
The geography of Finland is characterized by its northern position, its ubiquitous landscapes of intermingled boreal forests and lakes, and its low population density. Finland can be divided into three areas: archipelagoes and coastal lowlands, a slightly higher central lake plateau and uplands to north and northeast. Bordering the Baltic Sea, Gulf of Bothnia, and Gulf of Finland, as well as Sweden, Norway, and Russia, Finland is the northernmost country in the European Union. Most of the population and agricultural resources are concentrated in the south. Northern and eastern Finland are sparsely populated containing vast wilderness areas. Taiga forest is the dominant vegetation type.

Tavastia is a historical province in the south of Finland. It borders Finland Proper, Satakunta, Ostrobothnia, Savonia and Uusimaa.

Savonia is a historical province in the east of Finland. It borders Tavastia, Ostrobothnia and Karelia. Currently, Savonia is divided into two provinces: Northern Savonia and Southern Savonia. The largest cities in Savonia by population are Kuopio, Mikkeli, Savonlinna, Varkaus and Iisalmi.
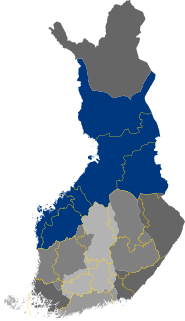
Ostrobothnia, Swedish: Österbotten, Finnish: Pohjanmaa is a historical province comprising a large western and northern part of modern Finland. It is bounded by Karelia, Savonia, Tavastia and Satakunta in the south, the Bothnian Sea, Bothnian Bay and Swedish Västerbotten in the west, Laponia in the north and Russia in the east.

Häme is the name of a geographical region in Finland, associated with the Tavastians, or Häme people (hämäläiset), a subgroup of the Finnish people. The precise area referred to can vary depending on the context.

The historical provinces of Finland are a legacy of the country's joint history with Sweden. The provinces ceased to be administrative entities in 1634 when they were superseded by the counties, a reform which remained in force in Finland until 1997. The provinces remain as a tradition, but have no administrative function today. The spread of Finnish language dialects approximately follows their borders.

Southern Finland was a province of Finland from 1997 to 2009. It bordered the provinces of Western Finland and Eastern Finland. It also bordered the Gulf of Finland and Russia.

Finland is divided into 19 counties

The municipalities represent the local level of administration in Finland and act as the fundamental, self-governing administrative units of the country. The entire country is incorporated into municipalities and legally, all municipalities are equal, although certain municipalities are called cities or towns. Municipalities have the right to levy a flat percentual income tax, which is between 16 and 22 percent, and they provide two thirds of public services. Municipalities control many community services, such as schools, health care and the water supply, and local streets. They do not maintain highways, set laws or keep police forces, which are responsibilities of the central government.
The former Province of Southern Finland in Finland was divided into six regions, 16 sub-regions, and 88 municipalities.
Finland is divided into 69 sub-regional units. The sub-regions are formed by groups of municipalities within the 19 regions of Finland. The sub-regions represent a LAU 1 level of division used in conjunction with the Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics.

Satakunta is a region of Finland, part of the former Western Finland Province. It borders the regions of Southwest Finland, Pirkanmaa, South Ostrobothnia and Ostrobothnia. The capital city of the region is Pori. The name of the region literally means Hundred. The historical province of the same name was a larger area within Finland, covering modern Satakunta as well as much of Pirkanmaa.

Central Finland is a region in Finland. It borders the regions of Päijät-Häme, Pirkanmaa, South Ostrobothnia, Central Ostrobothnia, North Ostrobothnia, North Savo, and South Savo. The city of Jyväskylä is the regional centre and by far the largest city in the area.
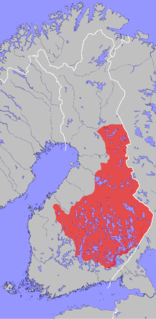
The Savonian dialects are forms of the Finnish language spoken in Savonia and other parts of Eastern Finland. It belongs to the eastern Finnish dialects and it is divided into more specific dialect groups.
There are thirteen constituencies in Finland, nowadays called electoral districts by the Finnish Parliament. The citizens of each electoral district elect from 6 to 35 MPs, depending on the population of the district, but 05 Åland only elects one. The boundaries of the electoral districts are based on the province division in use from 1634 to 1997 and has remained basically the same since the first parliamentary election in 1907. In 1939, the constituency of Northern Oulu was divided between the constituencies of Lapland and Oulu. The constituency of Southern Oulu was renamed to Oulu in the process. After the Continuation War, the electoral districts of Eastern and Western Viipuri, which lost much of their territories to the Soviet Union, were united to the new constituency of Kymi. At the same time, Åland became a distinct constituency. In 1954, Helsinki was cut from the constituency of Uusimaa. In 1962, the southern and northern Vaasa constituencies were united. In 2015, the constituencies of Kymi and Southern Savonia were united, forming the constituency of South-Eastern Finland; similarly, the constituencies of Northern Savonia and North Karelia were united to form the constituency of Savonia-Karelia.
Jaatinen is a Finnish surname.
Sutinen is a Finnish surname.
Sihvo is a Finnish surname.
Tyyskä is a Finnish surname.













