
Bacoor, officially the City of Bacoor, is a 1st class component city in the province of Cavite, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 664,625 people, making it the 15th most populous city in the Philippines and the second largest city in the province of Cavite after Dasmariñas.

Noveleta, officially the Municipality of Noveleta, formerly known as Tierra Alta during the Spanish colonial era, is a 1st class municipality in the province of Cavite, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 49,452 people.
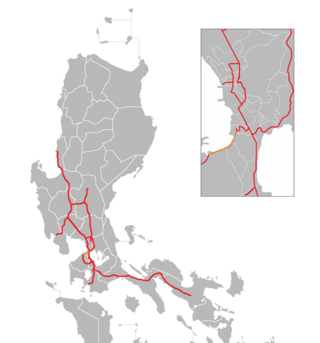
The Manila–Cavite Expressway, signed as E3 of the Philippine expressway network and R-1 of Metro Manila's arterial road network, is a 14-kilometer-long (8.7 mi) controlled-access highway linking Manila to the southern province of Cavite in the Philippines. At its north end, it feeds into and from Roxas Boulevard in the city of Parañaque in Metro Manila, also part of R-1. At the south end, it splits into two termini, both along the north coast in Kawit, Cavite. The first feeds into the intersection of Covelandia Road, Tirona Highway and Antero Soriano Highway. The second southern terminus is an exit-only to Tirona Highway in Barangay Marulas.

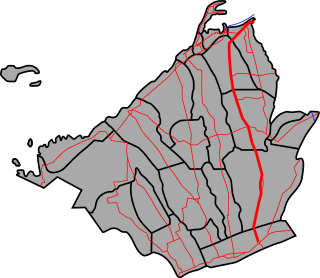
The Cavite Peninsula is a peninsula extending northeast into Manila Bay from the coastal town of Noveleta in Cavite province in the Philippines. The northern tip of the peninsula is geographically the northernmost part of the province of Cavite.

Radial Road 1 (R-1), informally known as the R-1 Road, is a network of roads and bridges that all together form the first arterial road of Metro Manila in the Philippines. Spanning some 42.67 kilometers (26.51 mi), it connects the cities and municipalities of Bacoor, General Trias, Imus, Kawit, Las Piñas, Manila, Naic, Noveleta, Parañaque, Pasay, and Tanza in Cavite and Metro Manila.

Radial Road 2 (R-2), informally known as the R-2 Road, is a network of roads and bridges that all together form the second arterial road of Metro Manila in the Philippines. Spanning some 56.51 kilometers (35.11 mi), it connects the cities and municipalities of Bacoor, Dasmariñas, Imus, Las Piñas, Manila, Parañaque, Pasay, Silang, and Tagaytay in Cavite and Metro Manila.
The Emilio Aguinaldo Highway,, alternatively known as Cavite–Batangas Road and Cavite-Manila South Road, is a four-to-six lane, 41.4-kilometer (25.7 mi), network of primary and secondary highways passing through the busiest towns and cities of Cavite, Philippines. It is the busiest and most congested of the three major highways located in the province, the others are Governor's Drive and Antero Soriano Highway.

The Antero Soriano Highway, also partly known as Centennial Road, is a two-to-six lane, 21.6-kilometer (13.4 mi) highway traversing through the western coast of Cavite. It is one of the three major highways located in the province, the others are Aguinaldo Highway and Governor's Drive.

The Battle of Binakayan–Dalahican was a simultaneous battle during the Philippine Revolution that was fought on November 9–11, 1896 that led to a decisive Filipino victory. The twin battle took place at the shores of Binakayan, in the town of Cavite Viejo ; Dalahican and Dagatan in Noveleta; and, to minimal extent, in Imus and Bacoor towns in Cavite, Philippines that lasted for two days before the Spanish army retreated demoralized and in disarray. The result of the battle was the first significant Filipino victory in the country's history.
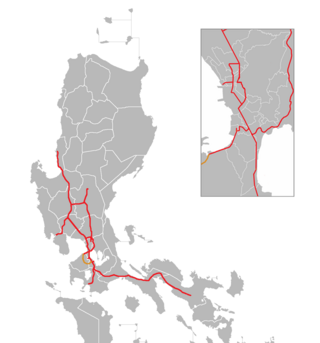
The Cavite–Laguna Expressway, signed as E3 of the Philippine expressway network, is a partially operational controlled-access toll expressway in the provinces of Cavite and Laguna, Philippines. The construction of the 44.63-kilometer-long (27.73 mi) expressway, which began in June 2017, costs an estimated ₱35.43 billion. Once completed, it will connect the Manila–Cavite Expressway in Kawit to the South Luzon Expressway in Biñan and is expected to ease the traffic congestion in the Cavite–Laguna area, particularly along the Aguinaldo Highway, Governor's Drive, and the Santa Rosa–Tagaytay Road.

Alabang–Zapote Road is a four-lane national road which travels east–west through the southern limits of Metro Manila, Philippines. It runs parallel to Dr. Santos Avenue in the north and is named for the two barangays that it links: Alabang in the city of Muntinlupa and Zapote in both the cities of Bacoor and Las Piñas.

Daang Hari, also known as the Las Piñas–Muntinlupa–Laguna–Cavite Link Road, is a collector road that links southern Metro Manila to the province of Cavite in the Philippines. It begins as a north–south road from Commerce Avenue, just south of the Alabang–Zapote Road running for 5.9 kilometers (3.7 mi) on the boundary of Las Piñas and Muntinlupa. It then runs east–west for about 9.2 kilometers (5.7 mi) from its junction with Daang Reyna, winding through the cities of Bacoor, Imus, Dasmariñas, and General Trias.

Elpidio Quirino Avenue, also known simply as Quirino Avenue, is a major north-south collector road in Parañaque, southern Metro Manila, Philippines. It is a four-lane undivided arterial running parallel to Roxas Boulevard and its extension, the Manila–Cavite Expressway, to the west from Baclaran at Parañaque's border with Pasay in the north to San Dionisio right by the border with Las Piñas in the south. It is a continuation of Harrison Avenue from Pasay and was originally a segment of the coastal highway called Calle Real. The entire road is a component of Radial Road 2 (R-2) of Manila's arterial road network, while its segment south of NAIA Road is a component of National Route 62 (N62) of the Philippine highway network. It was named after President Elpidio Quirino. The road's name is also applied alternatively to Diego Cera Avenue in Las Piñas.

Padre Diego Cera Avenue, or simply Diego Cera Avenue, is a major north-south collector road in Las Piñas, Metro Manila, Philippines. It is a four-lane undivided arterial running parallel to the Manila–Cavite Expressway to the west from Manuyo Uno at Las Piñas' border with Parañaque in the north to Zapote near the border with Bacoor in the south. It is a continuation of Elpidio Quirino Avenue from Parañaque and was originally a segment of Calle Real in Las Piñas. The road is a component of the National Route 62 (N62) of the Philippine highway network and Radial Road 2 (R-2) of Manila's arterial road network.
The Light Rail Transit Line 6 is a proposed rapid transit system in Cavite, Philippines. There have been two proposals for the line, with the first one shelved immediately in 2018. Another proposal emerged in 2017 and is currently under review by the National Economic and Development Authority (NEDA).
Expressway 3 (E3) forms part of the Philippine expressway network. Its main route runs from Parañaque to Kawit, Cavite as Manila–Cavite Expressway and from Kawit, Cavite to Biñan, Laguna as Cavite–Laguna Expressway.
National Route 622 (N622) forms part of the Philippine highway network. It is one of the national secondary roads with two non-contiguous sections, one which runs through the municipalities of Kawit and Noveleta in Cavite, while the other road runs through the municipality of Daet in Camarines Norte; both of these roads are located in Luzon island.

The Tirona Highway is a two-to-four lane, primary highway in Cavite, Philippines. It connects the city of Bacoor and the municipality of Kawit. It was named for Filipino revolutionary leader Daniel Tirona. The Aguinaldo Shrine, the site of the Philippine Declaration of Independence and residence of Emilio Aguinaldo, is located along the road.
National Route 401 (N401) forms part of the Philippine highway network. It connects the municipalities of Noveleta to the city of General Trias through the municipality of Rosario.

The Dasmariñas – Las Piñas Transmission Line is a 230,000 volt, double-circuit transmission line in Metro Manila and Calabarzon, Philippines that connects Dasmariñas and Las Piñas substations of National Grid Corporation of the Philippines (NGCP).





















