
In primates, and specifically in humans, the labia majora, also known as the outer lips or outer labia, are two prominent longitudinal skin folds that extend downward and backward from the mons pubis to the perineum. Together with the labia minora, they form the labia of the vulva.

The labia minora, also known as the inner labia, inner lips, or nymphae, are two flaps of skin that are part of the primate vulva, extending outwards from the vaginal and urethral openings to encompass the vestibule. The labia minora are situated between the labia majora and together form the labia. They vary widely in size, color and shape from individual to individual.

The labia are the major externally visible portions of the vulva. In humans and other primates, there are two pairs of labia: the labia majora are large and thick folds of skin that cover the vulva's other parts while the labia minora are the inner folds of skin between the outer labia that surround and protect the openings. Inside the vestibule are the introitus of the vagina and the meatus of the urethra. Upward from the labia minora is the clitoral hood that protects the clitoral glans.
Labium is the Latin word for lip. In English, it may refer to:

Anisolabididae is a family of earwigs, in the suborder Forficulina and the order Dermaptera. It is one of nine families in the suborder Forficulina, and contains thirty-eight genera spread across thirteen subfamilies.
Ctenisolabis is a genus of earwigs in the subfamily Brachylabinae. It was cited by Srivastava in Part 2 of Fauna of India. It was also cited at an earlier date by Steinmann in his publication, The Animal Kingdom in 1986, 1989, 1990, and 1993.
Idolopsalis is a genus of earwigs, the sole member of the subfamily Idolopsalinae. It was cited by Srivastava in Part 2 of Fauna of India. It was also cited at an earlier date by Steinmann in his publication, The Animal Kingdom in 1986, 1989, 1990, and 1993.

Labiinae, whose members are commonly known as little earwigs, is a moderately sized subfamily of earwigs in the suborder Forficulina. It is a cosmopolitan family, whose members are small, winged earwigs, generally less than 1.5 centimetres (0.59 in) in length.
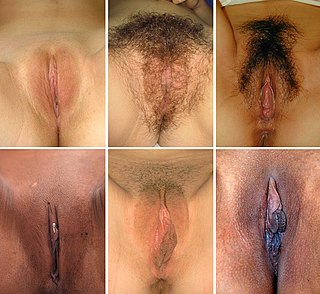
In mammals, the vulva consists of the external female genitalia. The human vulva includes the mons pubis, labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, vestibular bulbs, vulval vestibule, urinary meatus, the vaginal opening, hymen, and Bartholin's and Skene's vestibular glands. The urinary meatus is also included as it opens into the vulval vestibule. Other features of the vulva include the pudendal cleft, sebaceous glands, the urogenital triangle, and pubic hair. The vulva includes the entrance to the vagina, which leads to the uterus, and provides a double layer of protection for this by the folds of the outer and inner labia. Pelvic floor muscles support the structures of the vulva. Other muscles of the urogenital triangle also give support.

Labia minor, the lesser earwig or small earwig, is a species of earwig. It is widespread globally in temperate climates, preferring warm locations such as compost heaps in parts of its range. It is 4–7 mm long, including the pincer, and chocolate brown in color.

Acrida is a genus of grasshoppers in the family Acrididae. The genus contains around 40 species which are found in Africa, Europe, Asia, North America, Hawaii, and Australia. Insects of this genus are omnivorous and a well-known pest of many agricultural crops.

Spongiphoridae is a family of little earwigs in the suborder Neodermaptera. There are more than 40 genera and 510 described species in Spongiphoridae.

Anechura is a family of earwigs in the family Forficulidae.

Chelidura is a genus of earwigs in the family Forficulidae from mainland Europe including southern Scandinavia.
Irdex is a genus of earwigs belonging to the subfamily Spongiphorinae.
Haplodiplatys is a genus of Asian earwigs erected by Walter Douglas Hincks in 1955. It is the only member of the monotypic family Haplodiplatyidae, with many species originally placed in the genus Diplatys; a key to them was prepared by Alan Brindle.
Diplatys is a genus of Asian earwigs, in the family Diplatyidae, erected by Jean Guillaume Audinet-Serville in 1831. The recorded distribution of species is from Indochina, although this may be incomplete; it is also worth noting that other genera in subfamily Diplatyinae and the genus Haplodiplatys historically have been placed here.
Liparura is a genus of earwigs within the family Forficulidae.










