993, Kaisiepo was posthumously declared a National Hero of Indonesia for his lifelong efforts to unite West Irian with Indonesia. As the representative of Papua province, he was involved in the Malino Conference, where the formation of the United States of Indonesia was discussed.

The Marind or Marind-Anim are an ethnic group of New Guinea, residing in the province of South Papua, Indonesia.

New Guinea is the world's second-largest island, with an area of 785,753 km2 (303,381 sq mi). Located in Melanesia in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is separated from Australia by the 150-kilometre wide Torres Strait, though both landmasses lie on the same continental shelf, and were united during episodes of low sea level in the Pleistocene glaciations as the combined landmass of Sahul. Numerous smaller islands are located to the west and east. The island's name was given by Spanish explorer Yñigo Ortiz de Retez during his maritime expedition of 1545 due to the resemblance of the indigenous peoples of the island to those in the African region of Guinea.

Boven Digoel Regency is an inland regency (kabupaten) in the northeastern part of the Indonesian province of South Papua. It was split off from Merauke Regency on 12 November 2002. It is bordered to the south by the residual Merauke Regency, to the west by Mappi Regency, and to the north by the province of Highland Papua. At the same time, to the east lies the international border with Papua New Guinea.

Mappi Regency is a regency (kabupaten) in the Indonesian province of South Papua. It was split off from Merauke Regency on 12 November 2002. It covers an area of 25,609.94 km2, and had a population of 81,658 at the 2010 Census and 108,295 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 110,291. The administrative centre is the town of Kepi.
Korowai (Kolufaup) is a Trans-New-Guinean language spoken in South Papua, Indonesia. It is spoken by the Korowai people who live along the Becking River.

Operation Trikora was a combined Soviet-Indonesian military operation which aimed to seize and annex the Dutch overseas territory of Netherlands New Guinea in 1961 and 1962. After negotiations, the Netherlands signed the New York Agreement with Indonesia on 15 August 1962, relinquishing control of Western New Guinea to the United Nations.

Major TNI Marthen Indey (1912–1986) was a colonial police officer in New Guinea, Dutch East Indies who later became nationalist fighter in the Indonesian National Revolution and a supporter of Papua becoming part of Indonesia. He was declared a National Hero of Indonesia in 1993 along with two other people of Papuan descent, Frans Kaisiepo and Silas Papare.

The Brazza River is a river in Papua province, Indonesia. The Brazza River has its source at over 3000 meters of elevation in the Jayawijaya or Maoke Mountains of central Papua in Yahukimo Regency and flows south to the lowland rainforests of Asmat Regency before meeting the Pulau River, which flows southeast to the Arafura Sea.
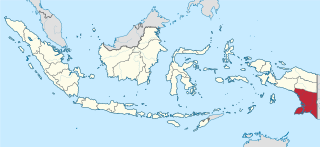
South Papua, officially the South Papua Province, is an Indonesian province located in the southern portion of Papua, following the borders of the Papuan customary region of Anim Ha. Formally established on 11 November 2022 and including the four most southern regencies that were previously part of the province of Papua and before 11 December 2002 had comprised a larger Merauke Regency, it covers a land area of 129,715.02 km2, about the same area as Pennsylvania. This area had a population of 513,617 at the 2020 Census, while the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 537,973, making it the least populous province in Indonesia.

Okaba is a coastal town in Merauke Regency, South Papua, Indonesia.
Bupul is an inland village in Merauke Regency, South Papua, Indonesia.
Isyaman is an inland village in Mappi Regency, South Papua, Indonesia.

Central Papua, officially the Central Papua Province is an Indonesian province located in the central region of Western New Guinea. It was formally established on 11 November 2022 from the former eight western regencies of the province of Papua. It covers an area of 61,072.91 km2 and had an officially estimated population of 1,452,810 in mid 2023. It is bordered by the Indonesian provinces of West Papua to the west, the province of Papua to the north and northeast, by Highland Papua to the east, and by South Papua to the southeast. The administrative capital is located in Wanggar District in Nabire Regency, although Timika is a larger town.


















