
A mold or mould is one of the structures that certain fungi can form. The dust-like, colored appearance of molds is due to the formation of spores containing fungal secondary metabolites. The spores are the dispersal units of the fungi. Not all fungi form molds. Some fungi form mushrooms; others grow as single cells and are called microfungi.

Zygomycota, or zygote fungi, is a former division or phylum of the kingdom Fungi. The members are now part of two phyla: the Mucoromycota and Zoopagomycota. Approximately 1060 species are known. They are mostly terrestrial in habitat, living in soil or on decaying plant or animal material. Some are parasites of plants, insects, and small animals, while others form symbiotic relationships with plants. Zygomycete hyphae may be coenocytic, forming septa only where gametes are formed or to wall off dead hyphae. Zygomycota is no longer recognised as it was not believed to be truly monophyletic.
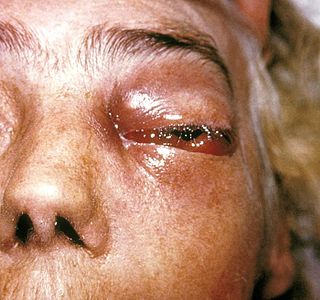
Zygomycosis is the broadest term to refer to infections caused by bread mold fungi of the zygomycota phylum. However, because zygomycota has been identified as polyphyletic, and is not included in modern fungal classification systems, the diseases that zygomycosis can refer to are better called by their specific names: mucormycosis, phycomycosis and basidiobolomycosis. These rare yet serious and potentially life-threatening fungal infections usually affect the face or oropharyngeal cavity. Zygomycosis type infections are most often caused by common fungi found in soil and decaying vegetation. While most individuals are exposed to the fungi on a regular basis, those with immune disorders (immunocompromised) are more prone to fungal infection. These types of infections are also common after natural disasters, such as tornadoes or earthquakes, where people have open wounds that have become filled with soil or vegetative matter.

The Mucorales is the largest and best-studied order of zygomycete fungi. Members of this order are sometimes called pin molds. The term mucormycosis is now preferred for infections caused by molds belonging to the order Mucorales.

Mucor is a microbial genus of approximately 40 species of molds in the family Mucoraceae. Species are commonly found in soil, digestive systems, plant surfaces, some cheeses like Tomme de Savoie, rotten vegetable matter and iron oxide residue in the biosorption process.
Rhizopus arrhizus is a fungus of the family Mucoraceae, characterized by sporangiophores that arise from nodes at the point where the rhizoids are formed and by a hemispherical columella. It is the most common cause of mucormycosis in humans and occasionally infects other animals.

Apophysomyces is a genus of filamentous fungi that are commonly found in soil and decaying vegetation. Species normally grow in tropical to subtropical regions.

Mucor mucedo, commonly known as the common pinmould, is a fungal plant pathogen and member of the phylum Mucoromycota and the genus Mucor. Commonly found on soil, dung, water, plants and moist foods, Mucor mucedo is a saprotrophic fungus found world-wide with 85 known strains. It is often mistaken for Rhizopus rots on fruits due to similar mould growth shape and colour. Contrastingly, however, Mucor mucedo is found to grow on a wide range of stored grains and plants, including cucumber and tomato. Discovered in Italy in 1729 by P.A. Micheli and later noted by Carl Linnaeus in 1753 in the Species Plantarum, Mucor mucedo was originally classified as Mucor vulgaris by Micheli but later classified synonymous under name Mucor mucedo. The species was redescribed as Ascophora mucedo by H.J. Tode in 1790 but this type resided in a stoloniferous habitat and was later made the type of new genus Rhizopus.

Phycomycetes is an obsolete polyphyletic taxon for certain fungi with aseptate hyphae. It is used in the Engler system. Asexual reproduction takes place by zoospores (motile) or by Aplanospores (non-motile). These spores are endogenously produced in sporangium. A zygospore is formed by fusion of two gametes. These gametes are similar in morphology (isogamous) or dissimilar.
Mucor amphibiorum is a fungus found in Australia that causes infections in amphibians and platypuses. Because M. amphibiorum belongs to the genus Mucor, the infection is classified as a form of mucormycosis. The fungus was first reported from a German zoo in 1972 where it caused disease in a species of green tree frog that was imported from Australia and infected frogs, toads, and salamanders in neighboring exhibits. It is most commonly found in frogs and toads in Queensland, New South Wales, and Northern Territory, and in platypuses in Tasmania.

Spinellus fusiger, commonly known as bonnet mold, is a species of fungus in the phylum Mucoromycota. It is a pin mold that is characterized by erect sporangiophores that are simple in structure, brown or yellowish-brown in color, and with branched aerial filaments that bear the zygospores. It grows as a parasitic mold on mushrooms, including several species from the genera Mycena, including M. haematopus, M. pura, M. epipterygia, M. leptocephala, and various Collybia species, such as C. alkalivirens, C. luteifolia, C. dryophila, and C. butyracea. It has also been found growing on agaric species in Amanita, Gymnopus, and Hygrophorus.

Jiuqu, also simply known as qu is a type of dried fermentation starter used in the production of traditional Chinese alcoholic beverages. The word jiuqu specifically refers to a type of yeast used to make alcohol such as huangjiu, baijiu and jiuniang.

Apophysomyces variabilis is an emerging fungal pathogen that can cause serious and sometimes fatal infection in humans. This fungus is a soil-dwelling saprobe with tropical to subtropical distribution. It is a zygomycete that causes mucormycosis, an infection in humans brought about by fungi in the order Mucorales. Infectious cases have been reported globally in locations including the Americas, Southeast Asia, India, and Australia. Apophysomyces variabilis infections are not transmissible from person to person.
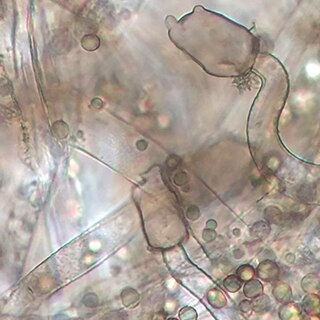
Mucor plumbeus is a fungus in the family Mucoraceae that is very common, abundant and distributed worldwide. Mucor plumbeus is not known to be a plant or animal pathogen; however it is able to elicit an immune response in humans by activating the complement system. This species is commonly found in various types of soils over a range of pH, although alkaline soils seem more conducive to its growth. It is also known from the roots of wheat, oat and barley. In addition, M. plumbeus is a common fungal contaminant of indoor built environments. This species shares many similarities with M. racemosus, another fungus that belongs to the family Mucoraceae which is known to cause mucormycosis. Mucor plumbeus is a common spoilage agent of cheese, apples, apple cider and yogurt.

Rhizopus oryzae is a filamentous heterothallic microfungus that occurs as a saprotroph in soil, dung, and rotting vegetation. This species is very similar to Rhizopus stolonifer, but it can be distinguished by its smaller sporangia and air-dispersed sporangiospores. It differs from R. oligosporus and R. microsporus by its larger columellae and sporangiospores. The many strains of R. oryzae produce a wide range of enzymes such as carbohydrate digesting enzymes and polymers along with a number of organic acids, ethanol and esters giving it useful properties within the food industries, bio-diesel production, and pharmaceutical industries. It is also an opportunistic pathogen of humans causing mucormycosis.

Syzygites is a monotypic genus in Zygomycota. The sole described species is Syzygites megalocarpus, which was the first fungus for which sex was reported and the main homothallic representative in the research that allowed for the classification of fungi as homothallic or heterothallic. It is also the fungus from which the term "zygospore" was coined.
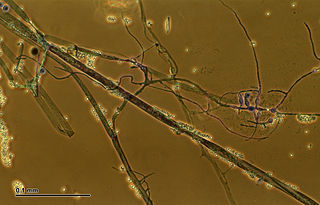
Thamnidium is a genus of fungi belonging to the family Mucoraceae.

Mucoromycota is a division within the kingdom fungi. It includes a diverse group of various molds, including the common bread molds Mucor and Rhizopus. It is a sister phylum to Dikarya.
Rhizopus niveus is a filamentous fungi that can be found almost anywhere in the world. It is used in industry for the production of enzymes. Rhizopus niveus was originally isolated from Qū for Jiuniang manufactured in Hangzhou, China. Similarly to other Rhizopus species, Rhizopus niveus is saprophytic and grows commonly on many organic substrates. Unlike other Rhizopus species, it has the capacity to ferment galactose.













