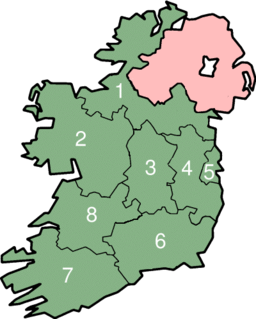
The Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics (NUTS) is a geocode standard for referencing the subdivisions of Ireland for statistical purposes. [1] The standard is developed and regulated by the European Union. [2] The NUTS standard is instrumental in delivering the European Union's Structural Funds. The NUTS code for Ireland is IE and a hierarchy of three levels is established by Eurostat. Below these is a further levels of geographic organisation - the local administrative unit (LAU). In Ireland, the LAUs are electoral divisions.
Standardization or standardisation is the process of implementing and developing technical standards based on the consensus of different parties that include firms, users, interest groups, standards organizations and governments Standardization can help to maximize compatibility, interoperability, safety, repeatability, or quality. It can also facilitate commoditization of formerly custom processes. In social sciences, including economics, the idea of standardization is close to the solution for a coordination problem, a situation in which all parties can realize mutual gains, but only by making mutually consistent decisions. This view includes the case of "spontaneous standardization processes", to produce de facto standards.

Ireland, also known as the Republic of Ireland, is a country in north-western Europe occupying 26 of 32 counties of the island of Ireland. The capital and largest city is Dublin, which is located on the eastern side of the island. Around a third of the country's population of 4.8 million people resides in the greater Dublin area. The sovereign state shares its only land border with Northern Ireland, a part of the United Kingdom. It is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, with the Celtic Sea to the south, St George's Channel to the south-east, and the Irish Sea to the east. It is a unitary, parliamentary republic. The legislature, the Oireachtas, consists of a lower house, Dáil Éireann, an upper house, Seanad Éireann, and an elected President who serves as the largely ceremonial head of state, but with some important powers and duties. The head of government is the Taoiseach, who is elected by the Dáil and appointed by the President; the Taoiseach in turn appoints other government ministers.

The European Union (EU) is a political and economic union of 28 member states that are located primarily in Europe. It has an area of 4,475,757 km2 (1,728,099 sq mi) and an estimated population of about 513 million. The EU has developed an internal single market through a standardised system of laws that apply in all member states in those matters, and only those matters, where members have agreed to act as one. EU policies aim to ensure the free movement of people, goods, services and capital within the internal market, enact legislation in justice and home affairs and maintain common policies on trade, agriculture, fisheries and regional development. For travel within the Schengen Area, passport controls have been abolished. A monetary union was established in 1999 and came into full force in 2002 and is composed of 19 EU member states which use the euro currency.