
A pearl is a hard, glistening object produced within the soft tissue of a living shelled mollusk or another animal, such as fossil conulariids. Just like the shell of a mollusk, a pearl is composed of calcium carbonate in minute crystalline form, which has deposited in concentric layers. The ideal pearl is perfectly round and smooth, but many other shapes, known as baroque pearls, can occur. The finest quality of natural pearls have been highly valued as gemstones and objects of beauty for many centuries. Because of this, pearl has become a metaphor for something rare, fine, admirable and valuable.

The Wadden Sea is an intertidal zone in the southeastern part of the North Sea. It lies between the coast of northwestern continental Europe and the range of low-lying Frisian Islands, forming a shallow body of water with tidal flats and wetlands. It has a high biological diversity and is an important area for both breeding and migrating birds. In 2009, the Dutch and German parts of the Wadden Sea were inscribed on UNESCO's World Heritage List and the Danish part was added in June 2014.

Mussel is the common name used for members of several families of bivalve molluscs, from saltwater and freshwater habitats. These groups have in common a shell whose outline is elongated and asymmetrical compared with other edible clams, which are often more or less rounded or oval.

Harlingen is a municipality and a city in the northern Netherlands, in the province of Friesland.

The Schleswig-Holstein Wadden Sea National Park is a national park in the Schleswig-Holstein area of the German Wadden Sea. It was founded by the Parliament of Schleswig-Holstein on 1 October 1985 by the National Park Act of 22 July 1985 and expanded significantly in 1999. Together with the Lower Saxon Wadden Sea National Park, the Hamburg Wadden Sea National Park and those parts of Elbe estuary which are not nature reserves, it forms the German part of the Wadden Sea.

The Frisian Islands, also known as the Wadden Islands or the Wadden Sea Islands, form an archipelago at the eastern edge of the North Sea in northwestern Europe, stretching from the northwest of the Netherlands through Germany to the west of Denmark. The islands shield the mudflat region of the Wadden Sea from the North Sea.
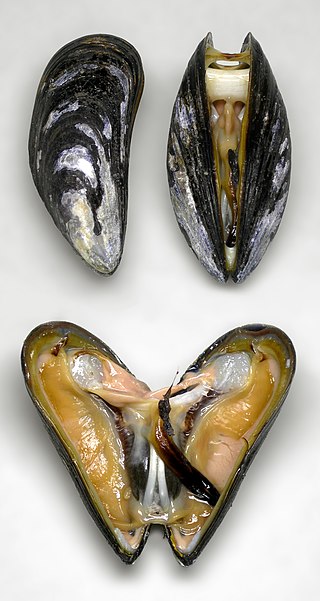
The blue mussel, also known as the common mussel, is a medium-sized edible marine bivalve mollusc in the family Mytilidae, the mussels. Blue mussels are subject to commercial use and intensive aquaculture. A species with a large range, empty shells are commonly found on beaches around the world.

The round goby is a euryhaline bottom-dwelling species of fish of the family Gobiidae. It is native to Central Eurasia, including the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea. Round gobies have established large non-native populations in the Baltic Sea, several major Eurasian rivers, and the North American Great Lakes.

The German Bight is the southeastern bight of the North Sea bounded by the Netherlands and Germany to the south, and Denmark and Germany to the east. To the north and west it is limited by the Dogger Bank. The Bight contains the Frisian and Danish Islands. The Wadden Sea is approximately ten to twelve kilometres wide at the location of the German Bight. The Frisian islands and the nearby coastal areas are collectively known as Frisia. The southern portion of the bight is also known as the Heligoland Bight. Between 1949 and 1956 the BBC Sea Area Forecast used "Heligoland" as the designation for the area now referred to as German Bight.

Perna canaliculus, the New Zealand green-lipped mussel, also known as the New Zealand mussel, the greenshell mussel, kuku, and kutai, is a bivalve mollusc in the family Mytilidae. P. canaliculus has economic importance as a cultivated species in New Zealand.

Yerseke is a village situated on the southern shore of the Oosterschelde estuary in the Dutch province of Zeeland. A separate municipality until 1970, it today forms part of the municipality of Reimerswaal. As of 2010 Yerseke had a recorded population of 6,695 inhabitants, living in 2,680 households.

The pea crab, Pinnotheres pisum, is a small crab in the family Pinnotheridae that lives as a parasite in oysters, clams, mussels, and other species of bivalves.

Perna perna, the brown mussel, is an economically important mussel, a bivalve mollusc belonging to the family Mytilidae. It is harvested as a food source but is also known to harbor toxins and cause damage to marine structures. It is native to the waters of Africa, Europe, and South America and was introduced in the waters of North America.

Wadden Sea National Park was designated a Danish national park on 17 January 2008, effective 2010. The Wadden Sea National Park is - except Greenland by far the largest of Denmark's national parks and covers the Danish part of the Wadden Sea from Ho Bugt to the German border, and includes the islands of Fanø, Mandø and Rømø, as well as Skallingen, the Varde Å valley, and many of the marshlands of Tjæreborgmarsken, Ribemarsken, Margrethekogen and De Ydre Diger in Tøndermarsken.

The Lower Saxon Wadden Sea National Park was established in 1986 and embraces the East Frisian Islands, mudflats and salt marshes between the Bay of Dollart on the border with the Netherlands in the west and Cuxhaven as far as the Outer Elbe shipping channel in the east. The national park has an area of about 345,800 hectares (1,335 sq mi). The National Park organisation is located in Wilhelmshaven. In June 2009, the National Park became a UNESCO World Heritage Site along with the Schleswig-Holstein Wadden Sea and the Dutch Wadden Sea, highlighting its unique intertidal ecosystem and high biodiversity.
A sandplain is an area where the soil is sand deposited from elsewhere by processes such as wind or ocean, rather than direct weathering of bedrock.

Stylophora pistillata, commonly known as hood coral or smooth cauliflower coral, is a species of stony coral in the family Pocilloporidae. It is native to the Indo-Pacific region and is commonly used in scientific investigations.
Pseudoklossia is a genus in the phylum Apicomplexa. Species in this genus infect marine molluscs, although one species infects in an ascidian worm. The life cycle is heteroxenous.
Sabine Dittmann is an Australian-based marine biologist and expert on the ecology of tidal flats. She is Associate Professor of Marine Biology at Flinders University in Adelaide, and is President of the Australian Marine Sciences Association.
Mytilicola orentalis is an intestinal copepod parasite of bivalves with a direct life cycle. It is native to the waters around Japan and was first described in the Japanese Sea and was introduced to Europe in the 1960s and 70's with oyster imports. Since then it has also been observed in the Wadden and the Baltic Sea. It has a wide range of host species in both its native range and in Europe.















