The politics of Tuvalu takes place in a framework of a parliamentary representative democratic monarchy, whereby the monarch is the head of state, represented by the governor-general, while the prime minister is the head of government. Executive power is exercised by the government.
Tuvalu elects a legislature on a national level. The Parliament of Tuvalu has 16 members, elected for a four-year term in 8 double-seat constituencies. Tuvalu is a de facto non-partisan democracy since it does not have political parties. The political system is based on personal alliances and loyalties derived from clan and family connections. It does tend to have both a distinct government and a distinct opposition. The 16 members of the current parliament are elected from eight two-seat constituencies via plurality block voting.
The Parliament of Tuvalu is the unicameral national legislature of Tuvalu. The place at which the parliament sits is called the Vaiaku maneapa. The maneapa on each island is an open meeting place where the chiefs and elders deliberate and make decisions.

Sir Kamuta Latasi is a political figure from the Pacific nation of Tuvalu from Funafuti atoll. He was elected to the Parliament of Tuvalu in 1992. Latasi served as the 4th prime minister, and foreign minister, from 1993 until 1996. He has served as the Speaker of parliament from 2006 to September 2010 and again from December 2010 to March 2014.

Willy Telavi is a Tuvaluan politician who was Prime Minister of Tuvalu from 2010 to 2013.

Sir Iakoba Taeia Italeli is a Tuvaluan politician who was the governor-general of Tuvalu from 16 April 2010, until 22 August 2019, when he resigned to contest in the 2019 general election. He was not successful in that election, however he was elected as a member of parliament in the 2024 Tuvaluan general election.
Parliamentary elections were held in Tuvalu on 16 September 2010. Voters elected fifteen members of the Parliament to a four-year term. All candidates were independents, as there are no political parties in the country. Ten out of the fifteen incumbent members were re-elected. The remaining five incumbents, including Deputy Prime Minister Tavau Teii, did not retain their seats. The incumbent Prime Minister, Apisai Ielemia, retained his seat in Vaitupu constituency. On 29 September, Maatia Toafa from Nanumea won eight of the fifteen votes to become Prime Minister.

Enele Sosene Sopoaga PC is a Tuvaluan diplomat and politician who was Prime Minister of Tuvalu from 2013 to 2019.
The Cabinet of Tuvalu is the executive branch of the government of Tuvalu.
Pelenike Tekinene Isaia served in the Parliament of Tuvalu from 2011 to 2015. Before her election as an MP she worked for the Tuvalu Cooperative Society, as its branch manager in Nui.
A by-election was held in the Nukufetau constituency in Tuvalu on 28 June 2013. It followed the death of MP and Minister for Finance Lotoala Metia, who died suddenly on 21 December 2012.
Elisala Pita OBE was a Tuvaluan politician.

The governor-general of Tuvalu is the representative of the Tuvaluan monarch, currently King Charles III, in the country of Tuvalu.

The Tuvaluan constitutional crisis was a political dispute in Tuvalu between the government, led by Prime Minister Willy Telavi, and the opposition, led by Enele Sopoaga, that was precipitated by the death of the Minister of Finance, Lotoala Metia MP on 21 December 2012, which eliminated the government's majority. The dispute was eventually resolved in August 2013 by a motion of no confidence in Prime Minister Willy Telavi, following which Enele Sopoaga was elected Prime Minister.

The Telavi Ministry was the 13th ministry of the Government of Tuvalu, led by Prime Minister Willy Telavi. It succeeded the Second Toafa Ministry upon its swearing in by Governor-General Iakoba Italeli on 24 December 2010 after a vote of no confidence in former Prime Minister Maatia Toafa. Following Telavi's removal as prime minister, his ministry was subsequently brought down by the opposition's vote of no confidence and was succeeded by the Sopoaga Ministry, led by Enele Sopoaga, on 5 August 2013.
The Sopoaga Ministry was the 14th ministry of the Government of Tuvalu, led by Prime Minister Enele Sopoaga. It succeeds the Telavi Ministry upon its swearing in by Governor-General Sir Iakoba Italeli on 5 August 2013.
A by-election was held in the Nui constituency in Tuvalu on 10 September 2013. It was triggered by the resignation of the incumbent, MP Taom Tanukale, the Minister for Health, in the government of Willy Telavi.
A by-election was held in the Nanumaga constituency in Tuvalu on 14 January 2014. It followed the seat being declared vacant because of the ill-health of the incumbent Opposition MP Dr. Falesa Pitoi, on health grounds.
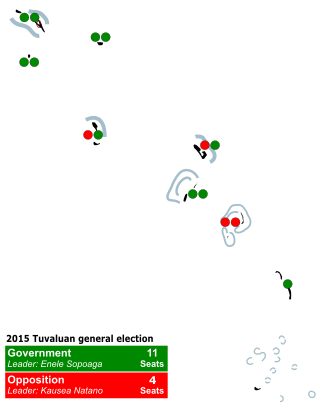
General elections were held in Tuvalu on 31 March 2015. The state of emergency created by Cyclone Pam resulted in the election being delayed twice. The election was originally scheduled for 19 March, then after Cyclone Pam caused damage to the islands, the election was rescheduled for 26 March.







