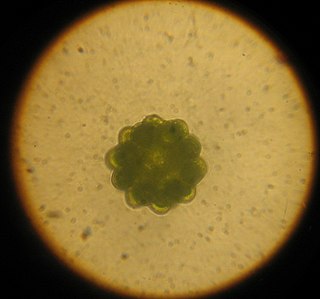
Coelastrum is a genus of green algae in the Scenedesmaceae family. It is a common component of the phytoplankton in freshwater habitats such as ponds, lakes, waterfalls, and temporary pools of water, particularly eutrophic ones. The genus has a more or less cosmopolitan distribution, although some species appear to have more restricted geographical distributions.

Selenastraceae is a family of green algae in the order Sphaeropleales. Members of this family are common components of the phytoplankton in freshwater habitats worldwide. A few species have been found in brackish and marine habitats, such as in the Baltic Sea.

Botryococcus is a genus of green algae. The cells form an irregularly shaped aggregate. Thin filaments connect the cells. The cell body is ovoid, 6 to 10 μm long, and 3 to 6 μm wide. Fossils of the genus are known since Precambrian times, and form the single largest biological contributor to crude oil, and are a major component of oil shales.

Ankistrodesmus is a genus of green algae in the family Selenastraceae. It is one of the most common types of phytoplankton in freshwater habitats around the world.

Dimorphococcus is a genus of fresh water green algae in the family Scenedesmaceae. It is found as a component of the phytoplankton of freshwater ponds, lakes, and peat bogs. It is widespread, but usually not very common.
Enallax is a genus of green algae in the family Scenedesmaceae. It is found in freshwater habitats, such as peat bogs or wet rocks.

Lagerheimia is a genus of green algae in the family Oocystaceae. It is commonly found in freshwater habitats all over the world, although some species are rare and have only been recorded from Europe or the United States.
Podohedriella is a genus of green algae in the family Selenastraceae. It is found in freshwater habitats or on damp wood.
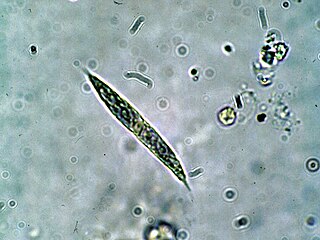
Quadrigula is a genus of green algae in the family Selenastraceae. It is commonly found in freshwater habitats as phytoplankton.
Raphidocelis is a genus of green algae in the family Selenastraceae. They are found in freshwater habitats.

Schroederia is a genus of green algae in the family Schroederiaceae. Schroederiaceae is a monotypic taxon; Schroederia is its only genus.

Selenastrum is a genus of green algae in the family Selenastraceae. It is common in freshwater habitats around the world. Most species prefer temperate or warm-temperate waters.
Treubaria is a genus of green algae, the sole genus in the family Treubariaceae. Treubaria is found in freshwater habitats and has a cosmopolitan distribution.

Tetrastrum is a genus of green algae (Chlorophyta). It is a common component of the phytoplankton of freshwater habitats, particularly eutrophic and alkaline waters.

Characiaceae is a family of green algae in the order Sphaeropleales. It contains epiphytic or planktonic algae that are unicellular or colonial. The cells are heteropolar, with basal and apical ends having different shapes. The daughter cells are often retained in the cell wall of the old mother cell, whose cell wall becomes gelatinized.
Deuterocharacium is a genus of green algae in the family Characiaceae. It is found in freshwater habitats, attached to algae or detritus. It is rare and has only been recorded from Europe.

Marthea is a genus of green algae in the family Characiaceae, containing the single species Marthea tetras. It is an extremely rare genus; it has only been recorded once, as freshwater phytoplankton from its original locality in the Bohemian Forest region of the Czech Republic.
Korshikoviella is a genus of green algae in the family Characiaceae.
Pseudokirchneriella is a genus of green algae in the family Selenastraceae. It is found as phytoplankton in freshwater ponds, lakes, and pools. It has been reported from Europe and North America.
Chlorolobion, sometimes spelled Chlorolobium, is a genus of algae belonging to the family Selenastraceae. The species of this genus are found in freshwater habitats in Europe and America.












