Konica was a Japanese manufacturer of, among other products, film, film cameras, camera accessories, photographic and photo-processing equipment, photocopiers, fax machines and laser printers. The company merged with Japanese peer Minolta in 2003, with the new company named Konica Minolta.

The Pentax Auto 110 and Pentax Auto 110 Super are single-lens reflex cameras made by Asahi Pentax that use Kodak's 110 film cartridge. The Auto 110 was introduced with three interchangeable lenses in 1978. Three more lenses were introduced in 1981, and then the Super model was released in 1982. The camera system was sold until 1985. The complete system is sometimes known as the Pentax System 10, apparently for its official Pentax name, although most Pentax advertising only uses the camera name or Pentax-110. This model represented the only complete ultraminiature SLR system manufactured for the 110 film format, although several fixed-lens 110 SLRs were sold. The camera system also claims to be the smallest interchangeable-lens SLR system ever created.

Schneider-Kreuznach is the abbreviated name of the company Jos. Schneider Optische Werke GmbH, which is sometimes also simply referred to as Schneider. They are a manufacturer of industrial and photographic optics. The company was founded on 18 January 1913 by Joseph Schneider as Optische Anstalt Jos. Schneider & Co. at Bad Kreuznach in Germany. The company changed its name to Jos. Schneider & Co., Optische Werke, Kreuznach in 1922, and to the current Jos. Schneider Optische Werke GmbH in 1998.

Kodak EasyShare is a sub brand of Eastman Kodak Company products identifying a consumer photography system of digital cameras, snapshot thermal printers, snapshot thermal printer docks, all-in-one inkjet printers, accessories, camera docks, software, and online print services. The brand was introduced in 2001. The brand is no longer applied to all-in-one inkjet printers or online printing services. Thermal snapshot printers and printer docks product lines have been discontinued. In 2012, Kodak stopped manufacturing and selling all digital cameras and photo frames.

The Nikon F-mount is a type of interchangeable lens mount developed by Nikon for its 35mm format single-lens reflex cameras. The F-mount was first introduced on the Nikon F camera in 1959, and features a three-lug bayonet mount with a 44 mm throat and a flange to focal plane distance of 46.5 mm. The company continues, with the 2020 D6 model, to use variations of the same lens mount specification for its film and digital SLR cameras.

A full-frame digital single-lens reflex camera (DSLR) is one with an image sensor format that is the same size as 35 mm format film. Historically, 35 mm was considered a small film format compared with medium format, large format and even larger.

The Nikon F2 is a professional-level, interchangeable lens, 35 mm film, single-lens reflex (SLR) camera. It was manufactured by the Japanese optics company Nippon Kogaku K. K. in Japan from September 1971 to 1980. It used a horizontal-travel focal plane shutter with titanium shutter curtains and a speed range of 1 to 1/2000 second plus Bulb and Time, and flash X-sync of 1/80 second. It had dimensions of 98 mm height, 152.5 mm width, 65 mm depth and 730 g weight. It was available in two colors: black with chrome trim and all black.

The Nikon F5 is a 35 mm film-based single-lens reflex camera body manufactured by Nikon from 1996 through 2004. It was the fifth in Nikon's professional film camera line, which began in 1959 with the Nikon F. It followed the Nikon F4 of 1988, which had introduced in-body autofocus to Nikon's professional line. The F5 was in turn succeeded by the Nikon F6, as well as Nikon's parallel range of professional digital SLRs, beginning with the Nikon D1.
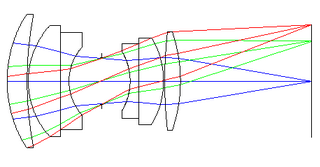
The double Gauss lens is a compound lens used mostly in camera lenses that reduces optical aberrations over a large focal plane.
The Kodak EasyShare V570 was a 5-megapixel digital camera manufactured by Eastman Kodak. Announced on January 2, 2006, it was an upper-end model in the consumer price range, advertised at $400 in the United States in January 2006. It had an innovative dual lens system, combining two periscopic groups each with its own sensor: one very wide angle equivalent to a 23 mm in 135 format and a 3X zoom equivalent to a 39–117 mm, totalizing a virtual 5X zoom, with a step between 23 and 39 mm. It is the first dual lens digital camera. The model won a gold medal in the 2006 Industrial Design Excellence Awards.

Nikonos is the brand name of a series of 35mm format cameras specifically designed for underwater photography launched by Nikon in 1963. The early Nikonos cameras were improvements of the Calypso camera, which was an original design by Jacques-Yves Cousteau and Belgian engineer Jean de Wouters. It was produced in France by La Spirotechnique until the design was acquired by Nikon to become the Nikonos. The Nikonos system was immensely popular with both amateur and professional underwater photographers. Its compact design, ease of use, and excellent optical quality set the standard for several decades of underwater imaging. Nikon ceased development and manufacture of new Nikonos cameras in 2001, but the camera remains popular, and there is a large and active secondary market.

The Kodak Pony camera was introduced with the 828 model in 1949 as the first in a series of six Kodak Pony cameras which was produced until 1959. While the initial version of this camera used paperbacked 828 film, the five later versions were adapted to use 35mm 135 film. The cameras were designed by Arthur H. Crapsey.

Retina was the brand-name of a long-running series of German-built Kodak 35mm cameras, produced from 1934 until 1969. Kodak Retina cameras were manufactured in Stuttgart-Wangen by the Kodak AG Dr. Nagel Werk which Kodak had acquired in December 1931.

The Contaflex series is a family of 35mm leaf-shuttered SLR cameras, produced by Zeiss Ikon in the 1950s and 1960s. The name was first used in 1935 on a 35mm Twin-lens reflex camera, the Contaflex TLR also by Zeiss Ikon, the -flex part in the name referring to integral mirror for the viewfinder. The first models, the Contaflex I and II have fixed lenses, while the later models have interchangeable lenses, and eventually the Contaflexes became a camera system with a wide variety of accessories.

The Kodak DC215 is a discontinued model of digital camera produced in Japan by the Eastman Kodak Company. This model does not have internal memory, but a 4MB card is supplied with the camera. The camera has a 1-megapixel sensor, a fixed focus lens with 2x optical zoom and macro-setting and a built-in flash. The viewfinder is optical, but it is possible to use the 1.8" rear LCD monitor as viewfinder, though Kodak did not recommend that due to high battery consumption. There was also a small LCD black and white screen on the top of the camera to show camera settings only. The DC215 also came in a "Millennium Edition" version which had a gold rather than silver case and came with some additional accessories.

The Kodak Retina Reflex is a discontinued series of four single-lens reflex cameras made by Kodak, continuing the brand Kodak Retina.

The Kodak Stereo Camera was a 35mm film stereo camera produced between 1954 and 1959. Similar to the Stereo Realist, the camera employed two lenses to take twin shots of scenes, which could then be viewed in dedicated image viewers. The lenses supported adjustable apertures and variable shutter speeds. The camera had a reputation for being easy to use, and sold approximately 100,000 units during the time it was produced.

The Kodak DC series was Kodak's pioneering consumer-grade line of digital cameras; as distinct from their much more expensive professional Kodak DCS series. Cameras in the DC series were manufactured and sold during the mid-to-late 1990s and early 2000s. Some were branded as "Digital Science". Most of these early digital cameras supported RS-232 serial port connections because USB hardware was not widely available before 1998. Some models in the DC series ran on the short lived DigitaOS, a camera operating system that allowed third party software to be installed.

The Kodak Cine Special 16mm Cameras (CKS) are a family of precision, versatile, spring-wound 16mm silent movie cameras produced by Eastman Kodak from the 1930s to the 1960s, and intended for advanced consumers and industry professionals. While its rectangular format was typical of earlier Kodak 16 mm cameras, the CKS 'box' was formed by two joined sections: the spring motor half with the user controls, winding cranks, and gear work to the shutter. The other half was a film magazine which docked to the motor. This allowed the cinematographer to pre-load multiple magazines of film for quick interchange of film.

















