
Condylarthra is an informal group – previously considered an order – of extinct placental mammals, known primarily from the Paleocene and Eocene epochs. They are considered early, primitive ungulates and is now largely considered to be a wastebasket taxon, having served as a dumping ground for classifying ungulates which had not been clearly established as part of either Perissodactyla or Artiodactyla, being composed thus of several unrelated lineages.

Phenacodus is an extinct genus of mammals from the late Paleocene through middle Eocene, about 55 million years ago. It is one of the earliest and most primitive of the ungulates, typifying the family Phenacodontidae and the order Perissodactyla.

Protungulatum is an extinct genus of eutherian mammals within extinct family Protungulatidae, and is possibly one of the earliest known placental mammals in the fossil record, that lived in North America from the Late Cretaceous to early Paleocene.

Barylambda is an extinct genus of pantodont mammal from the middle to late Paleocene, well known from several finds in the Wasatchian DeBeque Formation of Colorado and the Clarkforkian Wasatch Formation to Tiffanian Fort Union Formation in Wyoming. Three species of Barylambda are currently recognized. The creature likely lived a life similar to that of a modern tapir, browsing on foliage and soft vegetation. Barylambda seems to have been quite successful for an early pantodont, though eventually it seems to have been replaced in its ecosystem by other pantodonts, such as Coryphodon.

Mesonychidae is an extinct family of small to large-sized omnivorous-carnivorous mammals. They were endemic to North America and Eurasia during the Early Paleocene to the Early Oligocene, and were the earliest group of large carnivorous mammals in Asia. Once considered a sister-taxon to artiodactyls, recent evidence now suggests no close connection to any living mammal. Mesonychid taxonomy has long been disputed and they have captured popular imagination as "wolves on hooves", animals that combine features of both ungulates and carnivores. Skulls and teeth have similar features to early whales, and the family was long thought to be the ancestors of cetaceans. Recent fossil discoveries have overturned this idea; the consensus is that whales are highly derived artiodactyls. Some researchers now consider the family a sister group either to whales or to artiodactyls, close relatives rather than direct ancestors. Other studies define Mesonychia as basal to all ungulates, occupying a position between Perissodactyla and Ferae. In this case, the resemblances to early whales would be due to convergent evolution among ungulate-like herbivores that developed adaptations related to hunting or eating meat.

Periptychidae is a family of Cretaceous-Paleocene placental mammals, known definitively only from North America. The family is part of a radiation of early herbivorous and omnivorous mammals formerly classified in the extinct order "Condylarthra", which may be related to some or all living ungulates. Periptychids are distinguished from other "condylarths" by their teeth, which have swollen premolars and unusual vertical enamel ridges. The family includes both large and small genera, with the larger forms having robust skeletons. Known skeletons of periptychids suggest generalized terrestrial habits.

Uintacyon is an extinct paraphyletic genus of placental mammals from clade Carnivoraformes, that lived in North America from the early to middle Eocene.

Didymictis is an extinct genus of placental mammals from extinct subfamily Didymictinae within extinct family Viverravidae, that lived in North America and Europe from the late Paleocene to middle Eocene.
Pristinictis is an extinct genus of placental mammals from extinct subfamily Didymictinae within extinct family Viverravidae, that lived in North America during middle Paleocene.

Raphictis is an extinct genus of placental mammals from extinct subfamily Didymictinae within extinct family Viverravidae, that lived in North America during late Paleocene.

Meniscotherium is an extinct genus of dog-sized mammal which lived 54–38 million years ago. It was a herbivore and had hooves. Fossils have been found in Utah, New Mexico. and Colorado. Many individuals have been found together, indicating that it lived in groups.
The Clarkforkian North American Stage, on the geologic timescale, is the North American faunal stage according to the North American Land Mammal Ages chronology (NALMA), typically set from 56,800,000 to 55,400,000 years BP lasting 1.4 million years.
The Tiffanian North American Stage on the geologic timescale is the North American faunal stage according to the North American Land Mammal Ages chronology (NALMA), typically set from 60,200,000 to 56,800,000 years BP lasting 3.4 million years.

Hyopsodontidae is an extinct family of primitive mammals, initially assigned to the order Condylarthra, living from the Paleocene to the Eocene in North America and Eurasia. Condylarthra is now thought to be a wastebasket taxon; hyopsodontids have occasionally been speculated to be related to Afrotheria, but the most recent consensus is that they are related to Perissodactyla. Analysis of the inner ear shows shared characteristics with the Equoidea ; they may be a basal ungulate group near to perissodactyls.

Phenacodontidae is an extinct family of large herbivorous mammals traditionally placed in the “wastebasket taxon” Condylarthra, which may instead represent early-stage perissodactyls. They lived from the late early Paleocene to early middle Eocene and their fossil remains have been found in North America and Europe. The only unequivocal Asian phenacodontid is Lophocion asiaticus.

Palaeonictis is an extinct genus of placental mammals from extinct subfamily Palaeonictinae within extinct family Oxyaenidae, that lived in Europe and North America from the late Paleocene to the early Eocene.
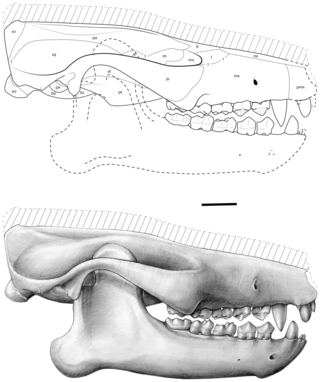
Ocepeia is an extinct genus of afrotherian mammal that lived in present-day Morocco during the middle Paleocene epoch, approximately 60 million years ago. First named and described in 2001, the type species is O. daouiensis from the Selandian stage of Morocco's Ouled Abdoun Basin. A second, larger species, O. grandis, is known from the Thanetian, a slightly younger stage in the same area. In life, the two species are estimated to have weighed about 3.5 kg (7.7 lb) and 10 kg (22 lb), respectively, and are believed to have been specialized leaf-eaters. The fossil skulls of Ocepeia are the oldest known afrotherian skulls, and the best-known of any Paleocene mammal in Africa.
Aletodon is a genus of ground dwelling insectivores, now extinct. The genus flourished from around 58.7 to 55.8 Ma. It was native to Colorado, Wyoming, and western North Dakota.
Orthaspidotherium was a European Paleocene genus of early herbivorous mammals of the family Pleuraspidotheriidae. It was included in the family Meniscotheriidae by Teilhard de Chardin in 1921-1922 and was subsequently separated into the family Pleuraspidotheriidae, before being placed in the family Phenacodontidae. The first complete skull of O. edwardsi was described in 2010, and the same paper once again places it in Pleuraspidotheriidae. A 2017 study further reiterates this view.

Protictis is an extinct paraphyletic genus of placental mammals from extinct subfamily Didymictinae within extinct family Viverravidae, that lived in North America from early Paleocene to middle Eocene.














