This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations .(August 2024) |
The following is a list of symbols associated with the occult. [1]
This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations .(August 2024) |
The following is a list of symbols associated with the occult. [1]
| Name | Image | Origins | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ankh |  | Ancient Egyptian religion | Ancient Egyptian symbol for eternal life; [2] now also associated with Kemetism and neo-paganism, as well as the Goth subculture. Yogi practitioners often claim they stretch an ankh symbol into their wrist. |
| Arrow (Belomancy) |  | Ancient divination | Arrows used to gain knowledge through divination. [3] |
| Bagua |   | I Ching , Taoism | Literally, "The 8 Directions," this early Chinese divination technique is described in the I Ching , and is typically visualized as 8 trigrams around a Yin and Yang symbol. [4] The bagua and trigrams are referenced throughout Chinese astronomy, astrology, geography, geomancy, anatomy, martial arts, Chinese medicine and various other cultural aspects. |
| Baphomet |  | Adopted by modern occultists and Satanists. Theistic Satanists may worship it as a deity or demon, while atheistic Satanists see it as a metaphorical symbol. The goat-headed Baphomet image seen here is a 19th-century drawing made by Eliphas Levi as a metaphorical symbol from Dogme et Rituel de la Haute Magie. It was not originally created as a Satanic symbol or a deity. See also: Sigil of Baphomet and Statue of Baphomet. | |
| Black Sun |  | Nazi occultism and later the neo-Nazi movement | A symbol of the sun composed of twelve sig runes first appearing on the floor of the north tower of Wewelsburg, after Heinrich Himmler ordered it to be remodeled. It gained modern popularity due to its use by Nazi occultists. It was later adopted by Satanists. The name "Black Sun" was coined by Wilhelm Landig of the Landig Group. |
| Solar symbol |  | Alchemy | The alchemical symbol for the sun and various sun gods. Also the alchemical symbol for gold which is the metal represented by the Sun which is the astral counterpart. |
| Eye of Horus |  | Ancient Egyptian religion | The eye of the god Horus, a symbol of protection, now associated with the occult and Kemetism, as well as the Goth subculture. |
| Eye of Providence (All-Seeing Eye, Eye of God) |  | Catholic iconography, | The eye of God within a triangle, representing the Holy Trinity, and surrounded by holy light, representing His omniscience. |
| Heptagram |   | Judaism, Thelema, Paganism, Alchemy | Represents the seven days of creation. It is the symbol of Babalon in Thelema. In Wicca, it is known as the Elven Star, Fairy Star or Septagram. |
| Hexagram |  | Mandala and Judaism | An ancient symbol of the Jewish faith, also found on the Seal of Solomon. |
| Icelandic magical staves |  | Icelandic magic | Sigils created with magical powers by the Icelandic people. Pictured is the stave known as Ægishjálmur. |
| I'itoi |  | Uto-Aztecan O'odham peoples of Arizona | The I'itoi is an indigenous spiritual symbol that signifies the challenging and balancing decisions in one's life that lead us to our ultimate dream state from the product of all of our choices. The ideal is to reach the center of this maze of decisions we make, which is a manifestation of our purpose and dream, and is accepted by the Sun God upon our death. |
| Inverted cross |  | Peter requested to be crucified upside down, as he felt unworthy to die in the same manner as Christ. | Used as a symbol of Saint Peter. A very common display in churches dedicated to Saint Peter. It has also been modernly used as an anti-Christian symbol. |
| Leviathan cross | 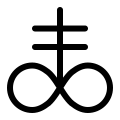 | Alchemy; Satanism | Alchemical symbol for black sulfur or brimstone, [5] [6] associated with the fire and brimstone of Hell. Also known as a "Satan's cross". This symbol is used in Anton LaVey's Satanic Bible . [7] The symbol is composed of an infinity symbol and a two-barred cross. The two-barred cross represents balance between the masculine and the feminine. [8] |
| Lilith Black Moon (Sigil of Lilith) |   | Judaism, Mesopotamian and Jewish mythology, Lilith Astrology | Depicts a crescent moon atop a cross with arms of equal length, representing mind and matter. In Jewish mythology, Lilith is considered to be the first feminist [ citation needed ] and first wife of Adam. The Sigil of Lilith symbolizes the she-demon Lilith, who was demonized for rebelling against God's word. |
| Monas Hieroglyphica |  | the works of John Dee | A symbol invented by John Dee, alchemist and astrologer at the court of Elizabeth I of England. It represents (from top to bottom): the moon; the sun; the elements; and fire. |
| Ouroboros |  | Ancient Egypt and Persia, Norse mythology | A serpent or dragon consuming its own tail, it is a symbol of infinity, unity, and the cycle of death and rebirth. |
| Pentacle |  | Mesopotamia | An ancient symbol of a unicursal five-pointed star circumscribed by a circle with many meanings, including but not limited to, the five wounds of Christ and the five elements (earth, fire, water, air, and soul). In Satanism, it is flipped upside-down. See also: Sigil of Baphomet. |
| Rose Cross |   | Rosicrucianism / Hermetic Order of the Golden Dawn | A symbol associated with Christian Rosenkreuz, with many different attributions of symbolism. |
| Runes |  | Norse mythology | Ancient alphabet used throughout North Europe and prominent in Scandinavia, used in modern times by various religious faiths, such as Asatru. |
| Seal of Solomon | 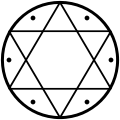  | Alchemy, Christian and Jewish esotericism | A ring attributed to king Solomon in Jewish and esoteric tradition. Also modernly used in Western occultism to symbolize the union of male and female through magic rituals. |
| Seal of the Theosophical Society |  | Theosophy (Blavatskian) | A seal consisting of a Manji, Star of David, Ankh, Om, and Ouroboros, used by the Theosophical Society, an organization formed in 1875 to advance Theosophy. |
| Septenary Sigil |  | Order of Nine Angles | The main symbol of the Order of Nine Angles, a neo-Nazi Satanic and Left-hand occult group based in the United Kingdom. |
| Sigil |  | Renaissance magic | Images created for magical purposes, sometimes attributed as signatures of demons, angels, and other beings. |
| Sigil of Lucifer |  | Grimorium Verum | A sigil used in rituals invoking Lucifer, first recorded in the 18th-century True Grimoire. Known among Theistic Satanists as the Seal of Satan, the symbol is also associated with music groups including Zeal & Ardor. |
| Sigil of Baphomet |    | 19th century French Occultism, Joy of Satan Ministries | Official emblem of the Church of Satan, consisting of the head of a goat transfixed upon a reversed pentagram flanked by the Hebrew letters of the word "Leviathan" (לִוְיָתָן). The right image is the same sigil in cuneiform from the Joy of Satan Ministries, a recreation of the sigil of Baphomet incorporated with cuneiform lettering instead of Hebrew to spell out "Satan", and made after Maxine Dietrich's reinterpretation of the ideology of spiritual Satanism. |
| Sigillum Dei (Seal of God) |  | Europe, late Middle Ages | A magical diagram, composed of two circles, a pentagram, and three heptagons, and is labeled with the name of God and his angels. |
| Squared circle |   | Alchemy | A symbol of the Philosopher's stone. Depicted on the left image is Michael Maier's Emblem XXI from Atalanta Fugiens . |
| Sriramachakra | 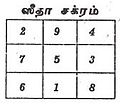 | Tamil mysticism | A mystic diagram used for astrology. |
| Sri Yantra |  | Shri Vidya school of Hinduism | A yantra consisting of nine interlocking triangles. Four upward ones which represent Shiva, and five downward ones representing Shakti that surround the central bindu point. In three dimensions, it represents Mahāmeru, and in particular, all yantras emerge from Sri Yantra. It symbolizes the evolution of the multiverse as a result of natural divine will of the mother goddess Aadi Paraa Shakti. |
| Sulfur cross | Sulfur/the combustible elements [9] | Alchemy | Alchemical symbols for sulfur, associated with the fire and brimstone of Hell. |
| Sun |  | Alchemy and Hermeticism | A symbol used with many different meanings, including but not limited to, gold, citrinitas, sulfur, the divine spark of man, nobility and incorruptibility. |
| Sun cross |  | Iron Age religions and later gnosticism and neo-paganism. | An ancient pagan symbol of the sun, adopted by gnostics, neopagans and occultists. |
| Supreme Polarity (Taijitu) | 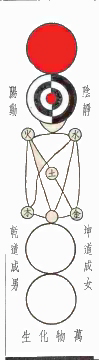 | Zhou Dunyi (1017-1073 AD), Taoism | "Explanation of the Diagram of the Supreme Ultimate", which became the cornerstone of Neo-Confucianist cosmology |
| Symbol of Chaos |   | Michael Moorcock, Aleister Crowley and chaos magic | A symbol originating from The Eternal Champion, later adopted by occultists and role-playing games. |
| Tetractys (Tetrad) |  | Greek school of Pythagoreanism | The tetractys is an equidistant and equiangular arrangement of ten points inside a triangle, akin to the fourth triangle number. It was developed by Pythagoras, and collectively signifies cosmic unity in the form of The Decad, as well as the musica universalis , or collective abstraction of the music generated by heavenly cosmic bodies. It also represents the four elements of nature, as well as the dimensional organization of space-time. Learning and adhering to its metaphysical knowledge was a requirement inside the occult Pythagorean religions. |
| Tetragrammaton |  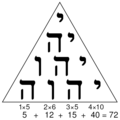  | Judaism, Kodesh, Kabbalah | Considered to be the unspeakable name of God, written as YHWH . The four letter name has many pronunciations and can be seen over 7,000 times throughout the Hebrew Bible. As symbol, it was incorporated into the Greek Tetractys by Jewish Kabbalistic occult tradition as an evolving arrangement of ten letters. In gematria, YHWH has a numerical value of 72 (center image). The right image contains the Tetragrammaton in tetractys formation, accompanied by the late-Renaissance Pentagrammaton, below. |
| Tree of Life (Kabbalah) |   | Kabbalah | The tree of life is a diagram used in various mystical traditions. It usually consists of 10 nodes symbolizing different archetypes and 22 lines connecting the nodes. The nodes are often arranged into three columns to represent that they belong to a common category |
| Unicursal hexagram |   | Aleister Crowley's Thelema | Symbol of the Thelema religion, a hexagram that can be drawn with one line. |
| Vishvarupa (Cosmic Man) |  | Vaishnavism, Hinduism | This iconographical form of the Hindu Trimurti god Visnu, whose body represents the structure and form of the entire cosmos. The different domains of Hell are represented by the legs and feet, with the Earthly and harmonious Heavenly realms represented by the upper stomach and chest, arms, and head; the navel represents the Unmanifest realm that is connected with pure sound and vibration, and absolute silence, which connects everything together. |
| Zodiac Man (Homo Signorum, or 'Man of Signs') |  | Astrology | A graph correlating zodiacal names with body parts. |
{{cite book}}: ISBN / Date incompatibility (help)CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link)