Related Research Articles

Kyanite is a typically blue aluminosilicate mineral, found in aluminium-rich metamorphic pegmatites and sedimentary rock. It is the high pressure polymorph of andalusite and sillimanite, and the presence of kyanite in metamorphic rocks generally indicates metamorphism deep in the Earth's crust. Kyanite is also known as disthene or cyanite.

Schist is a medium-grained metamorphic rock showing pronounced schistosity. This means that the rock is composed of mineral grains easily seen with a low-power hand lens, oriented in such a way that the rock is easily split into thin flakes or plates. This texture reflects a high content of platy minerals, such as micas, talc, chlorite, or graphite. These are often interleaved with more granular minerals, such as feldspar or quartz.

Metamorphic rocks arise from the transformation of existing rock to new types of rock in a process called metamorphism. The original rock (protolith) is subjected to temperatures greater than 150 to 200 °C and, often, elevated pressure of 100 megapascals (1,000 bar) or more, causing profound physical or chemical changes. During this process, the rock remains mostly in the solid state, but gradually recrystallizes to a new texture or mineral composition. The protolith may be an igneous, sedimentary, or existing metamorphic rock.

Metamorphism is the transformation of existing rock to rock with a different mineral composition or texture. Metamorphism takes place at temperatures in excess of 150 °C (300 °F), and often also at elevated pressure or in the presence of chemically active fluids, but the rock remains mostly solid during the transformation. Metamorphism is distinct from weathering or diagenesis, which are changes that take place at or just beneath Earth's surface.

Petrology is the branch of geology that studies rocks and the conditions under which they form. Petrology has three subdivisions: igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary petrology. Igneous and metamorphic petrology are commonly taught together because they both contain heavy use of chemistry, chemical methods, and phase diagrams. Sedimentary petrology is, on the other hand, commonly taught together with stratigraphy because it deals with the processes that form sedimentary rock.

A pelite or metapelite is a metamorphosed fine-grained sedimentary rock, i.e. mudstone or siltstone. The term was earlier used by geologists to describe a clay-rich, fine-grained clastic sediment or sedimentary rock, i.e. mud or a mudstone, the metamorphosed version of which would technically have been a metapelite. It was equivalent to the now little-used Latin-derived term lutite. A semipelite is defined in part as having similar chemical composition but being of a crystalloblastic nature.

Greenschists are metamorphic rocks that formed under the lowest temperatures and pressures usually produced by regional metamorphism, typically 300–450 °C (570–840 °F) and 2–10 kilobars (29,000–145,000 psi). Greenschists commonly have an abundance of green minerals such as chlorite, serpentine, and epidote, and platy minerals such as muscovite and platy serpentine. The platiness gives the rock schistosity Other common minerals include quartz, orthoclase, talc, carbonate minerals and amphibole (actinolite).

A porphyroblast is a large mineral crystal in a metamorphic rock which has grown within the finer grained matrix. Porphyroblasts are commonly euhedral crystals, but can also be partly to completely irregular in shape.

Lawsonite is a hydrous calcium aluminium sorosilicate mineral with formula CaAl2Si2O7(OH)2·H2O. Lawsonite crystallizes in the orthorhombic system in prismatic, often tabular crystals. Crystal twinning is common. It forms transparent to translucent colorless, white, and bluish to pinkish grey glassy to greasy crystals. Refractive indices are nα=1.665, nβ=1.672 - 1.676, and nγ=1.684 - 1.686. It is typically almost colorless in thin section, but some lawsonite is pleochroic from colorless to pale yellow to pale blue, depending on orientation. The mineral has a Mohs hardness of 8 and a specific gravity of 3.09. It has perfect cleavage in two directions and a brittle fracture.
Alfred Edward "Ted" Ringwood FRS FAA was an Australian experimental geophysicist and geochemist, and the 1988 recipient of the Wollaston Medal.
Geothermobarometry is the science of measuring the previous pressure and temperature history of a metamorphic or intrusive igneous rocks. Geothermobarometry is a combination of geobarometry, where a pressure of mineral formation is resolved, and geothermometry where a temperature of formation is resolved.
Sir Robert Keith O'Nions FRS HonFREng, is a British scientist and ex-President & Rector of Imperial College London. He is the former Director General of the Research Councils UK as well as Professor of the Physics and Chemistry of Minerals and Head of the Department of Earth Sciences at the University of Oxford.

Jillian Fiona Banfield is professor at the University of California, Berkeley with appointments in the Earth Science, Ecosystem Science and Materials Science and Engineering departments. She leads the Microbial Research initiative within the Innovative Genomics Institute, is affiliated with Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory and has a position at the University of Melbourne, Australia. Some of her most noted work includes publications on the structure and functioning of microbial communities and the nature, properties and reactivity of nanomaterials.

Timothy John Barrington Holland is a petrologist and Emeritus Professor in the Department of Earth Sciences at the University of Cambridge.

Mark S. Ghiorso is an American geochemist who resides in Seattle, Washington. He is best known for creating MELTS, a software tool for thermodynamic modeling of phase equilibria in magmatic systems.
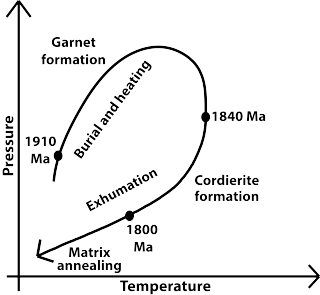
The Pressure-Temperature-time path is a record of the pressure and temperature (P-T) conditions that a rock experienced in a metamorphic cycle from burial and heating to uplift and exhumation to the surface. Metamorphism is a dynamic process which involves the changes in minerals and textures of the pre-existing rocks (protoliths) under different P-T conditions in solid state. The changes in pressures and temperatures with time experienced by the metamorphic rocks are often investigated by petrological methods, radiometric dating techniques and thermodynamic modeling.

The geology of the West Coast of New Zealand's South Island is divided in two by the Alpine Fault, which runs through the Region in a North-East direction. To the West of the fault Paleozoic basement rocks are interluded by plutones and both are unconformably covered in a sedimentary sequence. To the East of the Alpine Fault are the Mesozoic Alpine Schist and Greywacke of the Southern Alps. There are numerous active faults throughout the region.

A petrogenetic grid is a geological phase diagram that connects the stability ranges or metastability ranges of metamorphic minerals or mineral assemblages to the conditions of metamorphism. Experimentally determined mineral or mineral-assemblage stability ranges are plotted as metamorphic reaction boundaries in a pressure–temperature cartesian coordinate system to produce a petrogenetic grid for a particular rock composition. The regions of overlap of the stability fields of minerals form equilibrium mineral assemblages used to determine the pressure–temperature conditions of metamorphism. This is particularly useful in geothermobarometry.
Jane Selverstone is a geologist known for her research into tectonic processes, especially as they apply to the Eastern Alps.
References
- 1 2 Roger Powell at Library of Congress
- 1 2 3 "Professor Roger Powell FRS". London: The Royal Society. Archived from the original on 2 May 2015.
- 1 2 "Professor Roger Powell and Dr. Tim Holland: Featured Scientist Interview". sciencewatch.com. Archived from the original on 30 June 2013.
- 1 2 3 "Professor Roger Powell profile". University of Melbourne. Archived from the original on 6 April 2014.
- ↑ Holland, T. J. B.; Powell, R. (2004). "An internally consistent thermodynamic data set for phases of petrological interest". Journal of Metamorphic Geology. 16 (3): 309. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1314.1998.00140.x. S2CID 109930611.
- ↑ Powell, R.; Holland, T. J. B. (1988). "An internally consistent dataset with uncertainties and correlations: 3. Applications to geobarometry, worked examples and a computer program". Journal of Metamorphic Geology. 6 (2): 173. Bibcode:1988JMetG...6..173P. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1314.1988.tb00415.x.
- ↑ Roger Powell's publications indexed by the Scopus bibliographic database. (subscription required)
- ↑ Roger Powell publications indexed by Google Scholar
- ↑ Holland, T. J. B.; Powell, R. (1990). "An enlarged and updated internally consistent thermodynamic dataset with uncertainties and correlations: The system K₂–Na₂O–CaO–MgO–MnO–FeO–Fe₂O₃–Al₂O₃–TiO₂–SiO₂–C–H₂–O₂". Journal of Metamorphic Geology. 8: 89. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1314.1990.tb00458.x.
- ↑ "Professor Roger Powell profile". University of Melbourne. Archived from the original on 6 April 2014.
- ↑ Powell, Roger (1973). Mineral Equilibria in the Leven Schists near Fort William, Inverness-shire (DPhil thesis). University of Oxford. OCLC 500542740.
- ↑ Green, Eleanor (16 July 2023). "The official THERMOCALC website - homepage". The official THERMOCALC website. Retrieved 16 July 2023.
- ↑ "Ringwood Award". www.gsa.org.au. Retrieved 16 July 2023.
- ↑ "Jaeger Medal | Australian Academy of Science". www.science.org.au. Retrieved 16 July 2023.