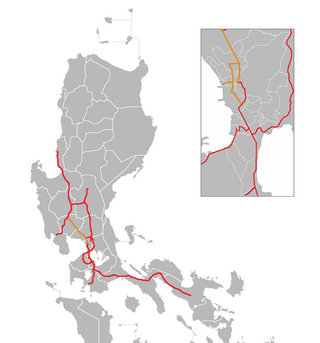
The North Luzon Expressway (NLEX), signed as E1 of the Philippine expressway network, partially as N160 of the Philippine highway network, and partially as R-8 of the Metro Manila arterial road network, is a controlled-access highway that connects Metro Manila to the provinces of the Central Luzon region in the Philippines. The expressway, which includes the main segment and its various spurs, has a total length of 101.8 kilometers (63.3 mi) and travels from its northern terminus at Santa Ines Interchange in Mabalacat, Pampanga, to its southern terminus at Balintawak Interchange in Quezon City, which is adjacent to its connection to Skyway, an elevated toll road that connects the expressway to its counterpart in the south, the South Luzon Expressway. The segment of the expressway between Santa Rita Exit in Guiguinto and the Balintawak Interchangeis part of Asian Highway 26 of the Asian highway network. Although its name implies a connection to northern Luzon, the expressway's northern end is actually in Central Luzon.
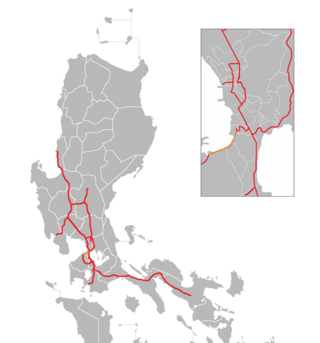
The Manila–Cavite Expressway, signed as E3 of the Philippine expressway network and R-1 of Metro Manila's arterial road network, is a 14-kilometer-long (8.7 mi) controlled-access highway linking Manila to the southern province of Cavite in the Philippines. At its north end, it feeds into and from Roxas Boulevard in Parañaque, Metro Manila, also part of R-1. At the south end, it splits into two termini along the north coast in Kawit, Cavite. The first feeds into the intersection of Covelandia Road, Tirona Highway and Antero Soriano Highway. The second southern terminus is an exit-only to Tirona Highway in Barangay Marulas.

The Subic–Clark–Tarlac Expressway (SCTEX), signed as E1 and E4 of the Philippine expressway network, is a controlled-access toll expressway in the Central Luzon region of the Philippines. From its northern terminus in Tarlac City to its southern terminus at Tipo in Dinalupihan, Bataan, the SCTEX serves as one of the main expressways in Luzon. The expressway is also connected to the Central Luzon Link Expressway, North Luzon Expressway, Tarlac–Pangasinan–La Union Expressway, and the Subic Freeport Expressway. The SCTEX is the country's longest expressway at 93.77 kilometers (58.27 mi) until the completion of Toll Road 4 of South Luzon Expressway (SLEX). The Subic–Clark–Tarlac Expressway was constructed to provide a more efficient transport corridor between Subic Bay Freeport, Clark, and the Central Techno Park in Tarlac, foster development on the municipalities served, and connect major infrastructures such as the Subic Seaport and Clark International Airport.

The Metro Manila Skyway, officially the Metro Manila Skyway System (MMSS) or simply the Skyway, is an elevated highway serving as the main expressway of Metro Manila, Philippines. It connects the North and South Luzon Expressways with access to Ninoy Aquino International Airport via the NAIA Expressway (NAIAX). It is the first fully grade-separated highway in the Philippines and one of the longest elevated highways in the world, with a total length of approximately 39.2 kilometers (24.4 mi).

The Port of Manila refers to the collective facilities and terminals that process maritime trade function in harbors in Metro Manila. Located in the Port Area and Tondo districts of Manila, facing Manila Bay, it is the largest and the premier international shipping gateway to the country. The Philippine Ports Authority, a government-owned corporation, manages the Port of Manila and most of the public ports in the country. It is composed of 3 major facilities, namely Manila North Harbor, Manila South Harbor, and the Manila International Container Terminal.

The Tarlac–Pangasinan–La Union Expressway (TPLEX), signed as E1 of the Philippine expressway network and R-8 of the Metro Manila arterial road network, is a controlled-access toll expressway that connects the Central Luzon region with the Ilocos Region. From its northern terminus at Rosario in La Union to its southern terminus at Tarlac City, the expressway has a length of 89.21-kilometer (55.43 mi), cutting through the various provinces in northern Central Luzon. The expressway also passes Nueva Ecija between Tarlac and Pangasinan, only that it is not included on the expressway's name because there are no exits to directly serve the province although the exits indirectly serving it are Central Luzon Link Expressway (CLLEX)/Tarlac City, Victoria, Pura, and Anao which are located in Tarlac.

Circumferential Road 5 (C-5), informally known as the C-5 Road, is a network of roads and bridges which comprise the fifth beltway of Metro Manila in the Philippines. Spanning some 43.87 kilometers (27.26 mi), it connects the cities of Las Piñas, Parañaque, Pasay, Pasig, Quezon City, Taguig, and Valenzuela.

Radial Road 8 (R-8), informally known as the R-8 Road, is a network of roads and bridges which comprise the eighth radial road of Metro Manila in the Philippines. It runs north-south through northern Metro Manila, linking the city of Manila with Quezon City, Caloocan, and Valenzuela into the northern provinces of Bulacan, Pampanga, Tarlac, Pangasinan, and La Union. The portion of R-8 between Guiguinto and Balintawak is also designated a component of the Pan-Philippine Highway network (AH26). It also has a spur segment in Quirino Highway from NLEX to its junction with R-7 at Commonwealth Avenue, both in Quezon City.

The Subic Freeport Expressway (SFEX), formerly the Subic–Tipo Road, Subic–Tipo Expressway and North Luzon Expressway Segment 7, is an 8.8-kilometer (5.5 mi) four-lane expressway that connects the Subic–Clark–Tarlac Expressway to the Subic Freeport Zone in the Philippines. Its alignment traverses the provinces of Bataan and Zambales.

Mindanao Avenue is an eight-to-ten-lane divided avenue connecting EDSA and NLEX and is a part of Circumferential Road 5 (C-5) in Metro Manila, Philippines. It is one of the three parallel roads that connects Tandang Sora and Congressional Avenues ; that is why it was named after the southernmost mainland of the Philippines, Mindanao. It used to be a 2-kilometer (1.2 mi) highway connecting North Avenue and Congressional Avenue, but as a part of the C-5 projects, Mindanao Avenue was extended to EDSA in the south and to Quirino Highway to the north. The new roads opened in 2000.
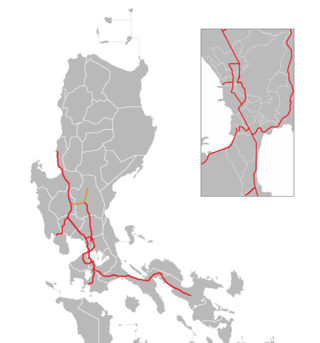
The Central Luzon Link Expressway (CLLEX), also known as the Central Luzon Link Freeway, is a partially operational expressway in the Central Luzon region of the Philippines. It will connect the Subic–Clark–Tarlac Expressway (SCTEX) and the Tarlac–Pangasinan–La Union Expressway (TPLEX) to the currently under-construction North Luzon East Expressway in Cabanatuan towards San Jose, Nueva Ecija. It is currently toll-free and exclusively open to Class 1 vehicles, but it will be tolled and opened to other classes of vehicles in the future.

Maysan Road is one of the main east–west thoroughfares of Valenzuela, Philippines. It is a narrow street with only one lane in each direction, making it one of the most congested streets in northern Metro Manila. It runs for approximately 4.5 kilometers (2.8 mi) from MacArthur Highway in barangay Malinta, past the North Luzon Expressway intersection, into North Caloocan. The road connects the central Valenzuela barangays of Malinta, Maysan, Paso de Blas, and Bagbaguin. It was the main access road for vehicles going to Valenzuela and the Manila North Harbor from the North Luzon Expressway before the construction of NLEX Segment 9, which parallels it to the south.

Circumferential Road 6 (C-6), informally known as the C-6 Road, is a network of roads and bridges which will comprise the sixth and outermost beltway of Metro Manila in the Philippines once completed.

The Balintawak Interchange, also known as the Balintawak Cloverleaf, is a two-level cloverleaf interchange in Quezon City, Metro Manila, Philippines, which serves as the junction between Epifanio de los Santos Avenue (EDSA) and the North Luzon Expressway (NLEX). Opened in 1968 as part of the initial 28-kilometer (17 mi) NLEX segment between Quezon City and Guiguinto, Bulacan, it was one of the first projects of the Construction and Development Corporation of the Philippines.
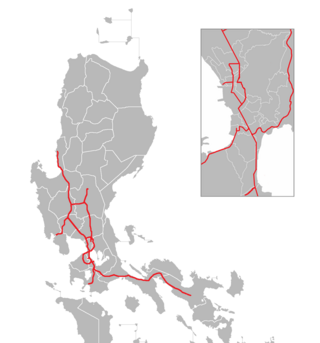
The Philippine expressway network, also known as the High Standard Highway Network, is a controlled-access highway network managed by the Department of Public Works and Highways (DPWH) which consists of all expressways and regional high standard highways in the Philippines.
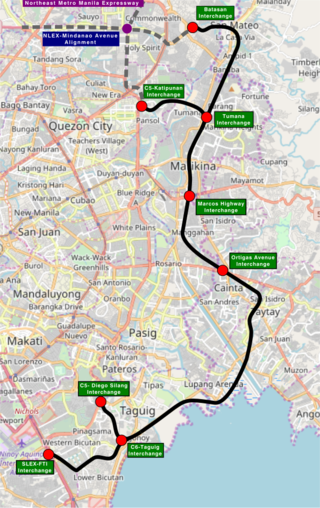
The Southeast Metro Manila Expressway (SEMME), also known as Skyway Stage 4, C-6 Expressway and formerly Metro Manila Expressway, is an on-hold 32.664-kilometer (20.296 mi) tolled expressway running across eastern Metro Manila and western Rizal. The expressway will help decongest the existing roadways across Metro Manila, such as EDSA and Circumferential Road 5. The expressway is part of the larger Circumferential Road 6 project, expanding from the original C-6 currently passing from General Santos Avenue in Taguig up to Highway 2000 in Taytay, will expand to Cainta, Pasig, Marikina, San Mateo, and in Quezon City.
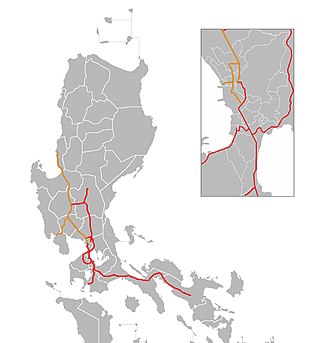
Expressway 1 (E1) forms part of the Philippine expressway network. It runs through western Luzon from Quezon City in the south to Rosario in the north.

NLEX Harbor Link, signed as E5 of the Philippine expressway network, is a four- to six-lane expressway that serves as a spur of North Luzon Expressway (NLEX) linking it to the Port of Manila to the west and Quezon City to the east. It runs from Katipunan and C.P. Garcia Avenues in Quezon City to Radial Road 10 in Navotas, leading to the Port of Manila. Currently, its segment from Mindanao Avenue in Valenzuela to Navotas is operational.

NLEX Corporation is a subsidiary of Metro Pacific Tollways Corporation (MPTC), a company owned by Metro Pacific Investments Corporation. It holds the concession rights to construct, operate and maintain the North Luzon Expressway (NLEX) and Subic–Clark–Tarlac Expressway (SCTEX). The company was acquired by the Metro Pacific group from Lopez Holdings Corporation in August 2008.

NLEX Connector, also known as the NLEX–SLEX Connector Road, NLEX Connector Road, and NLEX Segment 11 during the planning stages, is a 7.7-kilometer (4.8 mi), four-lane elevated expressway in Metro Manila, Philippines. It connects the NLEX Harbor Link to the Metro Manila Skyway, which connects further to the North and South Luzon Expressways. The highway traverses parallel to the PNR Metro Commuter Line. It has five interchanges, four of which are currently operational. Alongside NLEX Harbor Link, trucks are allowed to use it.






















