The macaques constitute a genus (Macaca) of gregarious Old World monkeys of the subfamily Cercopithecinae. The 23 species of macaques inhabit ranges throughout Asia, North Africa, and Europe. Macaques are principally frugivorous, although their diet also includes seeds, leaves, flowers, and tree bark. Some species such as the long-tailed macaque will supplement their diets with small amounts of meat from shellfish, insects, and small mammals. On average, a southern pig-tailed macaque in Malaysia eats about 70 large rats each year. All macaque social groups are arranged around dominant matriarchs.

The crab-eating macaque, also known as the long-tailed macaque and referred to as the cynomolgus monkey in laboratories, is a cercopithecine primate native to Southeast Asia. A species of macaque, the crab-eating macaque has a long history alongside humans. The species has been alternately seen as an agricultural pest, a sacred animal, and, more recently, the subject of medical experiments.

The rhesus macaque, colloquially rhesus monkey, is a species of Old World monkey. There are between six and nine recognised subspecies that are split between two groups, the Chinese-derived and the Indian-derived. Generally brown or grey in colour, it is 47–53 cm (19–21 in) in length with a 20.7–22.9 cm (8.1–9.0 in) tail and weighs 5.3–7.7 kg (12–17 lb). It is native to South, Central, and Southeast Asia and has the widest geographic range of all non-human primates, occupying a great diversity of altitudes and a great variety of habitats, from grasslands to arid and forested areas, but also close to human settlements. Feral colonies are found in the United States, thought to be either released by humans or escapees after hurricanes destroyed zoo and wildlife park facilities.

Southeast Sulawesi, is a province on the island of Sulawesi, forming the southeastern peninsula of that island, together with a number of substantial offshore islands such as Buton, Muna, Kabaena and Wawonii, together with many smaller islands. It is bordered by South Sulawesi and Central Sulawesi to the north, sharing a maritime border with Maluku and North Maluku to the east and East Nusa Tenggara to the south, as well a very narrow maritime border with East Timor to the south. The capital is the city of Kendari, on the east coast of the peninsula.

The Barbary macaque, also known as Barbary ape, is a macaque species native to the Atlas Mountains of Algeria, Tunisia and Morocco, along with a small introduced population in Gibraltar. It is the type species of the genus Macaca. The species is of particular interest because males play an atypical role in rearing young. Because of uncertain paternity, males are integral to raising all infants. Generally, Barbary macaques of both sexes and all ages contribute in alloparental care of young.

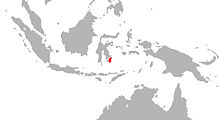
The Moor macaque is a macaque monkey with brown/black body fur with a pale rump patch and pink bare skin on the rump. It has ischial callosities, which are oval-shaped. It is about 50–58.5 cm long, and eats figs, bamboo seeds, buds, sprouts, invertebrates and cereals in tropical rainforests. It is sometimes called "dog-ape" because of its dog-like muzzle, although it is no more closely related to apes than any other Old World monkey is. It is endemic to the island of Sulawesi in Indonesia, which is an important biodiversity hotspot.

The lion-tailed macaque, also known as the wanderoo, is an Old World monkey endemic to the Western Ghats of South India.

The Celebes crested macaque, also known as the crested black macaque, Sulawesi crested macaque, or the black ape, is an Old World monkey that lives in the Tangkoko reserve in the north-eastern tip of the Indonesian island of Sulawesi (Celebes), as well as on smaller neighbouring islands.

The Assam macaque or Assamese macaque is a macaque of the Old World monkey family native to South and Southeast Asia. Since 2008, it has been listed as Near Threatened on the IUCN Red List, as it is experiencing significant declines due to poaching, habitat degradation, and fragmentation.

The booted macaque is a macaque of the Sulawesi Island, Indonesia. This Old World monkey is diurnal and spends most of the day in the trees. It is 50–59 cm long plus a tail of 35–40 cm.

The bonnet macaque, also known as zati, is a species of macaque endemic to southern India. Its distribution is limited by the Indian Ocean on three sides and the Godavari and Tapti Rivers, along with its related competitor the rhesus macaque in the north. Land use changes in the last few decades have resulted in changes in its distribution boundaries with the rhesus macaque, raising concern for its status in the wild.

The Formosan rock macaque, also known as the Formosan rock monkey or Taiwanese macaque, is a macaque endemic to the island of Taiwan, which has also been introduced to Japan. Besides humans, Formosan rock macaques are the only native primates living in Taiwan. The species was first described by Robert Swinhoe in 1862.

The Heck's macaque is a macaque of Sulawesi, Indonesia. This Old World monkey is diurnal.

The Nicobar long-tailed macaque is a subspecies of the crab-eating macaque, endemic to the Nicobar Islands in the Bay of Bengal. This primate is found on three of the Nicobar Islands—Great Nicobar, Little Nicobar and Katchal—in biome regions consisting of tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests.

The Sulawesi hornbill, also known as the Sulawesi tarictic hornbill, Temminck's hornbill or Sulawesi dwarf hornbill, is a relatively small, approximately 45 cm (18 in) long, black hornbill. The male has a yellow face and throat, and yellowish horn bill with black markings. The female has all-black plumage and a darker bill.

The southern pig-tailed macaque, also known as the Sundaland pig-tailed macaque and the Sunda pig-tailed macaque, is a medium-sized macaque that lives in Sundaland, southern Thailand, Malaysia, and Indonesia. It is known locally as berok.

The Sulawesi myna is a species of starling in the family Sturnidae. It is endemic to Sulawesi, Indonesia. Its natural habitat is subtropical or tropical moist lowland forests.

The Tonkean black macaque or Tonkean macaque is a species of primate in the family Cercopithecidae. It is endemic to central Sulawesi and the nearby Togian Islands in Indonesia. It is threatened by habitat loss. Widespread mining in central Sulawesi is believed to exacerbating the problems of habitat loss.

The Tibetan macaque, also known as the Chinese stump-tailed macaque or Milne-Edwards' macaque, is a macaque species found from eastern Tibet east to Guangdong and north to Shaanxi in China. It has also been reported from northeastern India. This species lives in subtropical forests at elevations from 800 to 2,500 m above sea level.

The Sulawesi lowland rain forests is a tropical moist forest ecoregion in Indonesia. The ecoregion includes the lowlands of Sulawesi and neighboring islands.