
Caesalpinioideae is a botanical name at the rank of subfamily, placed in the large family Fabaceae or Leguminosae. Its name is formed from the generic name Caesalpinia. It is known also as the peacock flower subfamily. The Caesalpinioideae are mainly trees distributed in the moist tropics, but include such temperate species as the honeylocust and Kentucky coffeetree. It has the following clade-based definition:
The most inclusive crown clade containing Arcoa gonavensisUrb. and Mimosa pudicaL., but not Bobgunnia fistuloides(Harms) J. H. Kirkbr. & Wiersema, Duparquetia orchidaceaBaill., or Poeppigia proceraC.Presl

Ptelea trifoliata, commonly known as common hoptree, wafer ash, stinking ash, and skunk bush, is a species of flowering plant in the citrus family (Rutaceae). It is native to North America, where it is found in Canada, Mexico, and the United States. It is a deciduous shrub or tree, with alternate, trifoliate leaves.

Acer negundo, also known as the box elder, boxelder maple, Manitoba maple or ash-leaved maple, is a species of maple native to North America. It is a fast-growing, short-lived tree with opposite, ash-like compound leaves. It is sometimes considered a weedy or invasive species, and has been naturalized throughout much of the world, including South America, Australia, New Zealand, South Africa, much of Europe, and parts of Asia.

Magnolia sieboldii, or Siebold's magnolia, also known as Korean mountain magnolia and Oyama magnolia, is a species of Magnolia native to east Asia in China, Japan, and Korea. It is named after the German doctor Philipp Franz von Siebold (1796–1866).

Argyrodendron actinophyllum, commonly known as black booyong, black jack, stave wood, Mackay tulip oak, crowsfoot elm, booyong, tulip oak or blush tulip oak, is a species of flowering plant in the family Malvaceae and is endemic to eastern Australia. It is a large tree with prominent buttress roots, palmately compound leaves with 5 to 9 lance-shaped leaflets, flower arranged in panicles, and winged samaras.

Gymnosphaera capensis, synonyms Alsophila capensis and Cyathea capensis, is a regionally widespread and highly variable species of tree fern. It is indigenous to Southern Africa and South America.

Fraxinus angustifolia, the narrow-leaved ash, is a species of Fraxinus native to Central Europe and Southern Europe, Northwest Africa, and Southwest Asia.
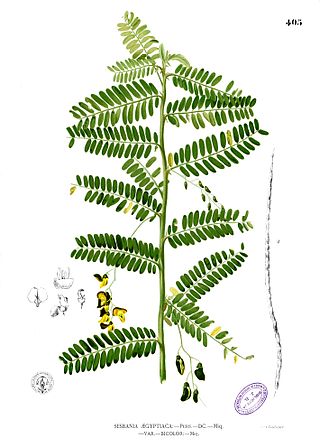
Sesbania sesban, the Egyptian riverhemp, is a species of plant in the legume family, a fast growing species, it has four varieties that are currently recognized.

Crassula tetragona is a succulent plant native to Southern Africa. It is widely distributed from the Orange River boundary of Namaqualand to beyond the Kei River in the Eastern Cape. "Tetragona" comes from the phyllotaxy of the leaves. It is popularly named the "miniature pine tree" among ornamental plant enthusiasts, for its popular use as a "pine tree" in Bonsai.
Leonardoxa is a genus of flowering plants in the family Fabaceae. It belongs to the subfamily Detarioideae.

Atractocarpus fitzalanii, commonly known as the brown gardenia or yellow mangosteen, is a species of plant in the coffee and madder family Rubiaceae. It is found in coastal parts of tropical Queensland, Australia. The beautifully scented flowers and glossy foliage has seen this plant enter cultivation in gardens of eastern Australia.

Leucospermum conocarpodendron is the largest species of the genus Leucospermum, reaching almost tree-like proportions of 5–6 m (16–20 ft) high with a firm trunk that is covered in a thick layer of cork that protects it from most fires. It has greyish or green narrow or broad inverted egg-shaped leaves with three to ten teeth near the tip and large yellow flowerheads, with firm, bent, yellow styles that stick far beyond the rest of the flower and give the impression of a pincushion. It is commonly known as the tree pincushion in English or goudsboom in Afrikaans. They naturally occur near Cape Town, South Africa.

Nematolepis squamea , commonly known as Satinwood, is an upright shrub or small tree species which is endemic to Australia.
Xerocladia viridiramis is a species of plant in the legume family (Fabaceae). It is the sole species in the monotypic genus Xerocladia.

Ficus subpisocarpa is a species of small deciduous tree native to Japan, China, Taiwan and southeast Asia to the Moluccas (Ceram). Two subspecies are recognised. Terrestrial or hemiepiphytic, it reaches a height of 7 m (23 ft). Ants predominantly of the genus Crematogaster have been recorded living in stem cavities. Ficus subpisocarpa is pollinated by Platyscapa ishiiana (Agaonidae).

Goniocheton arborescens, commonly known in Australia as Mossman mahogany, is a small tree in the mahogany family Meliaceae. It is native to rainforests of Malesia, Papuasia, Queensland and nearby islands.

Syzygium forte, commonly known as flaky-barked satinash, white apple or brown satinash, is a tree in the family Myrtaceae native to New Guinea and northern Australia.
Osodendron altissimum, formerly known as Albizia altissima, is a low branching tree within the Fabaceae family, it grows along river banks in the Lower and Upper Guinean and Congolian forests of west and central Africa.
Anthonotha fragrans is a medium to large sized tree commonly found in the rainforest environments of West and Central Africa; it belongs to the Fabaceae family. Its sapwood exudes a white to creamy exudate.

Berlinia grandiflora is a small to medium sized tree found in the West and West Central African region along riparian habitats or gallery forests habitat types.















