
Dromus dromas, the dromedary pearlymussel or dromedary naiad, is a rare species of freshwater mussel in the family Unionidae. This aquatic bivalve mollusk is native to the Cumberland and Tennessee River systems in the United States, where it has experienced a large population decline. It is a federally listed endangered species of the United States.
The Chipola slabshell is a part of the phylum Mollusca and the class Bivalvia. This species has suffered a large decrease with upwards of 75% of habitat lost. It is now confined to only a few remnant sites in small drainages within the Chipola River. The federal Endangered Species Act protects it as a designated threatened species by Florida's Endangered and Threatened Species Rule.

Fusconaia escambia, the narrow pigtoe, is a freshwater bivalve mussel found in Alabama and northwestern Florida. The narrow pigtoe was first discovered in the Escambia River in Alabama and Florida.

Hamiota perovalis, the orangenacre mucket or orange-nacre mucket, is a species of freshwater mussel, an aquatic bivalve mollusk in the family Unionidae, the river mussels.

Potamilus leptodon, the scaleshell mussel or scale shell, is a species of freshwater mussel in the family Unionidae, the river mussels. This aquatic bivalve mollusk has disappeared from much of its historical range. It is endemic to the United States, where it is now present in four or fewer states; it is only found with any regularity in Missouri. It is a federally listed endangered species of the United States.

The Louisiana pearlshell, Margaritifera hembeli, is a rare species of bivalve mollusk in the family Margaritiferidae. This freshwater mussel is native to Louisiana in the United States, and was previously present also in Arkansas. It grows to a length of about 10 cm (4 in) and lives on the sand or gravel stream-bed in riffles and fast flowing stretches of small streams. Its life cycle involves a stage where it lives parasitically inside a fish. This mollusk is sensitive to increased sedimentation and cannot tolerate impoundments. Because of its limited range and its population decline, the International Union for Conservation of Nature has rated this mollusk as being "critically endangered".

Medionidus conradicus is a species of freshwater mussel, an aquatic bivalve mollusk in the family Unionidae, the river mussels.

Medionidus parvulus, the Coosa moccasinshell, is a rare species of freshwater mussel in the family Unionidae, the river mussels. This aquatic bivalve mollusk is native to Georgia and Tennessee in the United States, and has been extirpated from the state of Alabama. It is a federally listed endangered species of the United States.

Medionidus penicillatus, the gulf moccasinshell, is a rare species of freshwater mussel in the family Unionidae, the river mussels. This aquatic bivalve mollusk is native to Alabama, Florida, and Georgia in the United States, where it is in decline and has been extirpated from most of the rivers it once inhabited. It is a federally listed endangered species of the United States.
The Ochlockonee moccasinshell is a species of freshwater mussel, an aquatic bivalve mollusk in the family Unionidae, the river mussels.

Obovaria olivaria is a species of freshwater mussel, an aquatic bivalve mollusk in the family Unionidae, the river mussels. It is commonly referred to as hickorynut.

Pegias is a monotypic genus of freshwater mussels in the family Unionidae. This genus contains the single species Pegias fabula, known commonly as the littlewing pearlymussel.

Pleurobema clava, the clubshell, club naiad or clubshell pearly mussel, is a species of freshwater mussel, an aquatic bivalve mollusk in the family Unionidae, the river mussels.
Pleurobema furvum, the dark pigtoe, is a species of freshwater mussel in the family Unionidae, the river mussels. This aquatic bivalve mollusk is native to Alabama in the United States, where it is mainly limited to the Black Warrior River. It is a federally listed endangered species of the United States.
Pleurobema marshalli, the flat pigtoe or Marshall's mussel, was a species of freshwater mussel in the family Unionidae, the river mussels. It was native to Alabama and Mississippi, but it has not been seen since 1980. Though it is still listed as critically endangered on the IUCN Red List and as an endangered species on the US Endangered Species List, it is likely extinct.

Pleurobema oviforme, the Tennessee clubshell, is a species of freshwater mussel in the family Unionidae, the river mussels. It is native to the eastern United States, where it occurs in Alabama, Kentucky, North Carolina, Tennessee, and Virginia. It also previously occurred in Mississippi.
Pleurobema taitianum, the heavy pigtoe or Judge Tait's mussel, is a species of freshwater mussel, an aquatic bivalve mollusk in the family Unionidae, the river mussels.
The triangular kidneyshell is a species of freshwater mussel, in the family Unionidae, the river mussels. It is endemic to Alabama in the United States, where it is known from several rivers and streams in the Mobile River Basin. It is a federally listed endangered species of the United States.
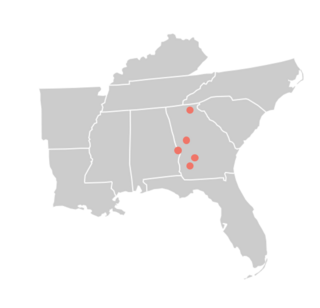
The Halloween darter is a small freshwater fish native to North America. It is found in Georgia and Alabama in the drainage basin of the Apalachicola River, specifically in the Flint River system and the Chattahoochee River system. It prefers shallow, fast-flowing areas with gravel bottoms in small and medium-sized rivers. It was first described in 2008, having not previously been distinguished from the Blackbanded darter (P. nigrofasciata), formerly though to occur in the same watershed. Blackbanded darter has since been split again with Westfall's darter now recognised from the Apalachicola drainage. The species is somewhat variable, being generally blackish dorsally, with some individuals having indistinct saddle-like barring. Males have orange and dark lateral striping while females have dark stripes and a yellowish-green belly. At a maximum standard length of 101 mm (4 in), males are slightly larger than females, and both sexes develop distinctive orange barring on the edge of the first dorsal fin during the breeding season.















