Honeysuckles are arching shrubs or twining vines in the family Caprifoliaceae, native to northern latitudes in North America and Eurasia. Approximately 180 species of honeysuckle have been identified in North America and Eurasia. Widely known species include Lonicera periclymenum, Lonicera japonica and Lonicera sempervirens. L. japonica is an aggressive, highly invasive species considered as a significant pest on the continents of North America, Europe, South America, Australia, and Africa.

Lonicera morrowii, the Morrow's honeysuckle, is a deciduous honeysuckle in the family Caprifoliaceae, native to Japan, Korea, and Northeast China. It is a shrub, reaching a height of 2–2.5 m, with oblong leaves 4–6 cm long. It leafs out quite early in the spring, and in North America is commonly the first deciduous shrub with foliage in March. The flowers are white to pale yellow, and the fruit is a dark red berry 7–8 mm diameter containing numerous seeds. The berries, while eaten frequently by birds, are considered poisonous to humans. It is colloquially called "bush honeysuckle" in the United States, and is considered an invasive species.

Lonicera japonica, known as Japanese honeysuckle and golden-and-silver honeysuckle, is a species of honeysuckle native to eastern Asia. It is often grown as an ornamental plant, but has become an invasive species in a number of countries. Japanese honeysuckle is used in traditional Chinese medicine.

Lonicera etrusca is a species of honeysuckle known by the common name Etruscan honeysuckle. It is native to Southern Europe, Western Asia and North Africa and it is known elsewhere, including the Pacific Northwest of North America, as an introduced species where it has escaped cultivation. It is kept in gardens as an ornamental plant.

Lonicera periclymenum, common names honeysuckle, common honeysuckle, European honeysuckle, or woodbine, is a species of flowering plant in the family Caprifoliaceae native to much of Europe, North Africa, Turkey and the Caucasus. It is found as far north as southern Norway and Sweden.

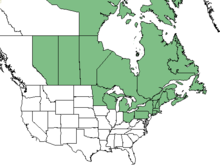
Lonicera caerulea, also known by its common names blue honeysuckle, sweetberry honeysuckle, fly honeysuckle, blue-berried honeysuckle, haskap, or the honeyberry, is a non-climbing honeysuckle native throughout the cool temperate Northern Hemisphere in countries such as Canada, Japan, Russia, and Poland.

Lonicera involucrata, the bearberry honeysuckle, bracted honeysuckle, twinberry honeysuckle, Californian Honeysuckle, twin-berry, or black twinberry, is a species of honeysuckle native to northern and western North America, from southern Alaska east across boreal Canada to Quebec, and south through the western United States to California, and to Chihuahua in northwestern Mexico. It grows at elevations from sea level to 2,900 m.
Fly honeysuckle is a common name for several plants and may refer to:

Lonicera maackii, the Amur honeysuckle, is a species of honeysuckle in the family Caprifoliaceae that is native to temperate western Asia; specifically in northern and western China south to Yunnan, Mongolia, Primorsky Krai in southeastern Siberia, Korea, and, albeit rare there, central and northern Honshū, Japan.

Lonicera ciliosa, the orange honeysuckle or western trumpet honeysuckle is a honeysuckle native to forests of western North America. A deciduous shrub growing to 6 m (20 ft) tall with hollow twigs, the leaves are opposite, oval, 4–10 cm (1.6–3.9 in) long with the last pair on each twig merged to form a disk. The flowers are orange-yellow, 2–4 cm (0.79–1.57 in) long, with five lobes and trumpet shaped; they are produced in whorls above the disk-leaf on the ends of shoots. The fruit is a translucent orange-red berry less than 1 cm (0.39 in) diameter.

Lonicera xylosteum, commonly known as fly honeysuckle, European fly honeysuckle, dwarf honeysuckle or fly woodbine is a deciduous shrub.

Lonicera sempervirens is a species of honeysuckle vine native to the eastern United States which is known for its reddish flowers.

Lonicera tatarica is a species of honeysuckle known by the common name Tatarian honeysuckle. It is native to Siberia and other parts of eastern Asia, but it is probably better known in North America, where it is a widespread introduced species and noxious weed. This plant, one of several exotic bush honeysuckles present in North America, was introduced as an ornamental plant in 1752. It is known across the continent west to Alaska and California, where it easily grows in disturbed habitat. It is a bushy shrub which may approach three meters (9.8 ft) in erect height. It is lined with oval or rounded leaves 3 to 6 centimetres long. The inflorescence is generally a pair of white to pink to crimson red flowers each about 1.5 centimetres (0.59 in) long. The flowers are somewhat tubular, their stamens and styles protruding. The fruit is a shiny orange or red berry up to a centimeter wide. The plant forms thickets and spreads easily when birds and other animals consume the fruits.

Lonicera nitida is a species of flowering plant in the honeysuckle family. In English, it is sometimes given the common names box honeysuckle or Wilson's honeysuckle. It is widely used as a low hedging plant, and for topiary. It is also a popular low-maintenance ground cover plant for urban landscaping.

Diervilla lonicera, commonly referred to as northern bush honeysuckle, low bush honeysuckle, dwarf bush honeysuckle, or yellow-flowered upright honeysuckle, is a deciduous shrub native to the northeastern United States and Canada. Its specific epithet, lonicera refers to its similarity in appearance to the true honeysuckles, genus Lonicera. It attracts bumblebees and is an important source of nectar for them.

Lonicera fragrantissima is a species of flowering plant in the honeysuckle family Caprifoliaceae, known by the common names winter-flowering honeysuckle, fragrant honeysuckle, kiss-me-at-the-gate, and sweet breath of spring. It is native to China and has been an introduced species to other parts of the world. It was brought to the attention of western gardeners by Scottish plant hunter Robert Fortune, who was plant hunting in China for the Royal Horticultural Society. Fortune introduced Lonicera fragrantissima to England in 1845, and a few years later it was introduced to the United States. In 1853 the editor of American gardening magazine The Horticulturist wrote that the previous year he had been sent a specimen from a plant that had been flowering in the gardens of Hatfield House, the Marquess of Salisbury's stately home in Hertfordshire. The first mention of a specimen for commercial sale in an American plant catalogue is in 1860.

Lonicera similis is a species of flowering plant in the family Caprifoliaceae, native to Western China. This honeysuckle is known in cultivation by the variety delavayi which is reported by some authorities to be synonymous with L. similis itself. It is a large, twining, semi-evergreen shrub growing to 8 m (26 ft) tall by 1.5 m (4.9 ft) broad, with a profusion of fragrant tubular flowers opening white and ageing to yellow, in late summer and autumn. The flowers are followed by black berries. The Latin specific epithet similis means “similar to”. It is similar in appearance to L. japonica, but larger and more robust. The name delavayi honours the French missionary and botanist Père Jean Marie Delavay (1834-1895).

Lonicera hildebrandiana, the giant Burmese honeysuckle, is a species of flowering plant in the family Caprifoliaceae, native to southeast Asia, in China, Thailand and Burma. Growing to at least 10 m (33 ft) tall and 8 m (26 ft) broad, with flowers and leaves up to 15 cm (5.9 in) long, this climbing, twining shrub is by far the largest of all the honeysuckles. The evergreen leaves are glossy, and the long thin tubular flowers open cream, turning to yellow and orange. The flowers, which have a strong honeysuckle fragrance, appear in pairs intermittently from spring throughout summer, and are followed in autumn by green berries.

Lonicera × bella, known as Bell's honeysuckle and showy fly honeysuckle, is a hybrid species of flowering plant in the family Caprifoliaceae. It was first described by Hermann Zabel in 1889. Zabel reported that he grew it in cultivation from seeds obtained from a plant of Lonicera morrowii, but that its appearance suggested the influence of L. tatarica. It has escaped from cultivation and become an aggressive invasive species in central and eastern parts of the United States.

Lonicera acuminata, commonly known as fragrant grove honeysuckle or vine honeysuckle, is a plant species of honeysuckle native to China to Southeast Asia and India.