
The glossopharyngeal nerve, also known as the ninth cranial nerve, cranial nerve IX, or simply CN IX, is a cranial nerve that exits the brainstem from the sides of the upper medulla, just anterior to the vagus nerve. Being a mixed nerve (sensorimotor), it carries afferent sensory and efferent motor information. The motor division of the glossopharyngeal nerve is derived from the basal plate of the embryonic medulla oblongata, whereas the sensory division originates from the cranial neural crest.

The parotid gland is a major salivary gland in many animals. In humans, the two parotid glands are present on either side of the mouth and in front of both ears. They are the largest of the salivary glands. Each parotid is wrapped around the mandibular ramus, and secretes serous saliva through the parotid duct into the mouth, to facilitate mastication and swallowing and to begin the digestion of starches. There are also two other types of salivary glands; they are submandibular and sublingual glands. Sometimes accessory parotid glands are found close to the main parotid glands.

The sublingual gland is a seromucous polystomatic exocrine gland. Located underneath the oral diaphragm, the sublingual gland is the smallest and most diffuse of the three major salivary glands of the oral cavity, with the other two being the submandibular and parotid. The sublingual gland provides approximately 3-5% of the total salivary volume.

The otic ganglion is a small parasympathetic ganglion located immediately below the foramen ovale in the infratemporal fossa and on the medial surface of the mandibular nerve. It is functionally associated with the glossopharyngeal nerve and innervates the parotid gland for salivation.

The pterygopalatine ganglion is a parasympathetic ganglion in the pterygopalatine fossa. It is one of four parasympathetic ganglia of the head and neck,.

The auriculotemporal nerve is a sensory branch of the mandibular nerve (CN V3) that runs with the superficial temporal artery and vein, and provides sensory innervation to parts of the external ear, scalp, and temporomandibular joint. The nerve also conveys post-ganglionic parasympathetic fibres from the otic ganglion to the parotid gland.

The ophthalmic nerve (CN V1) is a sensory nerve of the head. It is one of three divisions of the trigeminal nerve (CN V), a cranial nerve. It has three major branches which provide sensory innervation to the eye, and the skin of the upper face and anterior scalp, as well as other structures of the head.
Petrosal nerve may refer to:

The lingual nerve carries sensory innervation from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue. It contains fibres from both the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve (CN V3) and from the facial nerve (CN VII). The fibres from the trigeminal nerve are for touch, pain and temperature (general sensation), and the ones from the facial nerve are for taste (special sensation).
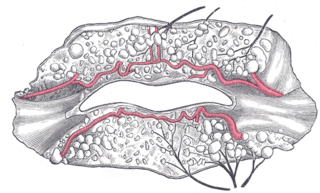
The inferior labial artery arises near the angle of the mouth as a branch of the facial artery; it passes upward and forward beneath the triangularis and, penetrating the orbicularis oris, runs in a tortuous course along the edge of the lower lip between this muscle and the mucous membrane.

The superior laryngeal nerve is a branch of the vagus nerve. It arises from the middle of the inferior ganglion of vagus nerve and additionally also receives a sympathetic branch from the superior cervical ganglion.
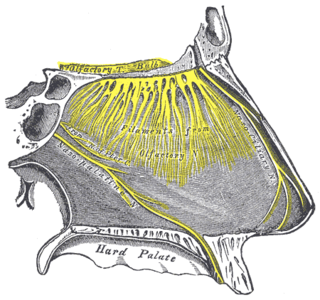
The nasopalatine nerve (also long sphenopalatine nerve) is a nerve of the head. It is a sensory branch of the maxillary nerve (CN V2) that passes through the pterygopalatine ganglion (without synapsing) and then through the sphenopalatine foramen to enter the nasal cavity, and finally out of the nasal cavity through the incisive canal and then the incisive fossa to enter the hard palate. It provides sensory innervation to the posteroinferior part of the nasal septum, and gingiva just posterior to the upper incisor teeth.

The tympanic nerve is a branch of the glossopharyngeal nerve found near the ear. It gives sensation to the middle ear, the Eustachian tube, the parotid gland, and mastoid air cells. It gives parasympathetic to supply to the parotid gland via the otic ganglion and the auriculotemporal nerve.

The lesser petrosal nerve is the general visceral efferent (GVE) nerve conveying pre-ganglionic parasympathetic secretomotor fibers for the parotid gland from the tympanic plexus to the otic ganglion. It passes out of the tympanic cavity through the petrous part of the temporal bone into the middle cranial fossa of the cranial cavity, then exits the cranial cavity through its own canaliculus to reach the infratemporal fossa.

The greater palatine nerve is a branch of the pterygopalatine ganglion. This nerve is also referred to as the anterior palatine nerve, due to its location anterior to the lesser palatine nerve. It carries both general sensory fibres from the maxillary nerve, and parasympathetic fibers from the nerve of the pterygoid canal. It may be anaesthetised for procedures of the mouth and maxillary (upper) teeth.

The intermediate nerve, nervus intermedius, nerve of Wrisberg or Glossopalatine nerve is the part of the facial nerve located between the motor component of the facial nerve and the vestibulocochlear nerve. It contains the sensory and parasympathetic fibers of the facial nerve. Upon reaching the facial canal, it joins with the motor root of the facial nerve at the geniculate ganglion. Alex Alfieri postulates that the intermediate nerve should be considered as a separate cranial nerve and not a part of the facial nerve.
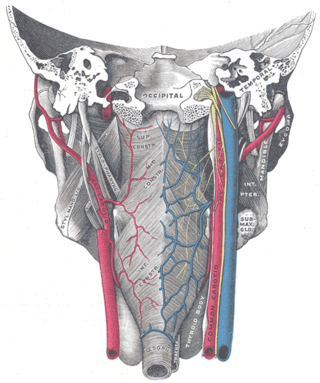
The pharyngeal plexus is a nerve plexus located upon the outer surface of the pharynx. It contains a motor component, a sensory component, and sympathetic component.

The salivatory nuclei are two parasympathetic general visceral efferent cranial nerve nuclei - the superior salivatory nucleus and the inferior salivatory nucleus - that innervate the salivary glands. Both are located in the pontine tegmentum of the brainstem.

Pseudunela cornuta is a species of minute sea slug, an acochlidian, a shell-less marine and temporarily brackish gastropod mollusk in the family Pseudunelidae. Adults are about 3 mm long and live in the spaces between sand grains.

The following diagram is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the human nervous system:















