
A meteorite is a solid piece of debris from an object, such as a comet, asteroid, or meteoroid, that originates in outer space and survives its passage through the atmosphere to reach the surface of a planet or moon. When the original object enters the atmosphere, various factors such as friction, pressure, and chemical interactions with the atmospheric gases cause it to heat up and radiate energy. It then becomes a meteor and forms a fireball, also known as a shooting star; astronomers call the brightest examples "bolides". Once it settles on the larger body's surface, the meteor becomes a meteorite. Meteorites vary greatly in size. For geologists, a bolide is a meteorite large enough to create an impact crater.

The Tunguska event was an approximately 12-megaton explosion that occurred near the Podkamennaya Tunguska River in Yeniseysk Governorate, Russia, on the morning of 30 June 1908. The explosion over the sparsely populated East Siberian taiga flattened an estimated 80 million trees over an area of 2,150 km2 (830 sq mi) of forest, and eyewitness reports suggest that at least three people may have died in the event. The explosion is generally attributed to a meteor air burst: the atmospheric explosion of a stony asteroid about 50–60 metres in size. The asteroid approached from the east-south-east, and probably with a relatively high speed of about 27 km/s (60,000 mph). Though it is classified as an impact event, the object is thought to have exploded at an altitude of 5 to 10 kilometres rather than having hit the surface of the Earth, leaving no impact crater.

An impact event is a collision between astronomical objects causing measurable effects. Impact events have physical consequences and have been found to regularly occur in planetary systems, though the most frequent involve asteroids, comets or meteoroids and have minimal effect. When large objects impact terrestrial planets such as the Earth, there can be significant physical and biospheric consequences, though atmospheres mitigate many surface impacts through atmospheric entry. Impact craters and structures are dominant landforms on many of the Solar System's solid objects and present the strongest empirical evidence for their frequency and scale.

Acraman crater is a deeply eroded impact crater in the Gawler Ranges of South Australia. Its location is marked by Lake Acraman, a circular ephemeral playa lake about 20 kilometres (12 mi) in diameter. The discovery of the crater and independent discovery of its ejecta were first reported in the journal Science in 1986. The evidence for impact includes the presence of shatter cones and shocked quartz in shattered bedrock on islands within Lake Acraman.
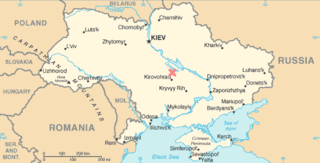
The Boltysh crater or Bovtyshka crater is a buried impact crater in the Kirovohrad Oblast of Ukraine, near the village of Bovtyshka. The crater is 24 kilometres (15 mi) in diameter and its age of 65.39 ± 0.14/0.16 million years, based on argon-argon dating techniques, less than 1 million years younger than Chicxulub crater in Mexico and the Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary. The Chicxulub impact is believed to have caused the mass extinction at the end of the Cretaceous period, which included the extinction of the non-avian dinosaurs. The Boltysh crater is currently thought to be unrelated to the Chicxulub impact, and to have not generated major global environmental effects.

Mistastin crater is a meteorite crater in Labrador, Canada which contains the roughly circular Mistastin Lake. The lake is approximately 16 km (9.9 mi) in diameter, while the estimated diameter of the original crater is 28 km (17 mi). The age of the crater is calculated to be 36.6 ± 2 million years (Eocene).

The Popigai impact structure is the eroded remnant of an impact crater in northern Siberia, Russia. It is tied with the Manicouagan structure as the fourth largest verified impact structure on Earth. A large bolide impact created the 100-kilometre (62 mi) diameter crater approximately 35 million years ago during the late Eocene epoch. It might be linked to the Eocene–Oligocene extinction event.

Suvasvesi is a lake in Eastern Finland near the town of Kuopio. Suvasvesi consists of two circular open lakes, Kuukkarinselkä in north and Haapaselkä in south. The lakes are separated by a group of islands. The lake has 688 islands in total. The area of the lake is 234 square kilometres (90 sq mi) making it the 18th largest lake in Finland. Kuukkarinselkä is the third deepest lake in Finland measuring 89.0 metres (292.0 ft) in the deepest point.

The Vredefort impact structure is the largest verified impact structure on Earth. The crater, which has since been eroded away, was around 180–300 km (100–200 mi) across when it was formed. The remaining structure, comprising the deformed underlying bedrock, is located in present-day Free State province of South Africa. It is named after the town of Vredefort, which is near its centre. The structure's central uplift is known as the Vredefort Dome. The impact structure was formed during the Paleoproterozoic Era, 2.023 billion years ago. It is the second-oldest known impact structure on Earth, after Yarrabubba.
Zapadnaya (Bilylivka) is an impact crater in Ukraine near the village of Bilylivka in the southeasternmost edge of Zhytomyr Oblast and near the border of Vinnytsia Oblast. It is situated in the northwestern part of the Ukrainian crystalline shield.

Lake Bosumtwi is the only natural lake in Ghana. It is situated within an ancient impact crater that is about 10.5 kilometres (6.5 mi) in diameter. It is about 30 km (19 mi) south-east of Kumasi, the capital of Ashanti, and is a popular recreational area. There are about 30 villages near the crater lake of Lake Bosumtwi, with a combined population of about 70,000. The most popular amongst the villages where tourists usually settle is Abono.

The Lac Wiyâshâkimî, also called the Clearwater Lakes in English and Allait Qasigialingat by the Inuit, are a pair of annular lakes on the Canadian Shield in Quebec, Canada, near Hudson Bay.
Lake Cheko is a small freshwater lake in Siberia, near the Podkamennaya Tunguska River, in what is now the Evenkiysky District of the Krasnoyarsk Krai.

Lonar Lake, also known as Lonar crater, is a notified National Geo-heritage Monument, saline, soda lake, located at Lonar in Buldhana district, Maharashtra, India. Lonar Lake is an astrobleme created by a meteorite impact during the Pleistocene Epoch. It is one of only four known hyper-velocity impact craters in basaltic rock anywhere on Earth. The other three basaltic impact structures are in southern Brazil. Lonar Lake has a mean diameter of 1.2 kilometres (3,900 ft) and is about 137 metres (449 ft) below the crater rim. The meteor crater rim is about 1.8 kilometres (5,900 ft) in diameter.

Central Island, also known as Crocodile Island, is a volcanic island located in the middle of Lake Turkana in Kenya. It is also the location of Central Island National Park, which is governed by the Kenya Wildlife Service.

Trouvelot is a crater on Mars, located in the Oxia Palus quadrangle at 16.2° north latitude and 13.1° west longitude near the crustal dichotomy in the circum-Chryse region. It is roughly located along the dichotomy between Arabia Terra to the northeast and the southernmost of the circum-Chryse outflow channels to the southwest. Trouvelot crater measures approximately 148.77 kilometres (92.44 mi) in diameter and was named after Étienne Léopold Trouvelot, a French astronomer (1827–1895). The name was adopted by IAU's Working Group for Planetary System Nomenclature in 1973.

Tikhonravov is a large, eroded crater in the Arabia quadrangle of Mars. It is 344 kilometres (214 mi) in diameter and was named after Mikhail Tikhonravov, a Russian rocket scientist. Tikhonravov is believed to have once held a giant lake that drained into the 4,500-kilometre-long (2,800 mi) Naktong-Scamander-Mamers lake-chain system. An inflow and outflow channel has been identified. Many craters once contained lakes.
The Bow City crater is a potential meteorite impact crater located in southern Alberta, Canada.


















