
A fossil is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the fossil record. Though the fossil record is incomplete, numerous studies have demonstrated that there is enough information available to give a good understanding of the pattern of diversification of life on Earth. In addition, the record can predict and fill gaps such as the discovery of Tiktaalik in the arctic of Canada.

Paleontology, also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to the start of the Holocene epoch. It includes the study of fossils to classify organisms and study their interactions with each other and their environments. Paleontological observations have been documented as far back as the 5th century BC. The science became established in the 18th century as a result of Georges Cuvier's work on comparative anatomy, and developed rapidly in the 19th century. The term has been used since 1822 formed from Greek παλαιός, ὄν, and λόγος.
The PaleozoicEra is the first of three geological eras of the Phanerozoic Eon. Beginning 538.8 million years ago (Ma), it succeeds the Neoproterozoic and ends 251.9 Ma at the start of the Mesozoic Era. The Paleozoic is subdivided into six geologic periods, Cambrian, Ordovician, Silurian, Devonian, Carboniferous and Permian. Some geological timescales divide the Paleozoic informally into early and late sub-eras: the Early Paleozoic consisting of the Cambrian, Ordovician and Silurian; the Late Paleozoic consisting of the Devonian, Carboniferous and Permian.

A flatfish is a member of the ray-finned demersal fish order Pleuronectiformes, also called the Heterosomata, sometimes classified as a suborder of Perciformes. In many species, both eyes lie on one side of the head, one or the other migrating through or around the head during development. Some species face their left sides upward, some face their right sides upward, and others face either side upward.

A trace fossil, also known as an ichnofossil, is a fossil record of biological activity by lifeforms but not the preserved remains of the organism itself. Trace fossils contrast with body fossils, which are the fossilized remains of parts of organisms' bodies, usually altered by later chemical activity or by mineralization. The study of such trace fossils is ichnology - the work of ichnologists.

Tephra is fragmental material produced by a volcanic eruption regardless of composition, fragment size, or emplacement mechanism.

Aulopiformes is a diverse order of marine ray-finned fish consisting of some 15 extant and several prehistoric families with about 45 genera and over 230 species. The common names grinners, lizardfishes and allies, or aulopiforms are sometimes used for this group. The scientific name means "Aulopus-shaped", from Aulopus + the standard fish order suffix "-formes". It ultimately derives from Ancient Greek aulós + Latin forma, the former in reference to the elongated shape of many aulopiforms.

Fossil collecting is the collection of the fossils for scientific study, hobby, or profit. Fossil collecting, as practiced by amateurs, is the predecessor of modern paleontology and many still collect fossils and study fossils as amateurs. Professionals and amateurs alike collect fossils for their scientific value. A commercial trade in fossils has also long existed, with some of this being practised illegally.

Ostriches are large flightless birds. Two living species are recognised, the common ostrich, native to large areas of sub-Saharan Africa, and the Somali ostrich, native to the Horn of Africa.
The Atapuerca Mountains is a karstic hill formation near the village of Atapuerca in the province of Burgos, northern Spain.

The geology of Antarctica covers the geological development of the continent through the Archean, Proterozoic and Phanerozoic eons.
The Cypriot mouse is a species of mouse endemic to Cyprus. Its primary habitat seems to be the vineyards and fields of the Troödos Mountains region.
The California State Teachers' Retirement System (CalSTRS) provides retirement, disability and survivor benefits for California's 965,000 prekindergarten through community college educators and their families. CalSTRS was established by law in 1913 and is part of the State of California's Government Operations Agency. As of September 2020, CalSTRS is the largest teachers' retirement fund in the United States. CalSTRS is also currently the eleventh largest public pension fund in the world. As of October 31, 2020, CalSTRS managed a portfolio worth $254.7 billion.
Ermoceras is a genus of ammonite belonging to the Thomboceratidae family of the Middle Jurassic found in deposites of central Arabia, Sinai, and Algeria with strong primary and secondary ribs and a single row of lateral tubercles; described as having a deep ventral groove
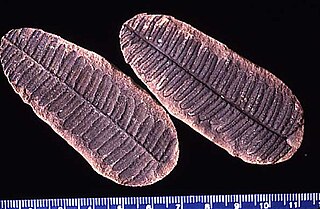
Pecopteris is a very common form genus of leaves. Most Pecopteris leaves and fronds are associated with the marattialean tree fern Psaronius. However, Pecopteris-type foliage also is borne on several filicalean ferns, and at least one seed fern. Pecopteris first appeared in the Devonian period, but flourished in the Carboniferous, especially the Pennsylvanian. Plants bearing these leaves became extinct in the Permian period, due to swamps disappearing and temperatures on Earth dropping.

Arthropods are invertebrates in the phylum Arthropoda. They possess an exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, often mineralised with calcium carbonate, a body with differentiated (metameric) segments, and paired jointed appendages. In order to keep growing, they must go through stages of moulting, a process by which they shed their exoskeleton to reveal a new one. They form an extremely diverse group of up to ten million species.

Darwinius is a genus within the infraorder Adapiformes, a group of basal strepsirrhine primates from the middle Eocene epoch. Its only known species, Darwinius masillae, lived approximately 47 million years ago based on dating of the fossil site.

The Salientia are a total group of amphibians that includes the order Anura, the frogs and toads, and various extinct proto-frogs that are more closely related to the frogs than they are to the Urodela, the salamanders and newts. The oldest fossil "proto-frog" appeared in the early Triassic of Madagascar, but molecular clock dating suggests their origins may extend further back to the Permian, 265 million years ago.

Baishiya Karst Cave is a high-altitude paleoanthropological site and a Tibetan Buddhist sanctuary located on the northeastern edge of the Tibetan Plateau in Xiahe County, Gansu, China. This karst cave is the site of the discovery of the earliest hominin fossil found on the Tibetan Plateau, the Xiahe mandible. The mandible, by way of palaeoproteomic analysis, is the first confirmed discovery of a Denisovan fossil outside of Denisova Cave. This fossil discovery shows that archaic hominins were present in a high-altitude, low-oxygen environment by around 160,000 years ago.













