
The 2002 Atlantic hurricane season was a near-average Atlantic hurricane season. It officially started on June 1, 2002, and ended on November 30, dates which conventionally limit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones develop in the Atlantic Ocean. The season produced fourteen tropical cyclones, of which twelve developed into named storms; four became hurricanes, and two attained major hurricane status. While the season's first cyclone did not develop until July 14, activity quickly picked up: eight storms developed in the month of September. It ended early however, with no tropical storms forming after October 6—a rare occurrence caused partly by El Niño conditions. The most intense hurricane of the season was Hurricane Isidore with a minimum central pressure of 934 mbar, although Hurricane Lili attained higher winds and peaked at Category 4 whereas Isidore only reached Category 3. However, Lili had a minimum central pressure of 938 mbar.

The 1977 Atlantic hurricane season was a very inactive Atlantic hurricane season, with only six named storms. The season officially began on Wednesday, June 1, 1977 and lasted until Wednesday, November 30, 1977. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclogenesis occurs in the Atlantic basin. The first tropical cyclone of the season developed over the western Caribbean Sea on June 13, 12 days after the start of the season. Three more organized during July and early August. Then, on August 29, the first named storm, Hurricane Anita formed and rapidly intensified to a Category 5 hurricane on September 1, before weakening slightly and striking Mexico as a high-end Category 4 hurricane on the Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale, bringing strong winds and heavy rainfall. At least 25,000 people were left homeless and 11 fatalities were reported, with total damages still yet to be known to date.

The 2006 Atlantic hurricane season was the least active since 1997 as well as the first season since 2001 in which no hurricanes made landfall in the United States, and was the first since 1994 in which no tropical cyclones formed during October. Following the intense activity of 2003, 2004, and 2005, forecasters predicted that the 2006 season would be only slightly less active. Instead, it turned out to be a below average season, as activity was slowed by a rapidly forming moderate El Niño event, the presence of the Saharan Air Layer over the tropical Atlantic, and the steady presence of a robust secondary high-pressure area to the Azores High centered on Bermuda. There were no tropical cyclones after October 2.

The 1936 Atlantic hurricane season was a fairly active season, with 20 tropical cyclones recorded, 17 of which became tropical storms. Seven storms became hurricanes, of which one became a major hurricane. In addition, the season was unusual in the fact that no storms moved across large portions of the Caribbean Sea. Seven storms, including three hurricanes, struck the United States.

The 1904 Atlantic hurricane season featured no tropical cyclones during the months of July and August. The season's first cyclone was initially observed in the southwestern Caribbean on June 10. After this storm dissipated on June 14, the next was not detected until September 8. The sixth and final system transitioned into an extratropical cyclone offshore South Carolina on November 4. Two of the six tropical cyclones existed simultaneously.

The 1899 Atlantic hurricane season featured the longest-lasting tropical cyclone in the Atlantic basin on record. There were nine tropical storms, of which five became hurricanes. Two of those strengthened into major hurricanes, which are Category 3 or higher on the modern day Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale. The first system was initially observed in the northeastern Gulf of Mexico on June 26. The tenth and final system dissipated near Bermuda on November 10. These dates fall within the period with the most tropical cyclone activity in the Atlantic. In post-season analysis, two tropical cyclones that existed in October were added to HURDAT – the official Atlantic hurricane database. At one point during the season, September 3 through the following day, a set of three tropical cyclones existed simultaneously.

The 1891 Atlantic hurricane season began during the summer and ran through the late fall of 1891. The season had ten tropical cyclones. Seven of these became hurricanes; one becoming a major Category 3 hurricane.

The 1880 Atlantic hurricane season ran through the summer and fall of 1880. This is the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Atlantic basin. In the 1880 Atlantic season there were two tropical storms, seven hurricanes, and two major hurricanes (Category 3+). However, in the absence of modern satellite and other remote-sensing technologies, only storms that affected populated land areas or encountered ships at sea were recorded, so the actual total could be higher. An undercount bias of zero to six tropical cyclones per year between 1851 and 1885 and zero to four per year between 1886 and 1910 has been estimated. Of the known 1880 cyclones, Hurricane Six was first documented in 1995 by José Fernández-Partagás and Henry Díaz. They also proposed large changes to the known tracks of several other storms for this year and 're-instated' Hurricane Ten to the database. A preliminary reanalysis by Michael Chenoweth, published in 2014, found thirteen storms, nine hurricanes, and four major hurricanes.

The 1870 Atlantic hurricane season lasted from mid-summer to late-fall and comprised one tropical storm and ten hurricanes, two of which became major hurricanes,. However, in the absence of modern satellite and other remote-sensing technologies, only storms that affected populated land areas or encountered ships at sea were recorded, so the actual total could be higher. An undercount bias of zero to six tropical cyclones per year between 1851 and 1885 and zero to four per year between 1886 and 1910 has been estimated.

The 1882 Atlantic hurricane season ran through the summer and early fall of 1882. This is the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Atlantic basin. In the 1882 Atlantic season there were two tropical storms, two Category 1 hurricanes, and two major hurricanes. However, in the absence of modern satellite and other remote-sensing technologies, only storms that affected populated land areas or encountered ships at sea were recorded, so the actual total could be higher. An undercount bias of zero to six tropical cyclones per year between 1851 and 1885 and zero to four per year between 1886 and 1910 has been estimated. Of the known 1882 cyclones, Hurricane One and Hurricane Five were both first documented in 1996 by Jose Fernandez-Partagas and Henry Diaz, while Tropical Storm Three was first recognised in 1997. Partagas and Diaz also proposed large changes to the known track of Hurricane Two while further re-analysis, in 2000, led to the peak strengths of both Hurricane Two and Hurricane Six being increased. In 2011 the third storm of the year was downgraded from a hurricane to a tropical storm.

The 1854 Atlantic hurricane season featured five known tropical cyclones, three of which made landfall in the United States. At one time, another was believed to have existed near Galveston, Texas in September, but HURDAT – the official Atlantic hurricane database – now excludes this system. The first system, Hurricane One, was initially observed on June 25. The final storm, Hurricane Five, was last observed on October 22. These dates fall within the period with the most tropical cyclone activity in the Atlantic. No tropical cyclones during this season existed simultaneously. One tropical cyclone has a single known point in its track due to a sparsity of data.

The 1879 Atlantic hurricane season ran from the summer to near the end of autumn in 1879. In 1879 there were two tropical storms, four hurricanes, and two major hurricanes. However, in the absence of modern satellite and other remote-sensing technologies, only storms that affected populated land areas or encountered ships at sea were recorded, so the actual total could be higher. An undercount bias of zero to six tropical cyclones per year between 1851 and 1885 and zero to four per year between 1886 and 1910 has been estimated. Of the known 1879 cyclones, Hurricane One were first documented in 1995 by Jose Fernandez-Partagas and Henry Diaz. They also proposed large changes to the known tracks of Hurricanes Two, Three, Seven and Eight. Later one storm was deemed not to be a tropical cyclone at all and was dropped from the database.

The 1878 Atlantic hurricane season lasted from the summer through much of the fall. Records show that 1878 featured a relatively active hurricane season. A total of twelve storms were observed during the year. There were twelve tropical storms, eight hurricanes and two major hurricanes. However, in the absence of modern satellite and other remote-sensing technologies, only storms that affected populated land areas or encountered ships at sea were recorded, so the actual total could be higher. An undercount bias of zero to six tropical cyclones per year between 1851 and 1885 and zero to four per year between 1886 and 1910 has been estimated. Of the known 1878 cyclones, both Hurricane Three and Hurricane Four were first documented in 1995 by Jose Fernandez-Partagas and Henry Diaz, who also proposed large changes to the known tracks of Hurricanes Two, Seven and Eight. Further analysis from 2000 onwards extended the duration of Hurricane Three by one day and identified major track changes for Hurricane Five.

The 1875 Atlantic hurricane season featured three landfalling tropical cyclones. However, in the absence of modern satellite and other remote-sensing technologies, only storms that affected populated land areas or encountered ships at sea were recorded, so the actual total could be higher. An undercount bias of zero to six tropical cyclones per year between 1851 and 1885 has been estimated. There were five recorded hurricanes and one major hurricane – Category 3 or higher on the modern-day Saffir–Simpson scale.
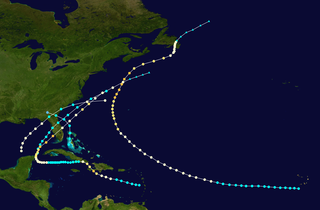
The 1873 Atlantic hurricane season was quiet, with only two tropical storms and three hurricanes, two of which were major hurricanes, being recorded. However, in the absence of modern satellite and other remote-sensing technologies, only storms that affected populated land areas or encountered ships at sea were recorded, so the actual total could be higher. An undercount bias of zero to six tropical cyclones per year between 1851 and 1885 and zero to four per year between 1886 and 1910 has been estimated. Of the known cyclones, large alterations were made to the tracks of Hurricane Two and Hurricane Five in 1995 by Jose Fernandez-Partagas and Henry Diaz, who also proposed smaller changes to the known track of Hurricane Three. All of the tropical cyclones, other than Hurricane Two, made landfall in Florida.

The 1866 Atlantic hurricane season was originally one of only four Atlantic hurricane seasons in which every known tropical cyclone attained hurricane status, along with 1852, 1858, and 1884. Initially, there were three known storms during the season, but a re-analysis confirmed the increased activity. There were also two other systems that were included as tropical cyclones at one time, although both were considered to have been other storms already in the database. All tropical activity occurred between the middle of July and the end of October. There may have been additional unconfirmed tropical cyclones during the season. Meteorologist Christopher Landsea estimates that up to six storms were missed from the official database, due to small tropical cyclone size, sparse ship reports, and relatively unpopulated coastlines.

The 1863 Atlantic hurricane season featured five landfalling tropical cyclones. In the absence of modern satellite and other remote-sensing technologies, only storms that affected populated land areas or encountered ships at sea were recorded, so the actual total could be higher. An undercount bias of zero to six tropical cyclones per year between 1851 and 1885 has been estimated. There were seven recorded hurricanes and no major hurricanes, which are Category 3 or higher on the modern day Saffir–Simpson scale. Of the known 1863 cyclones, seven were first documented in 1995 by José Fernández-Partagás and Henry Diaz, while the ninth tropical storm was first documented in 2003. These changes were largely adopted by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Atlantic hurricane reanalysis in their updates to the Atlantic hurricane database (HURDAT), with some adjustments.

Hurricane Leslie was an Atlantic tropical cyclone that caused minor damage in Bermuda and Atlantic Canada in September 2012. The twelfth tropical cyclone of the annual hurricane season, Leslie developed from a tropical wave located nearly 1,500 miles (2,400 km) east of the Leeward Islands on August 30. About twelve hours later, it strengthened into Tropical Storm Leslie. Tracking steadily west-northwestward, it slowly intensified due to only marginally favorable conditions. By September 2, the storm curved north-northwestward while located north of the Leeward Islands. Thereafter, a blocking pattern over Atlantic Canada caused Leslie to drift for four days. Late on September 5, Leslie was upgraded to a Category 1 hurricane. However, due to its slow movement, the storm causing upwelling, which decreased sea surface temperatures (SST's), weakening Leslie back to a tropical storm on September 7.

The 1926 Nova Scotia hurricane was one of the deadliest Canadian hurricanes in the 20th century. The second tropical cyclone and second hurricane of the season, the storm developed from a trough situated well east of the Leeward Islands on July 29. Over the next few days, it moved west-northwest, becoming a tropical storm by July 31. The cyclone turned to the northwest on August 1 and began strengthening rapidly, reaching hurricane intensity by the early afternoon. The next day, it became a major hurricane—equivalent to Category 3 intensity on the modern-day Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale. Over the next few days, the storm's track varied between north-northwest and northwest. Early on August 5, it peaked with winds of 120 mph (190 km/h). The hurricane then began weakening as it curved northward. The storm began losing tropical characteristics while approaching Atlantic Canada, transitioning into an extratropical cyclone on August 8. The remnants soon made landfall near Port Hawkesbury, Nova Scotia, with winds of 75 mph (121 km/h), before being last noted over Newfoundland later that day.












































