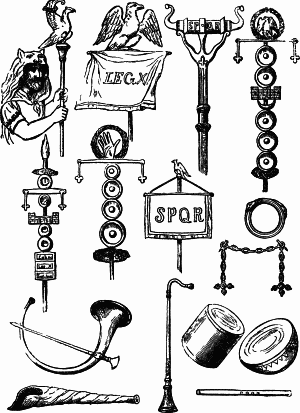The lorica segmentata, also called lorica lamminata, or banded armour is a type of personal armour that was used by soldiers of the Roman army, consisting of metal strips fashioned into circular bands, fastened to internal leather straps.

A manica or cheires by the Greeks was a type of iron or bronze arm guard, with curved and overlapping metal segments or plates, fastened to leather straps, worn by Roman gladiators called crupellarii, and later optionally by soldiers.
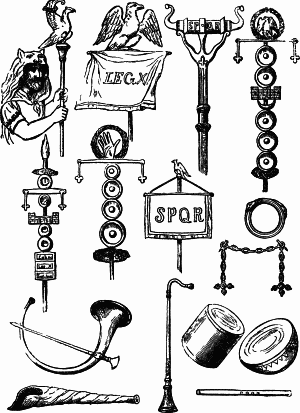
Roman military personal equipment was produced in large numbers to established patterns, and used in an established manner. These standard patterns and uses were called the res militaris or disciplina. Its regular practice during the Roman Republic and Roman Empire led to military excellence and victory. The equipment gave the Romans a very distinct advantage over their barbarian enemies, especially so in the case of armour. This does not mean that every Roman soldier had better equipment than the richer men among his opponents. Roman equipment was not of a better quality than that used by the majority of Rome's adversaries. Other historians and writers have stated that the Roman army's need for large quantities of "mass produced" equipment after the so-called "Marian Reforms" and subsequent civil wars led to a decline in the quality of Roman equipment compared to the earlier Republican era:
The production of these kinds of helmets of Italic tradition decreased in quality because of the demands of equipping huge armies, especially during civil wars...The bad quality of these helmets is recorded by the sources describing how sometimes they were covered by wicker protections, like those of Pompeius' soldiers during the siege of Dyrrachium in 48 BC, which were seriously damaged by the missiles of Caesar's slingers and archers.
It would appear that armour quality suffered at times when mass production methods were being used to meet the increased demand which was very high the reduced size cuirasses would also have been quicker and cheaper to produce, which may have been a deciding factor at times of financial crisis, or where large bodies of men were required to be mobilized at short notice, possibly reflected in the poor-quality, mass produced iron helmets of Imperial Italic type C, as found, for example, in the River Po at Cremona, associated with the Civil Wars of AD 69 AD; Russell Robinson, 1975, 67
Up until then, the quality of helmets had been fairly consistent and the bowls well decorated and finished. However, after the Marian Reforms, with their resultant influx of the poorest citizens into the army, there must inevitably have been a massive demand for cheaper equipment, a situation which can only have been exacerbated by the Civil Wars...

Metellina is a genus of tetragnathid spiders that occurs mostly in Eurasia, with two species found in North America. M. segmentata was introduced to Canada.

Metellina segmentata is a spider in the family Tetragnathidae with a Palaearctic distribution. This spider's name is often shortened to Meta segmentata, and some even call it Araneus segmentatus simply meaning, orb weaving spiders. It is primarily found in Europe, with the highest number in the United Kingdom, but the species has also been introduced to Canada.

The swallow-tailed nightjar is a species of nightjar in the family Caprimulgidae. It is found in Bolivia, Colombia, Ecuador, and Peru.

Strela is a Russian military communications satellite constellation operating in low Earth orbit. These satellites operate as mailboxes ("store-and-forward"): they remember the received messages and then resend them after the scheduled time, or by a command from the Earth. Some sources state the satellites are capable of only three months of active operation, but through coordination with others they can serve for about five years. The satellites are used for transmission of encrypted messages and images.
Kosmos 400, also known as DS-P1-M No.3 was a satellite which was used as a target for tests of anti-satellite weapons. It was launched by the Soviet Union in 1971 as part of the Dnepropetrovsk Sputnik programme, and used as a target for Kosmos 404, as part of the Istrebitel Sputnikov programme.
Kosmos 459, also known as DS-P1-M No.5 was a satellite which was used as a target for tests of anti-satellite weapons. It was launched by the Soviet Union in 1971 as part of the Dnepropetrovsk Sputnik programme, and used as a target for Kosmos 462, as part of the Istrebitel Sputnikov programme.
Kosmos 967 is a satellite which was used as a target for tests of anti-satellite weapons. It was launched by the Soviet Union in 1977 as part of the Dnepropetrovsk Sputnik programme, and used as a target for Kosmos 970 and Kosmos 1009, as part of the Istrebitel Sputnikov programme.
Kosmos 1241 was a target satellite which was used by the Soviet Union in the 1980s for tests of anti-satellite weapons as part of the Istrebitel Sputnikov programme. It was launched in 1981, and was itself part of the Dnepropetrovsk Sputnik programme. It was a target for Kosmos 1243 and Kosmos 1258.

Kosmos 97, also known as DS-U2-M No.1, was a Soviet satellite which was launched in 1965 as part of the Dnepropetrovsk Sputnik programme. It was a 267 kilograms (589 lb) spacecraft, which was built by the Yuzhnoye Design Bureau, and used to conduct tests involving atomic clocks.
Kosmos 145, also known as DS-U2-M No.2, was a Soviet satellite which was launched in 1967 as part of the Dnepropetrovsk Sputnik programme. It was a 250 kilograms (550 lb) spacecraft, which was built by the Yuzhnoye Design Bureau, and was used to conduct tests involving atomic clocks.
Kosmos 1109 was a Soviet US-K missile early warning satellite which was launched in 1979 as part of the Soviet military's Oko programme. The satellite was designed to identify missile launches using optical telescopes and infrared sensors.
Apolania is a monotypic genus of East African wandering spiders containing the single species, Apolania segmentata, first described from a male found by Eugène Simon in 1898. No females have been described yet, and it has only been found in Seychelles.
Palaeoplatoda is a genus from the Ediacaran biota. It is a soft-bodied organism with a segmented body that resembles Dickinsonia, another Ediacaran organism.

Metellina curtisi is a species of long-jawed orb weaver in the spider family Tetragnathidae. It is found in North America.

Metellina mimetoides is a species of long-jawed orb weaver in the spider family Tetragnathidae. It is found in North America.

Wilhelmus Egbertus Antonius Janssen, better known as Father Chrysanthus OFMCap, was a Dutch priest and biology teacher. He was known for his studies in arachnology. Initially he was concerned with the spiders of the Netherlands but he became a specialist on New Guinea spiders. Two spider species were named in his honor following his death.