
A bacteriophage, also known informally as a phage, is a virus that infects and replicates within bacteria and archaea. The term was derived from "bacteria" and the Greek φαγεῖν, meaning "to devour". Bacteriophages are composed of proteins that encapsulate a DNA or RNA genome, and may have structures that are either simple or elaborate. Their genomes may encode as few as four genes and as many as hundreds of genes. Phages replicate within the bacterium following the injection of their genome into its cytoplasm.
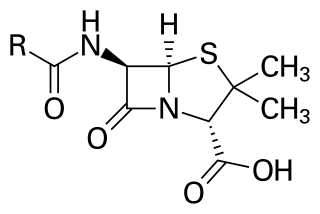
Penicillins are a group of β-lactam antibiotics originally obtained from Penicillium moulds, principally P. chrysogenum and P. rubens. Most penicillins in clinical use are synthesised by P. chrysogenum using deep tank fermentation and then purified. A number of natural penicillins have been discovered, but only two purified compounds are in clinical use: penicillin G and penicillin V. Penicillins were among the first medications to be effective against many bacterial infections caused by staphylococci and streptococci. They are still widely used today for various bacterial infections, though many types of bacteria have developed resistance following extensive use.

Ribosomes are macromolecular machines, found within all cells, that perform biological protein synthesis. Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order specified by the codons of messenger RNA molecules to form polypeptide chains. Ribosomes consist of two major components: the small and large ribosomal subunits. Each subunit consists of one or more ribosomal RNA molecules and many ribosomal proteins. The ribosomes and associated molecules are also known as the translational apparatus.
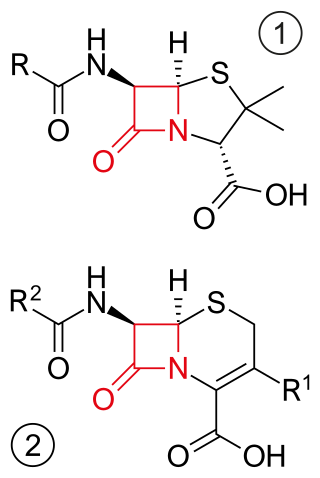
β-Lactam antibiotics are antibiotics that contain a β-lactam ring in their chemical structure. This includes penicillin derivatives (penams), cephalosporins and cephamycins (cephems), monobactams, carbapenems and carbacephems. Most β-lactam antibiotics work by inhibiting cell wall biosynthesis in the bacterial organism and are the most widely used group of antibiotics. Until 2003, when measured by sales, more than half of all commercially available antibiotics in use were β-lactam compounds. The first β-lactam antibiotic discovered, penicillin, was isolated from a strain of Penicillium rubens.

In molecular biology, molecular chaperones are proteins that assist the conformational folding or unfolding of large proteins or macromolecular protein complexes. There are a number of classes of molecular chaperones, all of which function to assist large proteins in proper protein folding during or after synthesis, and after partial denaturation. Chaperones are also involved in the translocation of proteins for proteolysis.

Helix-turn-helix is a DNA-binding domain (DBD). The helix-turn-helix (HTH) is a major structural motif capable of binding DNA. Each monomer incorporates two α helices, joined by a short strand of amino acids, that bind to the major groove of DNA. The HTH motif occurs in many proteins that regulate gene expression. It should not be confused with the helix–loop–helix motif.

In evolutionary biology, conserved sequences are identical or similar sequences in nucleic acids or proteins across species, or within a genome, or between donor and receptor taxa. Conservation indicates that a sequence has been maintained by natural selection.
Within the field of molecular biology, a protein-fragment complementation assay, or PCA, is a method for the identification and quantification of protein–protein interactions. In the PCA, the proteins of interest are each covalently linked to fragments of a third protein. Interaction between the bait and the prey proteins brings the fragments of the reporter protein in close proximity to allow them to form a functional reporter protein whose activity can be measured. This principle can be applied to many different reporter proteins and is also the basis for the yeast two-hybrid system, an archetypical PCA assay.

Filamentation is the anomalous growth of certain bacteria, such as Escherichia coli, in which cells continue to elongate but do not divide. The cells that result from elongation without division have multiple chromosomal copies.
Christopher Francis Higgins is a British molecular biologist, geneticist, academic and scientific advisor. He was the Vice-Chancellor of Durham University from 2007 to 2014. He took early retirement on 30 September 2014, following a discussion at Senate on limiting the powers of the Vice Chancellor. He was previously the director of the MRC Clinical Sciences Centre and Head of Division in the Faculty of Medicine at Imperial College London.

Beta-lactamases are a family of enzymes involved in bacterial resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics. In bacterial resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics, the bacteria have beta-lactamase which degrade the beta-lactam rings, rendering the antibiotic ineffective. However, with beta-lactamase inhibitors, these enzymes on the bacteria are inhibited, thus allowing the antibiotic to take effect. Strategies for combating this form of resistance have included the development of new beta-lactam antibiotics that are more resistant to cleavage and the development of the class of enzyme inhibitors called beta-lactamase inhibitors. Although β-lactamase inhibitors have little antibiotic activity of their own, they prevent bacterial degradation of beta-lactam antibiotics and thus extend the range of bacteria the drugs are effective against.

Dipeptidase 1 (DPEP1), or renal dipeptidase, is a membrane-bound glycoprotein responsible for hydrolyzing dipeptides. It is found in the microsomal fraction of the porcine kidney cortex. It exists as a disulfide-linked homodimer that is glygosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored to the renal brush border of the kidney. The active site on each homodimer is made up of a barrel subunit with binuclear zinc ions that are bridged by the Gly125 side-chain located at the bottom of the barrel.

Archaea is a domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms lack cell nuclei and are therefore prokaryotic. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria, but this term has fallen out of use.

The metallo-β-lactamase (MBL) superfamily constitutes a group of proteins found in all domains of life that share a characteristic αββα fold with the ability to bind transition metal ions. Such metal binding sites may have divalent transition metal ions like Zn(II), Fe(II)/Fe(III) and Mn(II), and are located at the bottom of a wide cleft able to accommodate diverse substrates. The name was adopted after the first members of the superfamily to be studied experimentally: a group of zinc-dependent hydrolytic enzymes conferring bacterial resistance to β-lactam antibiotics. These zinc-β-lactamases (ZBLs) inactivate β-lactam antibiotics through hydrolysis of the β-lactam ring. Early studies on MBLs were conducted on the enzyme βLII isolated from strain 569/H/9 of Bacillus cereus. It was named βLII because it was the second β-lactamase shown to be produced by the bacterium; the first one, βLI, was a non-metallic β-lactamase, i.e., insensitive to inhibition with EDTA.
Cephalosporins are a broad class of bactericidal antibiotics that include the β-lactam ring and share a structural similarity and mechanism of action with other β-lactam antibiotics. The cephalosporins have the ability to kill bacteria by inhibiting essential steps in the bacterial cell wall synthesis which in the end results in osmotic lysis and death of the bacterial cell. Cephalosporins are widely used antibiotics because of their clinical efficiency and desirable safety profile.
Radical SAM enzymes belong to a superfamily of enzymes that use an iron-sulfur cluster (4Fe-4S) to reductively cleave S-adenosyl-L-methionine (SAM) to generate a radical, usually a 5′-deoxyadenosyl radical (5'-dAdo), as a critical intermediate. These enzymes utilize this radical intermediate to perform diverse transformations, often to functionalize unactivated C-H bonds. Radical SAM enzymes are involved in cofactor biosynthesis, enzyme activation, peptide modification, post-transcriptional and post-translational modifications, metalloprotein cluster formation, tRNA modification, lipid metabolism, biosynthesis of antibiotics and natural products etc. The vast majority of known radical SAM enzymes belong to the radical SAM superfamily, and have a cysteine-rich motif that matches or resembles CxxxCxxC. Radical SAM enzymes comprise the largest superfamily of metal-containing enzymes.
Gabriel Waksman FMedSci, FRS, is Courtauld professor of biochemistry and molecular biology at University College London (UCL), and professor of structural and molecular biology at Birkbeck College, University of London. He is the director of the Institute of Structural and Molecular Biology (ISMB) at UCL and Birkbeck, head of the Department of Structural and Molecular Biology at UCL, and head of the Department of Biological Sciences at Birkbeck.

Peter Malcolm Colman is the head of the structural biology division at the Walter and Eliza Hall Institute of Medical Research in Melbourne, Australia.
Gerard D. Wright, PhD, FRSC, is a professor in the Department of Biochemistry and Biomedical Sciences, and Canada Research Chair in Antibiotic Biochemistry at McMaster University who studies chemical compounds that can combat antibiotic resistance in bacteria. He is also an Associate member of the Departments of Chemistry and Chemical Biology and Pathology and Molecular Medicine. Wright was Chair of the Department of Biochemistry and Biomedical Sciences from 2001 to 2007. He was the Director of McMaster's Michael G. DeGroote Institute for Infectious Disease Research from 2007 to 2022. He is currently the executive director of Canada's Global Nexus for Pandemics and Biological Threats. He is also founding director of the McMaster Antimicrobial Research Centre, and co-founder of the McMaster High Throughput Screening Facility.
Christopher Joseph Schofield is a Professor of Chemistry at the University of Oxford and a Fellow of the Royal Society. Chris Schofield is a professor of organic chemistry at the University of Oxford, Department of Chemistry and a Fellow of Hertford College. Schofield studied functional, structural and mechanistic understanding of enzymes that employ oxygen and 2-oxoglutarate as a co-substrate. His work has opened up new possibilities in antibiotic research, oxygen sensing, and gene regulation.













