
Cass Lake is a city in Cass County, Minnesota, United States, located within the boundaries of the Leech Lake Indian Reservation. It is surrounded by Pike Bay Township. Cass Lake had a population of 675 in the 2020 census. It is notable as the headquarters location of Minnesota Chippewa Tribe and Leech Lake Band of Ojibwe, as well as the Chippewa National Forest.

The Red Lake Indian Reservation covers 1,260.3 sq mi in parts of nine counties in Minnesota, United States. It is made up of numerous holdings but the largest section is an area around Red Lake, in north-central Minnesota, the largest lake in the state. This section lies primarily in the counties of Beltrami and Clearwater. Land in seven other counties is also part of the reservation. The reservation population was 5,506 in the 2020 census.
Sandy Lake Band of Mississippi Chippewa are a historical Ojibwa tribe located in the upper Mississippi River basin, on and around Big Sandy Lake in what today is in Aitkin County, Minnesota. Though politically folded into the Mille Lacs Band of Ojibwe, thus no longer independently federally recognized, for decades, Sandy Lake Band members have been leading efforts to restore their independent Federal recognition.

The White Earth Indian Reservation is home to the White Earth Band, in northwestern Minnesota. It is the largest Indian reservation in the state by land area. The reservation includes all of Mahnomen County, plus parts of Becker and Clearwater counties in the northwest part of the state along the Wild Rice and White Earth rivers. The reservation's land area is 1,093 square miles (2,830 km2). The population was 9,726 as of the 2020 census, including off-reservation trust land. The White Earth Indian Reservation is one of six bands that make up the Minnesota Chippewa Tribe, their governing body for major administrative needs. It is about 225 miles (362 km) from Minneapolis–Saint Paul and roughly 65 miles (105 km) from Fargo–Moorhead.

The Minnesota Chippewa Tribe is the centralized governmental authority for six Ojibwe bands in Minnesota. The tribe was created on June 18, 1934; the organization and its governmental powers are divided between the tribe, and the individual bands, which directly operate their reservations. The bands that make up the tribe are:
The White Earth Band of the Minnesota Chippewa Tribe, also called the White Earth Nation, is a federally recognized Native American band in northwestern Minnesota. The band's land base is the White Earth Indian Reservation.
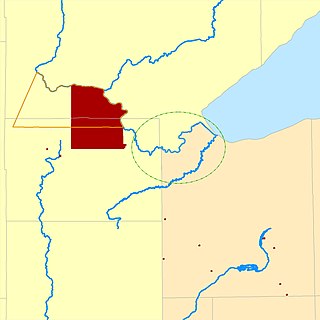
The Fond du Lac Indian Reservation is an Indian reservation in northern Minnesota near Cloquet in Carlton and Saint Louis counties. Off-reservation holdings are located across the state in Douglas County, in the northwest corner of Wisconsin. The total land area of these tribal lands is 154.49 square miles (400.1 km2). It is the land-base for the Fond du Lac Band of Lake Superior Chippewa. Before the establishment of this reservation, the Fond du Lac Band of Lake Superior Chippewa were located at the head of Lake Superior, closer to the mouth of the Saint Louis River, where Duluth has developed.

Fond du Lac Band of Lake Superior Chippewa is an Anishinaabe (Ojibwe) band located near Cloquet, Minnesota. Their land base is the Fond du Lac Indian Reservation, located mainly in Carlton and Saint Louis Counties, Minnesota, 20 miles west of Duluth.

The Leech Lake Reservation is an Indian reservation located in the north-central Minnesota counties of Cass, Itasca, Beltrami, and Hubbard. The reservation forms the land base for the federally recognized Leech Lake Band of Ojibwe, one of six bands comprising the Minnesota Chippewa Tribe, organized in 1934. The Leech Lake Reservation has the second highest population of any reservation in Minnesota with White Earth Nation being the largest Minnesota Ojibwe tribe, Leech Lake Nation has a resident population of 11,388 indicated by the 2020 census.
Mille Lacs Indian Reservation is the popular name for the land-base for the Mille Lacs Band of Ojibwe in Central Minnesota, about 100 miles (160 km) north of Minneapolis-St. Paul. The contemporary Mille Lacs Band reservation has significant land holdings in Mille Lacs, Pine, Aitkin and Crow Wing counties, as well as other land holdings in Kanabec, Morrison, and Otter Tail Counties. Mille Lacs Indian Reservation is also the name of a formal Indian reservation established in 1855. It is one of the two formal reservations on which the contemporary Mille Lacs Band retains land holdings. The contemporary Mille Lacs band includes several aboriginal Ojibwe bands and villages, whose members reside in communities throughout central Minnesota.
The Mille Lacs Band of Ojibwe, also known as the Mille Lacs Band of Chippewa Indians, is a federally recognized American Indian tribe in east-central Minnesota. The Band has 4,302 members as of 2012. Its homeland is the Mille Lacs Indian Reservation, consisting of District I, District II, District IIa, and District III.

The Lac Courte Oreilles Tribe is one of six federally recognized bands of Ojibwe people located in present-day Wisconsin. It had 7,275 enrolled members as of 2010. The band is based at the Lac Courte Oreilles Indian Reservation in northwestern Wisconsin, which surrounds Lac Courte Oreilles. The main reservation's land is in west-central Sawyer County, but two small plots of off-reservation trust land are located in Rusk, Burnett, and Washburn counties. The reservation was established in 1854 by the second Treaty of La Pointe.
Pillager Band of Chippewa Indians are a historical band of Chippewa (Ojibwe) who settled at the headwaters of the Mississippi River in present-day Minnesota. Their name "Pillagers" is a translation of Makandwewininiwag, which literally means "Pillaging Men". The French called them Pilleurs, also a translation of their name. The French and Americans adopted their autonym for their military activities as the advance guard of the Ojibwe in the invasion of the Dakota country.

The Sandy Lake Tragedy was the culmination in 1850 of a series of events centered in Big Sandy Lake, Minnesota that resulted in the deaths of several hundred Lake Superior Chippewa. Officials of the Zachary Taylor Administration and Minnesota Territory sought to relocate several bands of the tribe to areas west of the Mississippi River. By changing the location for fall annuity payments, the officials intended the Chippewa to stay at the new site for the winter, hoping to lower their resistance to relocation. Due to delayed and inadequate payments of annuities and lack of promised supplies, about 400 Ojibwe, mostly men and 12% of the tribe, died of disease, starvation and cold. The outrage increased Ojibwe resistance to removal. The bands effectively gained widespread public support to achieve permanent reservations in their traditional territories.
The Lake Superior Chippewa are a large number of Ojibwe (Anishinaabe) bands living around Lake Superior; this territory is considered part of northern Michigan, Wisconsin, and Minnesota in the United States. They migrated into the area by the seventeenth century, encroaching on the Eastern Dakota people who had historically occupied the area. The Ojibwe defeated the Eastern Dakota, who migrated west into the Great Plains after the final battle in 1745. While they share a common culture including the Anishinaabe language, this highly decentralized group of Ojibwe includes at least twelve independent bands in the region.
The St. Croix Chippewa Indians of Wisconsin are a federally recognized tribe of Ojibwe people located in Northwest Wisconsin, along the St. Croix River valley and watershed. The band had 1,054 members as of 2010.
An act for the relief and civilization of the Chippewa Indians in the State of Minnesota, commonly known as the Nelson Act of 1889, was a United States federal law intended to relocate all the Anishinaabe people in Minnesota to the White Earth Indian Reservation in the western part of the state, and expropriate the vacated reservations for sale to European settlers.

Hole-in-the-Day was a prominent chief of the Mississippi band of Ojibwe/Chippewa in Minnesota. The native pronunciation has been written with different spellings due different speakers variance in their enunciation, such as Bagone-giizhig, Bagwunagijik, Bug-o-nay-ki-shig, Pugonakeshig or Puk-O-Nay-Keshig. Hole-in-the-Day has also been called Hole-in-the-Sky. The name refers to a dream in which the guardian spirit was seen through an opening in the clouds. It also refers to the Anishinaabek name for the constellation of the same name, also known as the Pleiades.
Erma Jean Vizenor is an Ojibwe politician and educator. She served as the tribal chair of the White Earth Nation from 2004 to 2016. Under her leadership, White Earth adopted a new tribal constitution. She served as an educator in the White Earth Indian Reservation for 20 years. Vizenor was president of Leech Lake Tribal College in 2016.

Margaret "Peggy" Seelye Treuer (1943–2020) was an American Ojibwe judge and lawyer. She was Minnesota's first Native American woman lawyer, working as a federal magistrate and tribal court judge for the Bois Forte Band of Chippewa, the Red Lake Nation, and the Leech Lake Indian Reservation. A member of the Leech Lake Band of Ojibwe, she volunteered with the Native American Rights Fund and worked for the reestablishment of the Menominee Indian Reservation. She earned degrees from the law school of the Catholic University of America and St. Luke's School of Nursing. She received a Lifetime Achievement Award from the National Association of Women Judges.

















