
The National Power Corporation, is a Philippine government-owned and controlled corporation that is mandated to provide electricity to all rural areas of the Philippines by 2025, to manage water resources for power generation, and to optimize the use of other power generating assets. Prior to the deregulation of the power industry in 2001, NPC was a vertically integrated power utility engaged in the production, transmission and distribution of electric power and used to be the largest provider and generator of electricity in the Philippines. It was also the principal power provider for Manila Electric Company (Meralco), the only power distributor in the Metro Manila area and its nearby provinces. NPC also served as the operator and owner of the Philippine power grid and its related facilities and assets until the turnover of operations, maintenance, and ownership of the grid to another government-owned corporation National Transmission Corporation (TransCo) on March 1, 2003.

Bayan Telecommunications Inc. (BayanTel) is a telecommunications company headquartered in Quezon City, Philippines serving areas in Metro Manila, Bicol and local exchange service areas in the Visayas and Mindanao regions combined, cover a population of over 25 million, nearly 33% of the population of the Philippines. BayanTel now operates as a subsidiary of Globe Telecom.
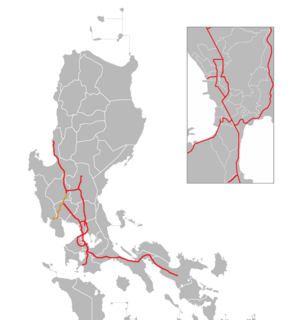
The Subic–Clark–Tarlac Expressway (SCTEX), signed as E1 and E4 of the Philippine expressway network and R-8 of the Metro Manila arterial road network, is controlled-access toll expressway in the Central Luzon region of the Philippines. From its northern terminus in Tarlac City to its southern terminus at Tipo in Hermosa, Bataan, the SCTEX serves as one of the main expressways in Luzon. The expressway is also connected to the Central Luzon Link Expressway, North Luzon Expressway, Tarlac–Pangasinan–La Union Expressway, and the Subic Freeport Expressway. The SCTEX is the country's longest expressway at 93.77 kilometers (58.27 mi). The Subic–Clark–Tarlac Expressway was constructed to provide a more efficient transport corridor between Subic Bay Freeport, Clark, and the Central Techno Park in Tarlac, foster development on the municipalities served, and connect major infrastructures such as the Subic Seaport and the Clark International Airport.

The Philippine Carabao Center an attached agency of the Department of Agriculture, was established at Science City of Muñoz in Nueva Ecija province in 1992 to breed and cross carabao based on high-yield Murrah buffalo in the Philippines as a multi-purpose animal that can be raised for milk, meat, hide, and draft.

Metro Pacific Investments Corporation (MPIC) is a Philippine-based unit investment holding company of First Pacific Company Limited through Metro Pacific Holdings, Inc. MPIC through its subsidiaries, provides water, sanitation, and sewerage services and also operates in real estate, and infrastructure projects. It also invests in some hospitals in the Philippines.
Energy Development Corporation is the largest producer of geothermal energy in the Philippines and the second largest in the world. It is involved in alternative energy projects, including geothermal, hydroelectric and wind energy projects. The company was formerly owned by the Philippine National Oil Company, a state corporation owned by the Republic of the Philippines engaged in the exploration of resources, production of energy and distribution of power supply to smaller electricity distributor. EDC was privatized and acquired by the Lopez Group as part of its energy and power supply utility business units.
DMCI Holdings, Inc. is the real estate arm of DMCI Holdings through its wholly owned subsidiary DMCI Project Developers, Inc. (PDI). It was incorporated and registered with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) on April 27, 1995. It ranked #146 in the Business World Top 1000 Corporations for 2014.
The Laguna Lakeshore Expressway Dike is a proposed expressway in the Philippines that will start from the coastal area of Laguna de Bay from Taguig in Metro Manila to Calamba and Los Baños in Laguna.

Casecnan Irrigation and Hydroelectric Plant is a dam diverting water from the Casecnan and Taan Rivers to the Pantabangan Reservoir through a 26-kilometre (16 mi) long tunnel located near Pantabangan and Muñoz in Nueva Ecija province of the Philippines. The multi-purpose dam provides water for irrigation and hydroelectric power generation while its reservoir affords flood control. It was considered one of the most expensive hydroelectric plants built in the country, being next only to San Roque Dam.

As of 2005, the Philippines was the ninth largest sugar producer in the world and second largest sugar producer among the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) countries, after Thailand, according to Food and Agriculture Organization. At least seventeen provinces of the Philippines have grown sugarcane, of which the two on Negros Island account for half of the nation's total production. As of crop year 2009-2010, 29 sugar mills are operational divided as follows: thirteen mills on Negros, six mills on Luzon, four mills on Panay, three mills in Eastern Visayas and three mills on Mindanao.

The total primary energy consumption of the Philippines in 2012 was 30.2 Mtoe, most of which came from fossil fuels. Electricity consumption in 2010 was 64.52 TWh, of which almost two-thirds came from fossil fuels, 21% from hydroelectric plants, and 13% from other renewable sources. The total generating capacity was 16.36 GW.
The Kaliwa Low Dam, proposed by the Philippine Government in 2012, was one of several bulk water supply projects on the upper portion of the Kaliwa River Watershed that have been proposed but ultimately shelved by the Philippine Government since the 1970s.

The electricity sector in the Philippines provides electricity through power generation, transmission, and distribution to many parts of the Philippines. The Philippines is divided into three electrical grids, one each for Luzon, the Visayas and Mindanao. As of June 2016, the total installed capacity in the Philippines was 20,055 megawatts (MW), of which 14,348 MW was on the Luzon grid. As of June, 2016, the all-time peak demand on Luzon was 9,726 MW at 2:00 P.M. on May 2, 2016; on Visayas was 1,878 MW at 2:00 P.M. on May 11, 2016; and on Mindanao was 1,593 MW at 1:35 P.M. on June 8, 2016. However, about 12% of Filipinos have no access to electricity. The Philippines is also one of the countries in the world that has a fully functioning electricity market since 2006 called the Philippine Wholesale Electricity Spot Market(WESM) and is operated by an independent market operator.
In 2013, renewable energy provided 26.44% of the total electricity in the Philippines and 19,903 gigawatt-hours (GWh) of electrical energy out of a total demand of 75,266 gigawatt-hours. The Philippines is a net importer of fossil fuels. For the sake of energy security, there is momentum to develop renewable energy sources. The types available include hydropower, geothermal power, wind power, solar power and biomass power. The government of the Philippines has legislated a number of policies in order to increase the use of renewable energy by the country.

The Metro Rail Transit Line 7, also known as MRT Line 7 or MRT-7, is a rapid transit line under construction in the Philippines. When completed, the line will be 22.8 kilometers (14.2 mi) long, with 14 stations, and the first line to have a third rail electrification. The line runs in a northeast–southwest direction, beginning at San Jose del Monte, Bulacan up to the North Triangle Common Station in North Avenue, Quezon City.

The North–South Commuter Railway (NSCR), also known as the Clark–Calamba Railway, is a 148-kilometer (92 mi) urban rail transit system under construction in the island of Luzon, Philippines, primarily in the Greater Manila Area. Running from New Clark City in Capas to Calamba, Laguna with 36 stations and four services, the railway was designed to improve connectivity within the region. It will be integrated into existing and future railway lines such as the LRT Line 1, LRT Line 2, MRT Line 3, and the Metro Manila Subway.
Aboitiz Power Corporation also known as AboitizPower (AP), a subsidiary of Aboitiz Equity Ventures (AEV), is a holding company engaged in power distribution, generation and retail electricity services.
ACEN is the listed energy platform of the Ayala Group. The company has over 3,000 MW of attributable capacity in the Philippines, Vietnam, Indonesia, India, and Australia. The company’s renewable share of capacity is at ~80%, among the highest in the region.


































