In biochemistry, isomerases are a general class of enzymes that convert a molecule from one isomer to another. Isomerases facilitate intramolecular rearrangements in which bonds are broken and formed. The general form of such a reaction is as follows:
Enoyl-CoA-(∆) isomerase (EC 5.3.3.8, also known as dodecenoyl-CoA- isomerase, 3,2-trans-enoyl-CoA isomerase, ∆3 ,∆2 -enoyl-CoA isomerase, or acetylene-allene isomerase, is an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of cis- or trans-double bonds of coenzyme A bound fatty acids at gamma-carbon to trans double bonds at beta-carbon as below:

Prolyl isomerase is an enzyme found in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes that interconverts the cis and trans isomers of peptide bonds with the amino acid proline. Proline has an unusually conformationally restrained peptide bond due to its cyclic structure with its side chain bonded to its secondary amine nitrogen. Most amino acids have a strong energetic preference for the trans peptide bond conformation due to steric hindrance, but proline's unusual structure stabilizes the cis form so that both isomers are populated under biologically relevant conditions. Proteins with prolyl isomerase activity include cyclophilin, FKBPs, and parvulin, although larger proteins can also contain prolyl isomerase domains.
In enzymology, a 2-chloro-4-carboxymethylenebut-2-en-1,4-olide isomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 4-hydroxyproline epimerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an aconitate Δ-isomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a farnesol 2-isomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a furylfuramide isomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a linoleate isomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a maleate isomerase, or maleate cis-tran isomerase, is a member of the Asp/Glu racemase superfamily discovered in bacteria. It is responsible for catalyzing cis-trans isomerization of the C2-C3 double bond in maleate to produce fumarate, which is a critical intermediate in citric acid cycle. The presence of an exogenous mercaptan is required for catalysis to happen.

In enzymology, maleylacetoacetate isomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a polyenoic fatty acid isomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Retinal isomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the isomerisation of all-trans-retinal in the eye into 11-cis-retinal which is the form that most opsins bind.
In enzymology, a retinol isomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a trans-2-decenoyl-[acyl-carrier protein] isomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a vinylacetyl-CoA Delta-isomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Prolycopene isomerase is an enzyme with systematic name 7,9,7',9'-tetracis-lycopene cis-trans-isomerase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

3-Maleylpyruvic acid, or 3-maleylpyruvate, is a dicarboxylic acid formed by the oxidative ring opening of gentisic acid by gentisate 1,2-dioxygenase during the metabolism of tyrosine. It is converted into 3-fumarylpyruvate by maleylpyruvate isomerase.
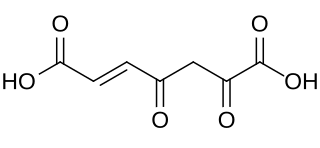
3-Fumarylpyruvic acid, or 3-fumarylpyruvate, is a dicarboxylic acid formed from the isomerisation of 3-maleylpyruvate by maleylpyruvate isomerase. It is converted into fumarate and pyruvate by 3-fumarylpyruvate hydrolase.






