This list of Ports and harbours in Djibouti details the ports, harbours around the coast of Djibouti.
This list of Ports and harbours in Djibouti details the ports, harbours around the coast of Djibouti.
| Port/Harbour name | Regions | City/Town name | Coordinates | UN/Locode | Max. draught (m) | Max. deadweight (t) | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Port of Djibouti | Djibouti City | Djibouti City | 11°36′N43°06′E / 11.600°N 43.100°E | DJJIB [1] | 16 | 156,198 | Medium-sized port [2] on the coast of the Gulf of Tadjoura. |
| Port of Tadjoura | Tadjourah Region | Tadjoura | 11°46′N43°06′E / 11.767°N 43.100°E | DJTDJ [1] | 12 | 65,000 [3] | The port is located on the northern coast of the Gulf of Tadjoura. |
| Port of Doraleh | Djibouti City | Djibouti City | 11°36′N42°58′E / 11.600°N 42.967°E | DJDCT [1] | 15.3 | 100,000 | The multipurpose port is located in the western part of Djibouti City. [3] |
| Port of Ghoubet | Arta Region | Ghoubet | 15 | 100,000 | The port is located 45 km south of the Ghoubbet-el-Kharab. [3] |

The economy of Djibouti is derived in large part from its strategic location on the Red Sea. Djibouti is mostly barren, with little development in the agricultural and industrial sectors. The country has a harsh climate, a largely unskilled labour force, and limited natural resources. The country's most important economic asset is its strategic location, connecting the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden. As such, Djibouti's economy is commanded by the services sector, providing services as both a transit port for the region and as an international transshipment and refueling centre.
Transport in Djibouti is overseen by the Ministry of Infrastructure & Transport. Over the last years, the Government of Djibouti have significantly increased funding for rail and road construction to build an infrastructure. They include highways, airports and seaports, in addition to various forms of public and private vehicular, maritime and aerial transportation.

Transport in Ethiopia is overseen by the Ministry of Transport and Communications. Over the last years, the Ethiopian federal authorities have significantly increased funding for rail and road construction to build an infrastructure, that allows better economic development.
The Spencer Gulf is the westernmost and larger of two large inlets on the southern coast of Australia, in the state of South Australia, facing the Great Australian Bight. It spans from the Cape Catastrophe and Eyre Peninsula in the west to Cape Spencer and Yorke Peninsula in the east.

Ismaïl Omar Guelleh is the current President of Djibouti. He has been in office since 1999, making him one of the longest-serving rulers in Africa. He is often referred to by his initials, IOG.

Djibouti is the eponymous capital of Djibouti, and has more people than the rest of Djibouti combined. It is located in the coastal Djibouti Region on the Gulf of Tadjoura.

The Djibouti national football team, nicknamed the Riverains de la Mer Rouge, is the national football team of Djibouti. It is controlled by the Djiboutian Football Federation, and is a member of the Confederation of African Football (CAF) and the Union of Arab Football Associations (UAFA). The Djibouti national football team's first win in a full FIFA-sanctioned international match was a 1–0 win vs. Somalia in the first round of the 2010 FIFA World Cup qualification.
Rail transport in Ethiopia is done within the National Railway Network of Ethiopia, which currently consists of three electrified standard gauge railway lines: the Addis Ababa–Djibouti Railway, the Awash–Weldiya Railway and the Weldiya–Mekelle Railway. Other lines are still in the planning phase. There is also an urban light rail system in the country's capital, the Addis Ababa Light Rail.

The Port of Djibouti is a port in Djibouti, the capital of Djibouti. It is strategically located at the crossroads of one of the busiest shipping routes in the world, linking Europe, the Far East, the Horn of Africa and the Persian Gulf. The port serves as a key refueling and transshipment center, and is the principal maritime outlet for imports to and exports from neighboring Ethiopia. An estimated 2,500 ships pass through and call through the port every day.

Djibouti, officially the Republic of Djibouti, is a country in the Horn of Africa, bordered by Somalia to the south, Ethiopia to the southwest, Eritrea in the north, and the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden to the east. The country has an area of 23,200 km2 (8,958 sq mi).
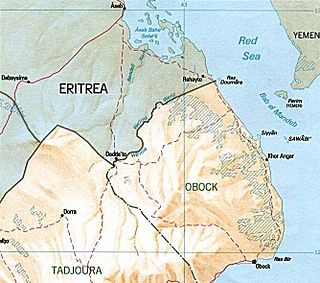
The Djiboutian–Eritrean border conflict between the forces of Djibouti and Eritrea occurred between June 10 and June 13, 2008. It was triggered by tension which began on April 16, 2008, when Djibouti reported that Eritrean armed forces had penetrated into Djibouti and dug trenches on both sides of the border. The crisis deepened when armed clashes broke out between the two armed forces in the border area on June 10, 2008. During the conflict, France provided logistical, medical and intelligence support to Djibouti, but did not participate in direct combat.
Railway stations in Djibouti are served by standard gauge railways of the Djiboutian Railway Company.
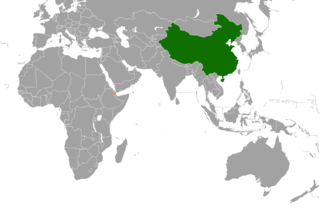
People's Republic of China–Djibouti relations refers to the current and historical relationship between the People's Republic of China and Djibouti. China and Djibouti established relations on January 8, 1979. China has financed a number of public works projects in Djibouti, including a stadium, the offices of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs and the People's Palace. In September 2010, Type 920 Hospital Ship, also known as the "Peace Ark", visited Djibouti.

Seair Seaplanes is a scheduled and charter airline based in Richmond, British Columbia, Canada. The airline flies routes between the Vancouver International Water Airport and the Nanaimo Harbour Water Airport, as well as other Gulf Islands in the Strait of Georgia, exclusively with float planes.

The Port of Cork is the main port serving the South of Ireland, County Cork and Cork City. It is one of the three "Ports of National Significance " as designated by National Ports Policy.

Operation Raahat was an operation of the Indian Armed Forces to evacuate Indian citizens and foreign nationals from Yemen during the 2015 military intervention by Saudi Arabia and its allies in that country during the Yemeni Crisis. The evacuation by sea began on 1 April 2015 from the port of Aden. The air evacuation by the Indian Air Force and Air India commenced on 3 April 2015 from Sana'a. More than 4,640 Indian citizens in Yemen were evacuated along with 960 foreign nationals from 41 countries. The air evacuation ended on 9 April 2015 while the evacuation by sea ended on 11 April 2015.

The Addis Ababa–Djibouti Railway is a new standard gauge international railway that serves as the backbone of the new Ethiopian National Railway Network. The railway was inaugurated by Prime Minister Hailemariam Desalegn on January 1, 2018. It provides landlocked Ethiopia with access to the sea, linking Ethiopia's capital of Addis Ababa with Djibouti and its Port of Doraleh. More than 95% of Ethiopia's trade passes through Djibouti, accounting for 70% of the activity at the Port of Djibouti.
The COVID-19 pandemic in Djibouti is part of the worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. The virus spread to Djibouti in March 2020. It is a novel infectious disease caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. Model-based simulations for Djibouti indicate that the 95% confidence interval for the time-varying reproduction number R t has been rising since August 2020 and exceeded 1.0 until April 2021.
Cannabis in Djibouti is illegal with penalties for the production, sale, and possession of marijuana for medicinal or recreational purposes. Offenders may be fined or receive up to five years in prison. Use of cannabis in Djibouti is low due to poor conditions for cultivation and the local preference for the legal drug khat.

BNZ Harbour Quays was a large office building on the waterfront in Wellington, New Zealand. It was built in 2009 and leased to the Bank of New Zealand, but suffered earthquake damage in the 2013 Seddon earthquake and the 2016 Kaikōura earthquake. The building was demolished in 2019.