See also
| Provinces | |
|---|---|
| Territories | |
This is a list of rivers that are in whole or partly in Nunavut, Canada:

Baffin Island, in the Canadian territory of Nunavut, is the largest island in Canada and the fifth-largest island in the world. Its area is 507,451 km2 (195,928 sq mi)—slightly larger than Spain, its population was 13,039 as of the 2021 Canadian census, and is located at 68°N70°W. It also contains the city of Iqaluit, the capital of Nunavut.

John Rae was a Scottish surgeon who explored parts of northern Canada.

Sir John Ross was a Scottish Royal Navy officer and polar explorer. He was the uncle of Sir James Clark Ross, who explored the Arctic with him, and later led expeditions to Antarctica.
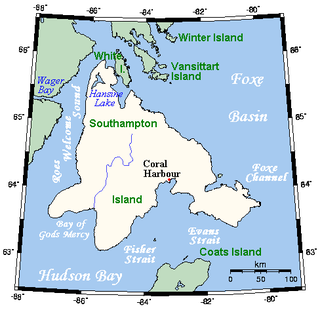
Southampton Island is a large island at the entrance to Hudson Bay at Foxe Basin. One of the larger members of the Arctic Archipelago, Southampton Island is part of the Kivalliq Region in Nunavut, Canada. The area of the island is stated as 41,214 km2 (15,913 sq mi) by Statistics Canada. It is the 34th largest island in the world and Canada's ninth largest island. The only settlement on Southampton Island is Coral Harbour, called Salliq in Inuktitut.

The Laurentide Ice Sheet was a massive sheet of ice that covered millions of square miles, including most of Canada and a large portion of the Northern United States, multiple times during the Quaternary glacial epochs, from 2.58 million years ago to the present.

Melville Peninsula is a large peninsula in the Canadian Arctic north of Hudson Bay. To the east is Foxe Basin and to the west the Gulf of Boothia. To the north the Fury and Hecla Strait separates it from Baffin Island. To the south Repulse Bay and Frozen Strait separate it from Southampton Island at the north end of Hudson Bay. On the southwest it is connected to the mainland by the Rae Isthmus, named after the Arctic explorer John Rae.
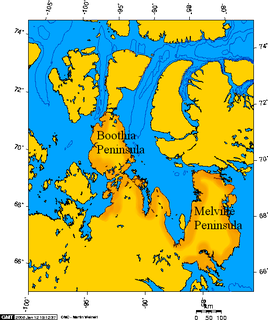
Boothia Peninsula is a large peninsula in Nunavut's northern Canadian Arctic, south of Somerset Island. The northern part, Murchison Promontory, is the northernmost point of mainland Canada.

Foxe Basin is a shallow oceanic basin north of Hudson Bay, in Nunavut, Canada, located between Baffin Island and the Melville Peninsula. For most of the year, it is blocked by sea ice and drift ice made up of multiple ice floes.

Coronation Gulf lies between Victoria Island and mainland Nunavut in Canada. To the northwest it connects with Dolphin and Union Strait and thence the Beaufort Sea and Arctic Ocean; to the northeast it connects with Dease Strait and thence Queen Maud Gulf.

Copper Inuit also known as Kitlinermiut) and Inuinnait are a Canadian Inuit group who live north of the tree line, in what is now Nunavut's Kitikmeot Region and the Inuvialuit Settlement Region in the Inuvik Region of the Northwest Territories. Most historically lived in the area around Coronation Gulf, on Victoria Island, and southern Banks Island.

Thomas Simpson was a Scottish Arctic explorer, Hudson's Bay Company fur trader, and cousin of Company Governor Sir George Simpson. He helped chart the northern coasts of Canada. He died by violence near the Turtle River while traveling through the wilderness in what is now the U.S. state of North Dakota, but was then part of the Territory of Iowa. The circumstances of his final hours—in which he allegedly killed himself after gunning down two companions—have long been a subject of controversy.

Volcanism of Northern Canada has produced hundreds of volcanic areas and extensive lava formations across Northern Canada. The region's different volcano and lava types originate from different tectonic settings and types of volcanic eruptions, ranging from passive lava eruptions to violent explosive eruptions. Northern Canada has a record of very large volumes of magmatic rock called large igneous provinces. They are represented by deep-level plumbing systems consisting of giant dike swarms, sill provinces and layered intrusions.
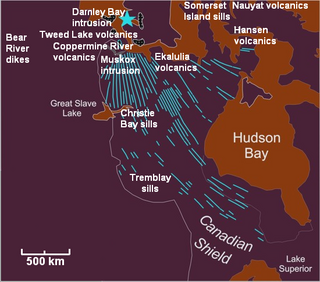
The Mackenzie Large Igneous Province (MLIP) is a major Mesoproterozoic large igneous province of the southwestern, western and northwestern Canadian Shield in Canada. It consists of a group of related igneous rocks that were formed during a massive igneous event starting about 1,270 million years ago. The large igneous province extends from the Arctic in Nunavut to near the Great Lakes in Northwestern Ontario where it meets with the smaller Matachewan dike swarm. Included in the Mackenzie Large Igneous Province are the large Muskox layered intrusion, the Coppermine River flood basalt sequence and the massive northwesterly trending Mackenzie dike swarm.

This timeline of European exploration lists major geographic discoveries and other firsts credited to or involving Europeans during the Age of Discovery and the following centuries, between the years AD 1418 and 1957.

Thomas Abernethy was a Scottish seafarer, gunner in the Royal Navy, and polar explorer. Because he was neither an officer nor a gentleman, he was little mentioned in the books written by the leaders of the expeditions he went on, but was praised in what was written. In 1857, he was awarded the Arctic Medal for his service as an able seaman on the 1824–25 voyage of HMS Hecla, the first of his five expeditions for which participants were eligible for the award. He was in parties that, for their time, reached the furthest north, the furthest south (twice), and the nearest to the South Magnetic Pole. In 1831, along with James Clark Ross's team of six, Abernethy was in the first party ever to reach the North Magnetic Pole.
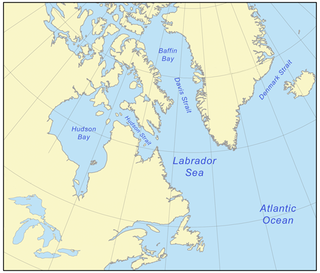
The Canadian Arctic Rift System is a major North American geological structure extending from the Labrador Sea in the southeast through Davis Strait, Baffin Bay and the Arctic Archipelago in the northwest. It consists of a series of interconnected rifts that formed during the Paleozoic, Mesozoic and Cenozoic eras. Extensional stresses along the entire length of the rift system have resulted in a variety of tectonic features, including grabens, half-grabens, basins and faults.