- Ventral reconstruction of Xylokorys
- Reconstruction of the head shield of Furca bohemica
- Fossil of "Furca mauretanica"
- Reconstruction of Mimetaster
- Restoration of Vachonisia
- Life restoration of Tomlinsonus
- Life restoration of Primicaris
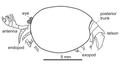
- Diagram of Skania
| Marrellomorpha | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Life restoration of Marrella (Marrellida) | |
 | |
| Diagram of Primicaris (Acercostraca) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | † Marrellomorpha Beurlen, 1930 |
| Subgroups | |
| |
Marrellomorpha are an extinct group of arthropods known from the Cambrian to the Early Devonian. [1] It is divided into two major groups, Marrellida and Acercostraca. They lacked mineralised hard parts, so are only known from areas of exceptional preservation, limiting their fossil distribution. The best known member is Marrella , with thousands of specimens found in the Cambrian aged Burgess Shale of Canada.