
Salamanders are a group of amphibians typically characterized by their lizard-like appearance, with slender bodies, blunt snouts, short limbs projecting at right angles to the body, and the presence of a tail in both larvae and adults. All ten extant salamander families are grouped together under the order Urodela from the group Caudata. Salamander diversity is highest in eastern North America, especially in the Appalachian Mountains; most species are found in the Holarctic realm, with some species present in the Neotropical realm.

The Cryptobranchidae are a family of fully aquatic salamanders commonly known as the giant salamanders. They include some of the largest living amphibians. The family is native to China, Japan, and the eastern United States. They constitute one of two living families—the other being the Asiatic salamanders belonging to the family Hynobiidae—within the Cryptobranchoidea, one of two main divisions of living salamanders.

The Caudata are a group of amphibians containing the extant salamanders and all extinct species of amphibians more closely related to salamanders than to frogs. They are typically characterized by a superficially lizard-like appearance, with slender bodies, blunt snouts, short limbs projecting at right angles to the body, and the presence of a tail in both larvae and adults.

The Cryptobranchoidea are a suborder of salamanders found in Asia, European Russia, and the United States. They are known as primitive salamanders, in contrast to Salamandroidea, the advanced salamanders. It has two living subdivisions, Cryptobranchidae, which includes Asian giant salamanders and hellbenders, and Hynobiidae, commonly known as Asian salamanders.

The Albanerpetontidae are an extinct family of small amphibians, native to the Northern Hemisphere during the Mesozoic and Cenozoic. The only members of the order Allocaudata, they are thought to be allied with living amphibians belonging to Lissamphibia. Despite a superficially salamander-like bodyform, their anatomy is strongly divergent from modern amphibians in numerous aspects. The fossil record of albanerpetontids spans over 160 million years from the Middle Jurassic to the beginning of the Pleistocene, about 2.13–2 million years ago.

Chunerpeton tianyiensis is an extinct species of salamander from the Late Jurassic Daohugou Beds in Ningcheng County, Nei Mongol, China. It is the only species classified under the genus Chunerpeton, which means "early creeping animal". It was a small animal measuring 18 cm in length. It was neotenic, with the retention of external gills into adulthood. In the original description it was placed in Cryptobranchidae, which contains modern giant salamanders. A redescription published in 2020 found it to be a stem-group caudatan outside the crown group of modern salamanders. A 2021 study found it to be a member of Cryptobranchoidea outside of Cryptobranchidae. In 2022 a more extensive analysis, with greater character and taxon sampling, recovered Chunerpeton tianyiense as a stem-group caudatan, outside the crown group of modern salamanders, and associated with Beiyanerpeton jianpingensis and Qinglongtriton gangouensis.
Jeholotriton is a genus of primitive salamander from the Daohugou Beds near Daohugou village of Inner Mongolia, China.
Comonecturoides is an extinct genus of prehistoric caudate amphibians, possibly a salamander, from Reed's Quarry 9 of the Morrison Formation, near Como Bluff, Wyoming; the type species is C. marshi. It is considered a nomen dubium because the name is based on non-distinctive remains which cannot be classified in detail.
Iridotriton is an extinct genus of prehistoric salamander known from a fossil found in stratigraphic zone 6 of the late Jurassic Morrison Formation in the Dinosaur National Monument. One species has been described, Iridotriton hechti. It is likely a member of Cryptobranchoidea.
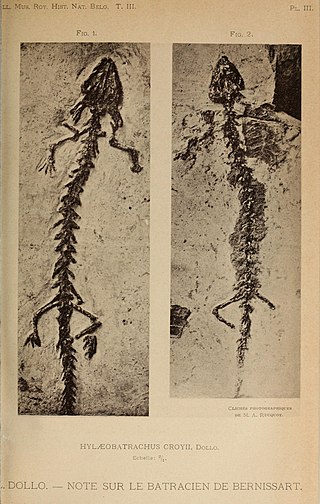
Hylaeobatrachus is an extinct genus of prehistoric salamander, known from the Early Cretaceous of Europe. The type species H. croyii is known from the Sainte-Barbe Clays Formation at the Iguanodon locality of Belgium, and was described by Louis Dollo. An unnamed Hylaeobatrachus-like taxon has also been reported from Las Hoyas, Spain. Both localities are of Barremian age. Hylaeobatrachus belongs to the crown group of modern salamanders, though its exact relationship with modern salamander groups is uncertain. It was neotenic, llike some modern salamanders.
Kokartus is an extinct genus of prehistoric stem-group salamander (Caudata) from the Middle Jurassic Balabansai Formation of Kyrgyzstan.

Marmorerpeton is an extinct genus of prehistoric stem group-salamanders that lived in Britain during the Bathonian stage of the Middle Jurassic. They are among the oldest known salamanders. Two species were named when the genus was first described by Susan E. Evans et al. in 1988, M. freemani, and M. kermacki, from fragmentary remains found via screenwashing in the Forest Marble Formation of England. Due to the size of their osteocytic lacunae suggesting a large genome size and some morphological characters, like the presence of calcified cartilage in the medulla of its humerus, it was assumed that Marmorerpeton was neotenic. New more complete remains of a new species M. wakei were described in 2022 from the Kilmaluag Formation of the Isle of Skye, Scotland. These conclusively demonstrated that Marmorerpeton was neotenic, and was a member of the family Karauridae, with the other two members of the family, Karaurus and Kokartus being known from the Middle-Late Jurassic of Central Asia. The teeth appear to have been weakly pedicellate.
Valdotriton is a genus of extinct prehistoric salamanders. Its only known species is Valdotriton gracilis. V. gracilis lived during the Late Barremian in what is now Spain. It was found in the Las Hoyas locality. It represents one of the oldest known members of Salamandroidea.

Pangerpeton is an extinct genus of salamanders. Its monotypic species is Pangerpeton sinensis.
Enneabatrachus is an extinct genus of prehistoric frogs known from the late Jurassic Morrison Formation of the United States and also the Late Jurassic-Early Cretaceous Ksar Metlili Formation of Morocco. The type species is E. hechti, whose remains have been recovered from stratigraphic zone 5.
Eobatrachus is a dubious genus of extinct frog known only from the holotype, YPM 1862, part of the right humerus, found in Reed's Quarry 9 near Como Bluff, Wyoming in the Late Jurassic-aged Morrison Formation. The type, and only species, E. agilis, was named by Othniel Charles Marsh in 1887 and he initially interpreted it as a mammal, although it was later re-classified as a genus of frog related to Comobatrachus and Eobatrachus is now seen as a dubious amphibian genus, possibly belonging to Anura (frogs) according to Foster (2007).
Beiyanerpeton is an extinct genus of salamandroid amphibians known from the Late Jurassic of western Liaoning Province, China. It contains a single species, B. jianpingensis. Alternative analyses suggest that B. jianpingensis is a stem salamander and not a salamandroid.

Liaodactylus is a genus of filter-feeding ctenochasmatid pterosaur from the Jurassic of China. The genus contains one species, L. primus, described by Zhou et al. in 2017. As an adaptation to filter-feeding, Liaodactylus had approximately 150 long, comb-like teeth packed closely together. It is both the earliest known ctenochasmatid and the first filter-feeding pterosaur from the Jurassic Tiaojishan Formation. Later and more specialized ctenochasmatids differ from Liaodactylus in having longer snouts, smaller openings in the skull, and more teeth. Within the Ctenochasmatidae, Liaodactylus was most closely related to the European Ctenochasma.

Triassurus is an extinct genus of amphibian, and the oldest member of Caudata. It is known from the Middle to Upper Triassic (Ladinian-Carnian) aged Madygen Formation in Kyrgyzstan. The type species is T. sixtelae.











