
Bulacan, officially the Province of Bulacan, is a province in the Philippines located in the Central Luzon region. Its capital is the city of Malolos. Bulacan was established on August 15, 1578, and part of the Metro Luzon Urban Beltway Super Region. This province is a part of the Greater Manila Area.

San Jose del Monte, officially the City of San Jose del Monte, is a component city in the province of Bulacan, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 651,813 people, making it the largest local government unit within the province of Bulacan and Central Luzon, and the 18th most populated city in the Philippines.

The South Luzon Expressway (SLEX), signed as E2 of the Philippine expressway network and R-3 of the Metro Manila arterial road network, is a controlled-access highway that connects Metro Manila to the provinces in the Calabarzon, Mimaropa and Bicol Region on the island of Luzon in the Philippines. The expressway has a length of 49.56 km, traveling from its northern terminus at the Magallanes Interchange in Makati to its southern terminus at Santo Tomas, Batangas, connecting it to the Southern Tagalog Arterial Road. A portion of the expressway from the Magallanes Interchange to the Calamba Exit is part of Asian Highway 26 of the Asian highway network. It will be the longest expressway in the Philippines starting with the completion of Toll Road 4 surpassing the Subic–Clark–Tarlac Expressway (SCTEX) as well as providing a gateway to Visayas upon the completion of Toll Road 5.

The Pampanga River is the second largest river on the island of Luzon in the Philippines and the country's fifth longest river. It is in the Central Luzon region and traverses the provinces of Pampanga, Bulacan, and Nueva Ecija.

Doña Remedios Trinidad, officially the Municipality of Doña Remedios Trinidad, known by its acronym as DRT, is a municipality in the province of Bulacan, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 28,656 people, making it the least populated municipality in the province.

Norzagaray, officially the Municipality of Norzagaray, is a municipality in the province of Bulacan, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 136,064 people.
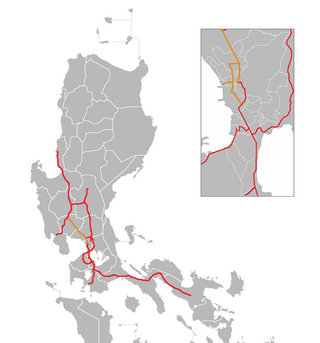
The North Luzon Expressway (NLEX), signed as E1 of the Philippine expressway network, partially as N160 of the Philippine highway network, and partially as R-8 of the Metro Manila arterial road network, is a controlled-access highway that connects Metro Manila to the provinces of the Central Luzon region in the Philippines. The expressway, which includes the main segment and its various spurs, has a total length of 101.8 kilometers (63.3 mi) and travels from its northern terminus at Santa Ines Interchange in Mabalacat, Pampanga, to its southern terminus at Balintawak Interchange in Quezon City, which is adjacent to its connection to Skyway, an elevated toll road that connects the expressway to its counterpart in the south, the South Luzon Expressway. The segment of the expressway between Santa Rita Exit in Guiguinto and the Balintawak Interchange is part of Asian Highway 26 of the Asian highway network. Although its name implies a connection to northern Luzon, the expressway's northern end is actually in Central Luzon.

Manila Water Company, Inc. has the exclusive right to provide water and used water (wastewater) services to over six million people in the East Zone of Metro Manila. It is a subsidiary of Enrique Razon's Trident Water Holdings Company, Inc., who acquired stakes from the country's oldest conglomerate, Ayala Corporationstarting in 2020 and completely taking over by 2024.

The Metro Manila Skyway, officially the Metro Manila Skyway System (MMSS) or simply the Skyway, is an elevated highway serving as the main expressway of Metro Manila, Philippines. It connects the North and South Luzon Expressways with access to Ninoy Aquino International Airport via the NAIA Expressway (NAIAX). It is the first fully grade-separated highway in the Philippines and one of the longest elevated highways in the world, with a total length of approximately 39.2 kilometers (24.4 mi).

The Tarlac–Pangasinan–La Union Expressway (TPLEX), signed as E1 of the Philippine expressway network and R-8 of the Metro Manila arterial road network, is a controlled-access toll expressway that connects the Central Luzon region with the Ilocos Region. From its northern terminus at Rosario in La Union to its southern terminus at Tarlac City, the expressway has a length of 89.21-kilometer (55.43 mi), cutting through the various provinces in northern Central Luzon. The expressway also passes Nueva Ecija between Tarlac and Pangasinan, only that it is not included on the expressway's name because there are no exits to directly serve the province although the exits indirectly serving it are Central Luzon Link Expressway (CLLEX)/Tarlac City, Victoria, Pura, and Anao which are located in Tarlac.
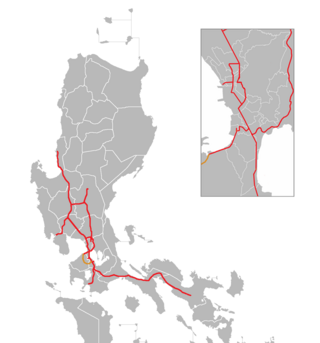
The Cavite–Laguna Expressway, signed as E3 of the Philippine expressway network, is a partially operational controlled-access toll expressway in the provinces of Cavite and Laguna, Philippines. The construction of the 44.63-kilometer-long (27.73 mi) expressway, which began in June 2017, costs an estimated ₱35.43 billion. Once completed, it will connect the Manila–Cavite Expressway in Kawit to the South Luzon Expressway in Biñan and is expected to ease the traffic congestion in the Cavite–Laguna area, particularly along the Aguinaldo Highway, Governor's Drive, and the Santa Rosa–Tagaytay Road.
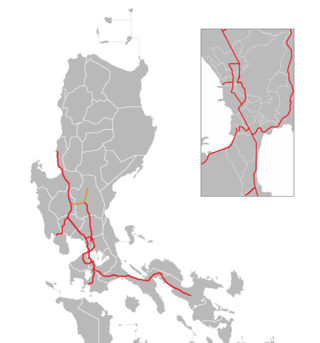
The Central Luzon Link Expressway (CLLEX), also known as the Central Luzon Link Freeway, is a partially operational expressway in the Central Luzon region of the Philippines. It will connect the Subic–Clark–Tarlac Expressway (SCTEX) and the Tarlac–Pangasinan–La Union Expressway (TPLEX) to the currently under-construction North Luzon East Expressway in Cabanatuan towards San Jose, Nueva Ecija. It is currently toll-free and exclusively open to Class 1 vehicles, but it will be tolled and opened to other classes of vehicles in the future.

Kellen Transport Incorporated or simply KTI is a city bus company formed as a subsidiary of former Jell Transport, Inc. or JTI. It plies the previous routes from Baclaran, Parañaque to Grotto, San Jose del Monte, Bulacan. Now they operating in EDSA Carousel route under the ES Consortium. It's a subsidiary of ES Transport Inc., which a parent company operates both city and provincial operations.

Circumferential Road 6 (C-6), informally known as the C-6 Road, is a network of roads and bridges which will comprise the sixth and outermost beltway of Metro Manila in the Philippines once completed.

The Angat Watershed Forest Reserve is a conservation area that protects the drainage basin in the southern Sierra Madre range north of Metro Manila in the Philippines where surface water empties into the Angat River and its distributaries. It is spread over an area of 62,309 hectares in the eastern portion of Bulacan and northern Rizal province at an altitude of between 490 and 1,206 metres. The conservation area also extends to the provinces of Nueva Ecija and Quezon and is centered on an artificial lake created by the Angat Dam which, together with the Ipo Dam located 7.5 kilometres (4.7 mi) downstream, supply 97% of the water requirement of Metro Manila via an aqueduct system to the La Mesa Dam and Reservoir and the Balara Filtration Plant in Quezon City. The Angat Dam and Reservoir is also a major source of hydroelectricity for Metro Manila and surrounding provinces, contributing some 200 megawatts to the Luzon grid. The watershed is a popular birdwatching site and is a biodiversity hotspot containing most of the remaining closed-canopy forests in Central Luzon.

The Pantabangan–Carranglan Watershed Forest Reserve is a conservation area located in the upper reaches of the Pampanga River in Nueva Ecija, Philippines, and borders the Sierra Madre and Caraballo Mountains in Aurora and Nueva Vizcaya. It encompasses 84,500 hectares of the drainage basin surrounding the Pantabangan Lake, an impoundment of the Pampanga River by the Pantabangan Dam. The multi-purpose dam is situated at the confluence of Pampanga River's two headwaters, namely the Pantabangan and Carranglan Rivers in the municipality of Pantabangan. It stretches above the dam site for 21 kilometres (13 mi) to where Carranglan River originates in the Caraballo on the north, and for 18 kilometres (11 mi) to where Pantabangan River originates in the Sierra Madre on the east. It is considered a critical watershed for the agricultural economy and hydroelectric power generation in the region of Central Luzon.

The Philippine expressway network, also known as the High Standard Highway Network, is a controlled-access highway network managed by the Department of Public Works and Highways (DPWH) which consists of all expressways and regional high standard highways in the Philippines.
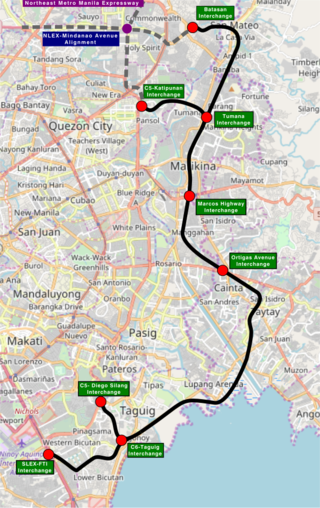
The Southeast Metro Manila Expressway (SEMME), also known as Skyway Stage 4, C-6 Expressway and formerly Metro Manila Expressway, is an proposed 32.664-kilometer (20.296 mi) tolled expressway running across eastern Metro Manila and western Rizal. The expressway will help decongest the existing roadways across Metro Manila, such as EDSA and Circumferential Road 5. The expressway is part of the larger Circumferential Road 6 project, expanding from the original C-6 currently passing from General Santos Avenue in Taguig up to Highway 2000 in Taytay, will expand to Cainta, Pasig, Marikina, San Mateo, and in Quezon City.

Plaridel Bypass Road is a 24.61-kilometer (15.29 mi) national secondary road in the province of Bulacan, Philippines. Traversing agricultural lands, it bypasses the town propers of Plaridel, Pulilan, Baliwag, and San Rafael and serves as an alternative route to the Pan-Philippine Highway.




















