
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced in a specific time period by a country or countries. GDP is most often used by the government of a single country to measure its economic health. Due to its complex and subjective nature, this measure is often revised before being considered a reliable indicator.

The metre is the base unit of length in the International System of Units (SI).

Measurement is the quantification of attributes of an object or event, which can be used to compare with other objects or events. In other words, measurement is a process of determining how large or small a physical quantity is as compared to a basic reference quantity of the same kind. The scope and application of measurement are dependent on the context and discipline. In natural sciences and engineering, measurements do not apply to nominal properties of objects or events, which is consistent with the guidelines of the International vocabulary of metrology published by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures. However, in other fields such as statistics as well as the social and behavioural sciences, measurements can have multiple levels, which would include nominal, ordinal, interval and ratio scales.

In mathematics, the concept of a measure is a generalization and formalization of geometrical measures and other common notions, such as magnitude, mass, and probability of events. These seemingly distinct concepts have many similarities and can often be treated together in a single mathematical context. Measures are foundational in probability theory, integration theory, and can be generalized to assume negative values, as with electrical charge. Far-reaching generalizations of measure are widely used in quantum physics and physics in general.

Probability theory or probability calculus is the branch of mathematics concerned with probability. Although there are several different probability interpretations, probability theory treats the concept in a rigorous mathematical manner by expressing it through a set of axioms. Typically these axioms formalise probability in terms of a probability space, which assigns a measure taking values between 0 and 1, termed the probability measure, to a set of outcomes called the sample space. Any specified subset of the sample space is called an event.

In probability theory and statistics, a probability distribution is the mathematical function that gives the probabilities of occurrence of different possible outcomes for an experiment. It is a mathematical description of a random phenomenon in terms of its sample space and the probabilities of events.
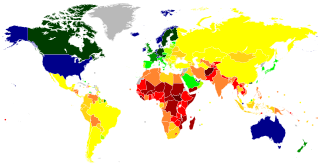
Per capita income (PCI) or total income measures the average income earned per person in a given area in a specified year. It is calculated by dividing the area's total income by its total population.
The International System of Units, internationally known by the abbreviation SI, is the modern form of the metric system and the world's most widely used system of measurement. Established and maintained by the General Conference on Weights and Measures (CGPM), it is the only system of measurement with an official status in nearly every country in the world, employed in science, technology, industry, and everyday commerce.

The hand is a non-SI unit of measurement of length standardized to 4 in (101.6 mm). It is used to measure the height of horses in many English-speaking countries, including Australia, Canada, the Republic of Ireland, the United Kingdom, and the United States. It was originally based on the breadth of a human hand. The adoption of the international inch in 1959 allowed for a standardized imperial form and a metric conversion. It may be abbreviated to "h" or "hh". Although measurements between whole hands are usually expressed in what appears to be decimal format, the subdivision of the hand is not decimal but is in base 4, so subdivisions after the radix point are in quarters of a hand, which are inches. Thus, 62 inches is fifteen and a half hands, or 15.2 hh.
The People's Choice Awards is an American awards show, recognizing people in entertainment, voted online by the general public and fans. The show has been held annually since 1975, with the winners originally determined using Gallup Polls until a switch to online voting in 2005.

The Church of England Assembly (Powers) Act 1919 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that enables the Church of England to submit primary legislation called Measures, for passage by Parliament. Measures have the same force and effect as Acts of Parliament. The power to pass measures was originally granted to the Church Assembly, which was replaced by the General Synod of the Church of England in 1970 by the Synodical Government Measure 1969.

A unit of measurement is a definite magnitude of a quantity, defined and adopted by convention or by law, that is used as a standard for measurement of the same kind of quantity. Any other quantity of that kind can be expressed as a multiple of the unit of measurement.
Height above mean sea level is a measure of the vertical distance of a location in reference to a historic mean sea level taken as a vertical datum. In geodesy, it is formalized as orthometric heights.