The Jurassic is a geologic period and stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic period 201.3 million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous period approximately 145 Mya. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of the Mesozoic Era. The Jurassic is named after the Jura Mountains in the European Alps, where limestone strata from the period were first identified.

Chimaeras are cartilaginous fish in the order Chimaeriformes, known informally as ghost sharks, rat fish, spookfish, or rabbit fish; the last three names are not to be confused with rattails, Opisthoproctidae, or Siganidae, respectively.
Liopleurodon is a genus of large, carnivorous marine reptile belonging to the Pliosauroidea, a clade of short-necked plesiosaurs. The two species of Liopleurodon lived from the Callovian Stage of the Middle Jurassic to the Kimmeridgian stage of the Late Jurassic Period. It was the apex predator of the Middle to Late Jurassic seas that covered Europe. The largest species, L. ferox, is estimated to have grown up to 6.4 metres (21 ft) in length.
In the geologic timescale, the Callovian is an age and stage in the Middle Jurassic, lasting between 166.1 ± 4.0 Ma and 163.5 ± 4.0 Ma. It is the last stage of the Middle Jurassic, following the Bathonian and preceding the Oxfordian.
In the geologic timescale, the Kimmeridgian is an age or stage in the Late or Upper Jurassic epoch or series. It spans the time between 157.3 ± 1.0 Ma and 152.1 ± 0.9 Ma. The Kimmeridgian follows the Oxfordian and precedes the Tithonian.

Dakosaurus is an extinct genus of crocodylomorph within the family Metriorhynchidae that lived during the Late Jurassic and Early Cretaceous. It was large, with teeth that were serrated and compressed lateromedially. The genus was established by Friedrich August von Quenstedt in 1856 for an isolated tooth named Geosaurus maximus by Theodor Plieninger in 1846. Dakosaurus was a carnivore that spent much, if not all, its life out at sea. The extent of its adaptation to a marine lifestyle means that it is most likely that it mated at sea, but since no eggs or nests have been discovered that have been referred to Dakosaurus, whether it gave birth to live young at sea like dolphins and ichthyosaurs or came ashore like turtles is not known. The name Dakosaurus means "biter lizard", and is derived from the Greek dakos ("biter") and σαῦρος -sauros ("lizard").

Goniopholis is an extinct genus of goniopholidid crocodyliform that lived in Europe and Africa during the Late Jurassic and Early Cretaceous. Being semi-aquatic it is very similar to modern crocodiles. It ranged from 2–4 metres in length, and would have had a very similar lifestyle to the American alligator or Nile crocodile.

Temnodontosaurus is an extinct genus of ichthyosaurs from the Early Jurassic, ranging between 200 and 175 million years ago, and known from Europe and Chile. They lived in the deeper areas of the open ocean. University of Bristol paleontologist Jeremy Martin described the genus Temnodontosaurus as “one of the most ecologically disparate genera of ichthyosaurs”.

Megalosauridae is a monophyletic family of carnivorous theropod dinosaurs within the group Megalosauroidea, closely related to the family Spinosauridae. Some members of this family include Megalosaurus, Torvosaurus, Eustreptospondylus, and Afrovenator. Appearing in the Middle Jurassic, megalosaurids were among the first major radiation of large theropod dinosaurs, although they became extinct by the end of the Jurassic period. They were a relatively primitive group of basal tetanurans containing two main subfamilies, Megalosaurinae and Afrovenatorinae, along with the basal genus Eustreptospondylus, an unresolved taxon which differs from both subfamilies.

Machimosaurus is an extinct genus of machimosaurid crocodyliform from the Late Jurassic and Early Cretaceous. The type species, Machimosaurus hugii, was found in Switzerland. Other fossils have been found in England, France, Germany, Portugal, Switzerland and Tunisia. Machimosaurus rex is the largest named teleosauroid and thalattosuchian, with an estimated length of approximately 7.2 metres. Machimosaurus is the largest known crocodyliform of the Jurassic.

Metriorhynchus is an extinct genus of marine crocodyliform that lived in the oceans during the Late Jurassic. The type species, M. brevirostris was named in 1829 as a species of Steneosaurus before being named as a separate genus by the German palaeontologist Christian von Meyer in 1832. The name Metriorhynchus means "Moderate snout", and is derived from the Greek Metrio- ("moderate") and -rhynchos ("snout").

Stenopterygius is an extinct genus of thunnosaur ichthyosaur known from Europe. This genus of ichthyosaur grew to a maximum length of 4 meters.
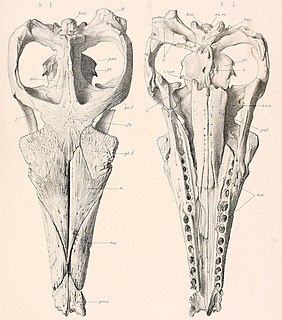
Suchodus is an extinct genus of marine crocodyliform from the Middle to Late Jurassic period of England and France.

Steneosaurus is a dubious genus of teleosaurid crocodyliform from the Middle or Late Jurassic of France. The genus has been used as a wastebasket taxon for thalattosuchian fossils for over two centuries, and almost all known historical species of teleosauroid have been included within it at one point. The genus has remained a wastebasket, with numerous species still included under the label ‘Steneosaurus’, many of which are unrelated to each other.

Saurorhynchus is an extinct genus of carnivorous bony fish. It is the youngest representative of the family Saurichthyidae and the order Saurichthyiformes. This family is known for its large, elongate jaws, similar to modern Belonidae. Saurichthyidae also includes the Permian genus Eosaurichthys and the Triassic genus Saurichthys.

The Jurassic Skyline tower was an observation tower on Weymouth Pier in Weymouth, Dorset, England. It was situated next to Weymouth Beach and the Weymouth Pavilion, where it overlooked Weymouth town, the beach, the Pavilion, the Old Harbour, Nothe Gardens, the Nothe Fort, and Portland Harbour. It opened on 22 June 2012.

Tyrannoneustes is an extinct genus of geosaurine metriorhynchid crocodyliform from the Callovian stage Oxford Clay Formation of England and the Marnes de Dives of France. It contains a single species, Tyrannoneustes lythrodectikos, meaning "blood-biting tyrant swimmer". The genus was rediscovered after a century of storage in a museum basement after being unearthed by fossil hunter Alfred Nicholson Leeds between the years of 1907 and 1909. Its lower jaw measured about 26 inches long and its teeth were blade-like, likely built to attack prey as large or larger than itself, similar to the Late Jurassic Dakosaurus, Torvoneustes, and Plesiosuchus.

Plesiochelys is a genus of late Jurassic European and Asian turtle. The type species is Plesiochelys etalloni.

Lemmysuchus is a genus of machimosaurid thalattosuchian from the Middle Jurassic Callovian of England and France. Like many other teleosauroids from Europe, it has had a convoluted taxonomic history.

Paracestracion is an extinct genus of heterodontid sharks from Early Jurassic to Early Cretaceous-aged rocks of England, France, Germany and Luxembourg. The genus, first described in 1911 by Ernst Hermann Friedrich von Koken in Karl Alfred von Zittel, contains five species: P. bellis from the Bathonian of England, the type species P. falcifer from the Tithonian and Kimmeridgian of Weymouth, England and Solnhofen, Germany, which was originally named as a species of Cestracion in 1857 by Johann Andreas Wagner, P. pectinatus from the Valanginian of France, P. sarstedtensis, originally classified as a species of Heterodontus, from the Toarcian and Aalenian of Germany, and P. viohli from the Tithonian-aged Painten Formation of Germany, with a sixth indeterminate species known from the Toarcian-aged Variabilis layer of the La Couche à Crassum of Luxembourg.


















