Schistosoma is a genus of trematodes, commonly known as blood flukes. They are parasitic flatworms responsible for a highly significant group of infections in humans termed schistosomiasis, which is considered by the World Health Organization to be the second-most socioeconomically devastating parasitic disease, with hundreds of millions infected worldwide.

Digenea is a class of trematodes in the Platyhelminthes phylum, consisting of parasitic flatworms with a syncytial tegument and, usually, two suckers, one ventral and one oral. Adults commonly live within the digestive tract, but occur throughout the organ systems of all classes of vertebrates. Once thought to be related to the Monogenea, it is now recognised that they are closest to the Aspidogastrea and that the Monogenea are more closely allied with the Cestoda. Around 6,000 species have been described to date.

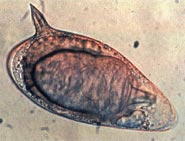
Echinostoma is a genus of trematodes (flukes), which can infect both humans and other animals. These intestinal flukes have a three-host life cycle with snails or other aquatic organisms as intermediate hosts, and a variety of animals, including humans, as their definitive hosts.

The red-rimmed melania, also known as Malayan livebearing snails or Malayan/Malaysian trumpet snails by aquarists, is a species of freshwater snail with an operculum, a parthenogenetic, aquatic gastropod mollusk in the family Thiaridae.

Leucochloridium paradoxum, the green-banded broodsac, is a parasitic flatworm. Its intermediate hosts are land snails, usually of the genus Succinea. The pulsating, green broodsacs fill the eye stalks of the snail, thereby attracting predation by birds, the primary host. These broodsacs visually imitate caterpillars, a prey of birds. The adult parasite lives in the bird's cloaca, releasing its eggs into the faeces.

Leucochloridium variae, the brown-banded broodsac, is a species of trematode whose life cycle involves the alternate parasitic infection of certain species of snail and bird. While there is no external evidence of the worm's existence within the bird host, the infection of the snail host is visible when its eye stalks become grotesquely engorged with the parasite's brood sacs. These brood sacks pulsate and move to imitate insect larva, attracting the parasite's next host, insectivore birds. The bird rips off the eye stalk and eats it, thus becoming infected. Later on, the parasite's eggs are dropped with the bird's feces. Similar life-histories are found in other species of the genus Leucochloridium, including Leucochloridium paradoxum.

Novisuccinea ovalis, commonly called the oval ambersnail, is a species of air-breathing land snail, a terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusk in the family Succineidae, the ambersnails.
Maritrema is a genus of trematodes (flukes) in the family Microphallidae, although some have suggested its placement in the separate family Maritrematidae. It was first described by Nikoll in 1907 from birds in Britain. Species of the genus usually infect birds, but several have switched hosts and are found in mammals, such as the marsh rice rat. Several species use the fiddler crab Uca pugilator as an intermediate host.

Bithynia siamensis is a species of a freshwater snail with a gill and an operculum, an aquatic prosobranch gastropod mollusk in the family Bithyniidae.

Spirorchiidae is a family of digenetic trematodes. Infestation by these trematodes leads to the disease spirorchiidiosis. Spirorchiids are mainly parasites of turtles. It has been synonymised with Proparorchiidae Ward, 1921, Spirorchidae Stunkard, 1921, and Spirorchiidae MacCallum, 1921.

Clinostomum marginatum is a species of parasitic fluke. It is commonly called the "Yellow grub". It is found in many freshwater fish in North America, and no fish so far is immune to this parasite. It is also found in frogs. Clinostomum marginatum can also be found in the mouth of aquatic birds such as herons and egrets. They are commonly present in the esophagus of fish-eating birds and reptiles. Eggs of these trematodes are shed in the feces of aquatic birds and released into water. Aquatic birds become hosts of this parasite by ingesting infected freshwater fish. The metacercariae are found right beneath the skin or in the muscles of host fish.
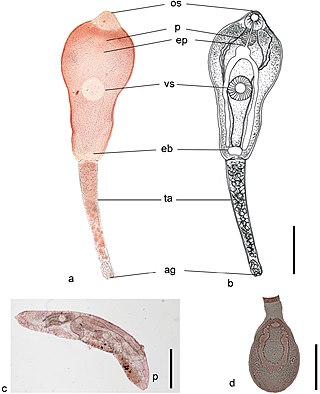
Philophthalmus gralli, commonly known as the Oriental avian eye fluke, parasitises the conjunctival sac of the eyes of many species of birds, including birds of the orders Galliformes and Anseriformes. In Brazil this parasite was reported in native Anseriformes species. It was first discovered by Mathis and Leger in 1910 in domestic chickens from Hanoi, Vietnam. Birds are definitive hosts and freshwater snail species are intermediate hosts. Human cases of philophthalmosis are rare, but have been previously reported in Europe, Asia, and America.

Gastrodiscoides is genus of zoonotic trematode under the class Trematoda. It has only one species, Gastrodiscoides hominis. It is a parasite of a variety of vertebrates, including humans. The first definitive specimen was described from a human subject in 1876. It is prevalent in Bangladesh, India, Burma, China, Kazakhstan, Philippines, Thailand, Vietnam, and the Volga Delta of Russia, with isolated cases from Africa, such as Nigeria. It is especially notable in the Assam, Bengal, Bihar, Madhya Pradesh, Orissa and Uttar Pradesh regions of India.

Opecoelidae is a family of trematodes. It is the largest digenean family with over 90 genera and nearly 900 species, almost solely found in marine and freshwater teleost fishes. It was considered by Bray et al. to belong in the superfamily Opecoeloidea Ozaki, 1925 or the Brachycladioidea Odhner, 1905.
Diplostomum pseudospathaceum is a species of trematode in the family Diplostomidae.
Opecoeloides is a genus of trematodes in the family Opecoelidae. It has been synonymised with Cymbephallus Linton, 1934 and Fimbriatus von Wicklen, 1946.
Acanthotrema is a genus of trematodes in the family Heterophyidae.
Echinostoma bolschewense is a species of echinostome from the Czech Republic, Russia, and the Slovak Republic.
Echinostoma miyagawai is a species of echinostome parasite that is found in Europe, Southeast Asia and Japan.













