
A mushroom or toadstool is the fleshy, spore-bearing fruiting body of a fungus, typically produced above ground, on soil, or on its food source. Toadstool generally denotes one poisonous to humans.

Flammulina filiformis is a species of edible agaric in the family Physalacriaceae. It is widely cultivated in East Asia, and well known for its role in Japanese and Chinese cuisine. Until recently, the species was considered to be conspecific with the European Flammulina velutipes, but DNA sequencing has shown that the two are distinct.

Morchella esculenta is a species of fungus in the family Morchellaceae of the Ascomycota. It is one of the most readily recognized of all the edible mushrooms and highly sought after. Each fruit body begins as a tightly compressed, grayish sponge with lighter ridges, and expands to form a large yellowish sponge with large pits and ridges raised on a large white stem. The pitted yellow-brown caps measure 2–7 centimetres broad by 2–10 cm (1–4 in) tall, and are fused to the stem at its lower margin, forming a continuous hollow. The pits are rounded and irregularly arranged. The hollow stem is typically 2–9 cm long by 2–5 cm (1–2 in) thick, and white to yellow. The fungus fruits under hardwoods and conifers during a short period in the spring, depending on the weather, and is also associated with old orchards, woods and disturbed grounds.

Phallus indusiatus, commonly called the basket stinkhorn, bamboo mushrooms, bamboo pith, long net stinkhorn, crinoline stinkhorn, bridal veil, or veiled lady, is a fungus in the family Phallaceae, or stinkhorns. It has a cosmopolitan distribution in tropical areas, and is found in southern Asia, Africa, the Americas, and Australia, where it grows in woodlands and gardens in rich soil and well-rotted woody material. The fruit body of the fungus is characterised by a conical to bell-shaped cap on a stalk and a delicate lacy "skirt", or indusium, that hangs from beneath the cap and reaches nearly to the ground. First described scientifically in 1798 by French botanist Étienne Pierre Ventenat, the species has often been referred to a separate genus Dictyophora along with other Phallus species featuring an indusium. P. indusiatus can be distinguished from other similar species by differences in distribution, size, color, and indusium length.

Tremella mesenterica is a common jelly fungus in the family Tremellaceae of the Agaricomycotina. The gelatinous, orange-yellow fruit body of the fungus, which can grow up to 7.5 cm (3 in) diameter, has a convoluted or lobed surface that is greasy or slimy when damp.

The yellow-footed rock-wallaby, formerly known as the ring-tailed rock-wallaby, is a member of the macropod family.

Craterellus lutescens, formerly sometimes called Cantharellus lutescens or Cantharellus xanthopus or Cantharellus aurora, commonly known as Yellow Foot, camagroc in Catalan, craterelle jaune in French, is a species of mushroom. It is closely related to Craterellus tubaeformis. Its hymenium is usually orange or white, whereas the hymenium of C. tubaeformis is grey. C. lutescens is also usually found in wetlands.

Lactifluus volemus, formerly known as Lactarius volemus, and commonly known as the weeping milk cap or bradley, is a species of fungus in the family Russulaceae. It is widely distributed in the northern hemisphere, in temperate regions of Europe, North America and Asia as well as some subtropical and tropical regions of Central America and Asia. A mycorrhizal fungus, its fruit bodies grow on the ground at the base of various species of trees from summer to autumn, either individually or in groups. It is valued as an edible mushroom, and is sold in markets in Asia. Several other Lactifluus mushrooms resemble L. volemus, such as the closely related edible species L. corrugis, but these can be distinguished by differences in distribution, visible morphology, and microscopic characteristics. L. volemus produces a white spore print and has roughly spherical spores about 7–8 micrometres in diameter.

Exsudoporus frostii, commonly known as Frost's bolete or the apple bolete, is a bolete fungus first described scientifically in 1874. A member of the family Boletaceae, the mushrooms produced by the fungus have tubes and pores instead of gills on the underside of their caps. Exsudoporus frostii is distributed in the eastern United States from Maine to Georgia, and in the southwest from Arizona extending south to Mexico and Costa Rica. A mycorrhizal species, its fruit bodies are typically found growing near hardwood trees, especially oak.

Xerocomellus zelleri, commonly known as Zeller's bolete, is an edible species of mushroom in the family Boletaceae. First described scientifically by American mycologist William Alphonso Murrill in 1912, the species has been juggled by various authors to several genera, including Boletus, Boletellus, and Xerocomus. Found solely in western North America from British Columbia south to Mexico, the fruit bodies are distinguished by their dark reddish brown to nearly black caps with uneven surfaces, the yellow pores on the underside of the caps, and the red-streaked yellow stems. The fungus grows in summer and autumn on the ground, often in Douglas fir forests or on their margins. The development of the fruit bodies is gymnocarpic, meaning that the hymenium appears and develops to maturity in an exposed state, not enclosed by any protective membrane.

Lignosus is a genus of polypore fungi in the family Polyporaceae. The genus was circumscribed in 1920 by mycologists Curtis Gates Lloyd and Camille Torrend, with L. sacer as the type species.

Microporus is a genus of fungi in the family Polyporaceae. The genus has a widespread distribution and, according to a 2008 estimate, contains 11 species. The genus name combines the Ancient Greek words μικρός ("small") and πόρος ("pore").

Pholiota flammans, commonly known as the yellow pholiota, the flaming Pholiota, or the flame scalecap, is a basidiomycete agaric mushroom of the genus Pholiota. Its fruit body is golden-yellow in color throughout, while its cap and stem are covered in sharp scales. As it is a saprobic fungus, the fruit bodies typically appear in clusters on the stumps of dead coniferous trees. P. flammans is distributed throughout Europe, North America, and Asia in boreal and temperate regions. Its edibility has not been clarified.

Lactarius alnicola, commonly known as the golden milkcap, is a species of fungus in the family Russulaceae. The fruit bodies produced by the fungus are characterized by a sticky, vanilla-colored cap up to 20 cm (7.9 in) wide with a mixture of yellow tones arranged in faint concentric bands. The stem is up to 5 cm (2.0 in) long and has yellow-brown spots. When it is cut or injured, the mushroom oozes a white latex, which has an intensely peppery taste. The acrid taste of the fruit bodies renders them unpalatable. The fungus is found in the western United States and Mexico, where it grows in mycorrhizal associations with various coniferous trees species, such as spruce, pine and fir, and deciduous species such as oak and alder. It has also been collected in India. Two varieties have been named: var. pitkinensis, known from Colorado, and var. pungens, from Michigan.
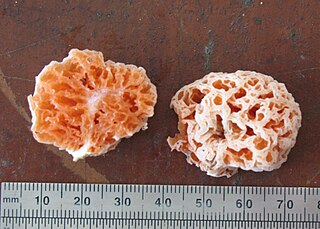
Spongiforma squarepantsii is a species of fungus in the family Boletaceae, genus Spongiforma. Found in Malaysia, it was described as new to science in 2011. It produces sponge-like, rubbery orange fruit bodies that have a fruity or musky odour. The fruit bodies reach dimensions of 10 cm (3.9 in) wide by 7 cm (2.8 in) tall. Like a sponge, they will resume their original shape if water is squeezed out. The spores, produced on the surfaces of the hollows of the sponge, are almond-shaped with rough surfaces, and measure 10‑12.5 μm by 6‑7 μm. The name of the fungus derives from the Nickelodeon cartoon character SpongeBob SquarePants from the show of the same name. S. squarepantsii is one of two species in Spongiforma; it differs from S. thailandica in its color, odour, and spore structure.

Phellinus ellipsoideus is a species of polypore fungus in the family Hymenochaetaceae, a specimen of which produced the largest fungal fruit body ever recorded. Found in China, the fruit bodies produced by the species are brown, woody basidiocarps that grow on dead wood, where the fungus feeds as a saprotroph. The basidiocarps are perennial, allowing them to grow very large under favourable circumstances. They are resupinate, measuring 30 centimetres (12 in) or more in length, though typically extending less than a centimetre from the surface of the wood. P. ellipsoideus produces distinct ellipsoidal spores, after which it is named, and unusual setae. These two features allow it to be readily differentiated microscopically from other, similar species. Chemical compounds isolated from the species include several steroidal compounds. These may have pharmacological applications, but further research is needed.

Volvariella bombycina, commonly known as the silky volvariella, silky sheath, silky rosegill, silver-silk straw mushroom, or tree mushroom, is a species of edible mushroom in the family Pluteaceae. It is an uncommon but widespread species, having been reported from Asia, Australia, the Caribbean, Europe, and North America. The fruit body (mushroom) begins developing in a thin, egg-like sac. This ruptures and the stem expands quickly, leaving the sac at the base of the stem as a volva. The cap, which can attain a diameter of up to 20 centimetres, is white to slightly yellowish and covered with silky hairs. On the underside of the cap are closely spaced gills, free from attachment to the stem, and initially white before turning pink as the spores mature. The mushroom grows singly or in clusters, often appearing in old knotholes and wounds in elms and maples. V. bombycina contains compounds with antibacterial properties.

Ramaria stricta, commonly known as the strict-branch coral or strict coral mushroom, is a coral fungus of the genus Ramaria. It has a cosmopolitan distribution, and grows on dead wood, stumps, trunks, and branches of both deciduous and coniferous trees. Its fruit body is up to 10 cm tall, made of multiple slender, compact, and vertical parallel branches. Its color is typically light tan to vinaceous-brown. All parts of the mushroom will bruise when handled. There are several lookalike corals that can usually be distinguished from R. stricta by differences in coloration, bruising reaction, or microscopic features. The fungus is inedible due to its unpleasant odor and bitter taste.

Russula crustosa, commonly known as the crusty russula, is a species of fungus in the family Russulaceae. It is found in Asia and North America.

Nigroporus vinosus is a species of poroid fungus in the family Steccherinaceae, and the type species of the genus Nigroporus. Its fruit bodies have brownish caps with tinges of purple or red. The cap underside has a pore surface the same colour as the cap, and minute pores. Nigroporus vinosus has a pantropical distribution. It has been recorded from Africa, North America, Central America, South America, Asia, and Oceania. It is a wood-decay fungus that causes a white rot.























