
Conus marmoreus, common name the "marbled cone", is a species of predatory sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Conidae, the cone snails, cone shells or cones. It is the type species for the genus Conus. This is a species which is believed to feed mostly on marine molluscs including other cone snails. This snail is venomous, like all cone snails.

Calliostoma ligatum, common name the blue top snail, is a small prosobranch trochid gastropod mollusk in the family Calliostomatidae, the Calliostoma top snails.

Steromphala divaricata, common name the divaricate gibbula, is a species of small sea snail, known as top snails or top shells, marine gastropod molluscs in the family Trochidae, the top snails.

Gibbula magus, common name the great top shell, is a species of small sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusc in the family Trochidae, the top snails.

Neptunea ventricosa is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Buccinidae, the true whelks.

Lischkeia imperialis, common name : the giant imperial margarite, is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Eucyclidae.

Tricolia pullus is a species of small sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Phasianellidae.

Margarites argentatus is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Margaritidae.
Margarites costalis, common name the boreal rosy margarite or the northern ridged margarite, is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Margaritidae.

Margarites groenlandicus, common name the Greenland margarite or wavy top shell, is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Margaritidae.
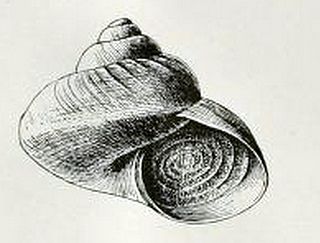
Margarites olivaceus, common name the eastern olive margarite, is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Margaritidae.

Margarites striatus, common name the striate margarite, is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Margaritidae.

Margarites is a genus of sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the family Margaritidae.
Solariella varicosa, common name the varicose solarielle, is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Solariellidae.

Calliostoma jujubinum, common name the jujube top shell, is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Calliostomatidae.

Monilea callifera, common name shrewd trochid, is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Trochidae, the top snails.
Margarites koreanicus is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Margaritidae.
Margarites pilsbryi is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Margaritidae,.

Margarites schantaricus is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Margaritidae.

Margarites scintillans is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Margaritidae.
















