
Ephedraceae is a family of gymnosperms belonging to Gnetophyta, it contains only a single extant genus, Ephedra, as well as a number of extinct genera from the Early Cretaceous.

The Cupedidae are a small family of beetles, notable for the square pattern of "windows" on their elytra, which give the family their common name of reticulated beetles.

Glaresis is a genus of beetles, sometimes called "Enigmatic scarab beetles", in its own family, the Glaresidae. It is closely related to, and was formerly included in, the family Scarabaeidae. Although its members occur in arid and sandy areas worldwide, only the nocturnal adults have ever been collected, and both the larvae and biology of Glaresis are as yet unknown. Due to their narrow habitat associations, a great number of these species occur in extremely limited geographic areas, and are accordingly imperiled by habitat destruction.

Snakeflies are a group of predatory insects comprising the order Raphidioptera with two extant families: Raphidiidae and Inocelliidae, consisting of roughly 260 species. In the past, the group had a much wider distribution than it does now; snakeflies are found in temperate regions worldwide but are absent from the tropics and the Southern Hemisphere. Recognisable representatives of the group first appeared during the Early Jurassic. They are a relict group, having reached their apex of diversity during the Cretaceous before undergoing substantial decline.

Pelecinidae is a family of parasitic wasps in the superfamily Proctotrupoidea. It contains only one living genus, Pelecinus, with three species known from the Americas. The earliest fossil species are known from the Jurassic, and the group was highly diverse during the Cretaceous. Members of Pelecinus are parasitic on larval beetles, flies, green lacewings, and sawflies.

Coptoclavidae is an extinct family of aquatic beetles in the suborder Adephaga. The Coptoclavidae lived from the Late Triassic to the Early Cretaceous. Coptoclavidae is a member of the adephagan clade Dytiscoidea, which contains other aquatic beetles. Suggested reasons for their extinction to include the rise of teleost fish, or competition with Gyrinidae and Dytiscidae, which possess defensive secretions and sucking channels in the mandibles of larvae, which coptoclavids likely lacked. It has been suggested that the genus Timarchopsis and the subfamily Timarchopsinae are only distantly related to other coptoclavids based on cladistic analysis, with Timarchopsis being more closely related to geadephagans like carabids and trachypachids instead. Another study also suggested similarly for Coptoclavisca and possibly other coptoclaviscines.

The Ommatidae are a family of beetles in the suborder Archostemata. The Ommatidae are considered the extant beetle family that has most ancestral characteristics. There are only seven extant species, confined to Australia and South America. However, the geographical distribution was much wider during the Mesozoic spanning across Eurasia and Australia, suggesting that they were widespread on Pangea. So far, over 26 extinct genera containing over 170 species of these beetles have been described. Three extant genera have been assigned to this family: Omma,Tetraphalerus and Beutelius. The family is considered to be a subfamily of Cupedidae by some authors, but have been found to be more closely related to Micromalthidae in molecular phylogenies. A close relationship with Micromalthidae is supported by several morphological characters, including those of the mandibles and male genitalia. Due to their rarity, their ecology is obscure, it is likely that their larvae feed on deadwood.
Eolepidopterigoidea is an extinct superfamily of moths, containing the single family Eolepidopterigidae, although the genus Undopterix is sometimes placed in a separate family Undopterigidae. The type-genus of the family is Eolepidopterix.
Protorabinae is an extinct subfamily of beetles in the family Carabidae. It contains 36 species in 13 genera, all extinct.
Brochocoleus is an extinct genus of beetles in the family Ommatidae, known from the Early Jurassic to the Early Late Cretaceous. 9 species are currently recognised, with many species being reassigned to other genera by Kirejtshuk's major systematic revision in 2020.

Cionocoleus is an extinct genus of beetles in the family Ommatidae.

Tetraphalerus is a genus of beetles in the family Ommatidae, It is currently known from two extant species native to South America and several fossil species from the Jurassic and Cretaceous of Asia.

Mesoraphidiidae is an extinct family of snakeflies in the suborder Raphidiomorpha. The family lived from the Late Jurassic through the Late Cretaceous and is known from twenty-five genera. Mesoraphidiids have been found as both compression fossils and as inclusions in amber. The family was first proposed in 1925 by the Russian paleoentomologist Andrey Vasilyevich Martynov based on Upper Jurassic fossils recovered in Kazakhstan. The family was expanded in 2002 by the synonymizing of several other proposed snakefly families. The family was divided into three subfamilies and one tribe in a 2011 paper, further clarifying the relationships of the included genera.

Artematopodidae is a family of soft-bodied plant beetles in the superfamily Elateroidea. They are mostly found in understory forest foliage. The life history of the group is obscure, larvae of the genera Eurypogon and Macropogon likely feed on moss, while the larvae of Artematopus have been fed insect remains. The oldest fossils of the family date to the Middle Jurassic.
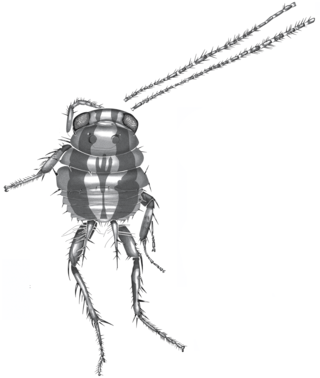
Blattulidae is an extinct family of cockroaches known from the Triassic to the Late Cretaceous. Their distinguishing characteristics include "forewing has long Sc, regular venation with distinct intercalaries and hindwing has simple CuP, branched A1."
Diluticupes is an extinct genus of beetle in the family Ommatidae.

Pareuryomma is an extinct genus of ommatid beetle. It is known from three species, P. angustum, P. cardiobasis and P. tylodes, all known from the Aptian aged Yixian Formation of China. The genus was first described in 2012, and formerly included the species Pareuryomma ancistrodonta from the Middle Jurassic Jiulongshan Formation, China, which was transferred to the genus Omma in 2020. The species P. angustum was formerly thought to be part of Brochocoleus. The genus is characterised by "slender body, long and subparallelsided or slightly narrowed head with moderately prominent eyes and more or less prominent temples, narrow pronotum with more or less explanate lateral carinae, elytra with the veins more or less well expressed and independently ending on Sc, large cells more or less arranged in rows on disc and moderately widely explanate sides of the elytra, and abdominal ventrites co-planar."
Yuripopovinidae is an extinct family of Coreoidea Hemipteran true bugs. Member species are known from the Early Cretaceous and early Late Cretaceous of Asia and northern Gondwana. Among the distinguishing characters are "the hemelytral costal vein apically much thickened and pterostigma-like, the corium with two large cells separated by one longitudinal straight vein." Dehiscensicoridae, described from the Yixian Formation of China has been deemed a junior synonym of Yuripopovinidae per Du et al. (2019). The family was named after Russian paleoentomologist Yuri Alexandrovich Popov.

Procercopidae is an extinct family of froghoppers. They are known from the Early Jurassic to early Late Cretaceous of Eurasia. They are one of two main families of Mesozoic froghoppers alongside Sinoalidae. Procercopidae are considered to be the ancestral group from which modern froghoppers are derived.

Eremochaetidae is an extinct family of brachyceran flies known from the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods of Asia. It is part of the extinct superfamily Archisargoidea. The morphology of the ovipositor of the only 3 dimensionally preserved genus Zhenia was initially interpreted as evidence of being an endoparasitoid of arthropods, however a subsequent study suggested that the ovipositor was used to deposit its eggs in plant material, similar to members of Tephritoidea. In a phylogenetic analysis, Ermochaetidae was found to be monophyletic, surrounded by a paraphyletic Archisargidae.















