Related Research Articles

Though the Ministry of Foreign Affairs (MOFA) is the government agency responsible for the conduct of foreign relations of Nepal, historically, it is the Office of Prime Minister (PMO) that has exercised the authority to formulate and conduct policies related to Nepal's foreign affairs. As a landlocked country wedged between two larger and far stronger powers, Nepal has tried to maintain good relations with both of its neighbors, People's Republic of China and Republic of India. Nepal's relationship with China, India, and the United States has remained utmost priority for successive Nepali governments. The relationship between Nepal and India however was significantly hampered during the 2015 Nepal blockade by pro-Indian anti-Nepal protestors, where the Government of Nepal accused India of using "Russia-Ukraine" tactics to cause unrest along Nepal's southern border using ethnically Indian residents of Nepal. India strictly denied the allegation and said the unrest were solely due to Madheshi protesters. For the most part though, Nepal has traditionally maintained a non-aligned policy and enjoys friendly relations with its neighboring countries and almost all the major countries of the world.

The Lhotshampa or Lhotsampa people are a heterogeneous Bhutanese people of Nepalese descent. "Lhotshampa", which means "southern borderlanders" in Dzongkha, began to be used by the Bhutanese state in the second half of the twentieth century to refer to the population of Nepali origin in the south of the country. After being displaced as a result of the state-run ethnic cleansing and living in refugee camps in eastern parts of Nepal, starting in 2007 most of the Bhutanese Refugees were resettled to various countries, such as the United States, Canada, Australia, the United Kingdom, and other European countries. As of 2021 the number of Lhotshampa in Nepal is significantly lower than that in the United States and other countries where they have resettled. People of Nepalese origin started to settle in uninhabited areas of southern Bhutan in the 19th century.

Nepal is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is mainly situated in the Himalayas, but also includes parts of the Indo-Gangetic Plain. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China to the north, and India in the south, east, and west, while it is narrowly separated from Bangladesh by the Siliguri Corridor, and from Bhutan by the Indian state of Sikkim. Nepal has a diverse geography, including fertile plains, subalpine forested hills, and eight of the world's ten tallest mountains, including Mount Everest, the highest point on Earth. Kathmandu is the nation's capital and the largest city. Nepal is a multi-ethnic, multi-lingual, multi-religious and multi-cultural state, with Nepali as the official language.

Nicolaus Copernicus was a Renaissance polymath, active as a mathematician, astronomer, and Catholic canon, who formulated a model of the universe that placed the Sun rather than Earth at its center. In all likelihood, Copernicus developed his model independently of Aristarchus of Samos, an ancient Greek astronomer who had formulated such a model some eighteen centuries earlier.

Man Mohan Adhikari (Magi) (Nepali: मन मोहन अधिकारी; 9 June 1920 – 26 April 1999) was the 31st Prime Minister of Nepal from 1994 to 1995, representing the Communist Party of Nepal (Unified Marxist-Leninist). He is the first communist Prime Minister in Nepal and one of the first communist politician in the world to be democratically elected as a head of government.

Biratnagar is a metropolitan city in Nepal, which serves as the capital of Koshi Province. With a population of 756,000 as per the 2022 census, it is the largest city in the province and also the headquarters of Morang district. As per the preliminary report of 2022 Nepal census, Biratnagar has an estimated city population of 7,56,000. It is the administrative center of the Greater Birat Development Area which incorporates the cities of Biratnagar-Itahari-Gothgau-Biratchowk-Dharan primarily located on the Koshi Highway in Eastern Nepal, with an estimated total urban agglomerated population of 804,300 people living in 159,332 households. Biratnagar is located 399 km (248 mi) east of the capital, Kathmandu, and 6 km (3.7 mi) north of the bordering town of Jogbani in the Indian state of Bihar.
Nepalese literature is the literature of Nepal. This is distinct from Nepali literature, which is the literature in only Nepali language. The major literary languages of Nepal are:

Israel–Nepal relations refer to the bilateral ties between the State of Israel and Nepal. The two countries established diplomatic relations on 1 June 1960, making Nepal the third country in South Asia to recognize Israel behind Ceylon and India, and the first South Asian state to establish full bilateral ties with it.

The Nepali Army, also referred as the Gorkhali Army, is the land service branch of the Nepali Armed Forces. After the Gorkha Kingdom was founded in 1559, its army was established in 1560, and was accordingly known as the Gorkhali Army. The army later became known as the Royal Nepali Army (RNA) following the Unification of Nepal, when the Gorkha Kingdom expanded its territory to include the whole country, by conquering and annexing the other states in the region, resulting in the establishment of a single united Hindu monarchy over all of Nepal. It was officially renamed simply to the Nepali Army on 28 May 2008, upon the abolition of the 240-year-old Nepalese monarchy, and of the 449-year-old rule of the Shah dynasty, shortly after the Nepalese Civil War.
Child Workers in Nepal (CWIN) is a non-governmental organization working as an advocate for children's rights. CWIN supports street children, children subjected to child labour, children who are sexually exploited, and also those victimized by violence. The organization's objective is to protect the rights of children in Nepal. It was established in 1987 by a group of students at Tribhuvan University who, upon investigating the conditions of children living on the streets in Kathmandu, Nepal, recognized the need for advocacy in this area. As a "watchdog" in the field of child rights in Nepal, CWIN acts as a voice for the disadvantaged and exploited children. It does this by lobbying, campaigning, and pressuring the government to protect and promote children's rights, and to end exploitation, abuse and discrimination against children.
Prithvinagar or Prithvinagar is a village development committee in Jhapa District in the Province No. 1 of south-eastern Nepal. At the time of the 1991 Nepal census it had a population of 15,612 people living in 2799 individual households.

The Nepal Rastra Bank was established April 26, 1956 A.D. under the Nepal Rastra Bank Act, 1955, to discharge the central banking responsibilities including guiding the development of the embryonic domestic financial sector. As of now, the NRB is functioning under the new Nepal Rastra Bank Act, 2002. The functions of NRB are to formulate required monetary and foreign exchange policies so as to maintain the stability in market prices, to issue currency notes, to regulate and supervise the banking and financial sector, to develop efficient payment and banking systems among others. The NRB is also the economic advisor to the government of Nepal. As the central bank of Nepal, it is the monetary, supervisory and regulatory body of all the commercial banks. development banks, finance companies and micro-finances institutions.
There is a large community of Nepalese people in Malaysia, recruited from Nepal, foreign workers and their families. In 2020, there were over 382,000 documented Nepali workers in Malaysia - the majority of which were working in the manufacturing sector.
Nepalis in Qatar are migrants from Nepal to Qatar, mostly migrant workers and permanent residents, as well as their locally born descendants. As of May 2017, 400 thousand Nepali Citizens lived in Qatar as migrant workers, Nepal is the second largest expatriate community in Qatar. While there are Nepalese working in the business and administrative sectors of Qatar, most workers from Nepal fall under the umbrella of unskilled labor, and hold jobs in sectors such as construction and landscaping. Many workers from Nepal are hired to work on the construction of stadiums and railways that are being designed for the 2022 FIFA World Cup to be held in Qatar. According to Time Magazine, due to the terrible working conditions in Qatar, a Nepali worker dies every other day.
The community of Nepalis in China consists of Nepalese immigrants and expatriates to China as well as Chinese citizens of Nepalese descent.

The Nepalese Ministry of Minister of Industry, Commerce and Supplies is a governmental body of Nepal to monitor and manage industries of the country.

The revolution of 1951 in Nepal, also referred to as Sat Salko Kranti, was a political movement against the direct rule by the Rana dynasty of Nepal which had lasted for 104 years. It marks the beginning of the political awakening and democratic movements in Nepal, and resulted in immediate abolition of the institutionalized hereditary Prime Minister system in Nepal.
Nepal has a labour force of 16.8-million-workers, the 37th largest in the world as of 2017. Although agriculture makes up only about 28 per cent of Nepal's GDP, it employs more than two-thirds of the workforce. Millions of men work as unskilled labourers in foreign countries, leaving the household, agriculture, and raising of children to women alone. Most of the working-age women are employed in agricultural sector, contributions to which are usually ignored or undervalued in official statistics. Few women who are employed in the formal sectors face discrimination and significant wage gap. Almost half of all children are economically active, half of which are child labourers. Millions of people, men, women and children of both sexes, are employed as bonded labourers, in slavery-like conditions. Trade unions have played a significant role in earning better working conditions and workers' rights, both at the company level and the national government level. Worker-friendly labour laws, endorsed by the labour unions as well as business owners, provide a framework for better working conditions and secure future for the employees, but their implementation is severely lacking in practice. Among the highly educated, there is a significant brain-drain, posing a significant hurdle in fulfilling the demand for skilled workforce in the country.
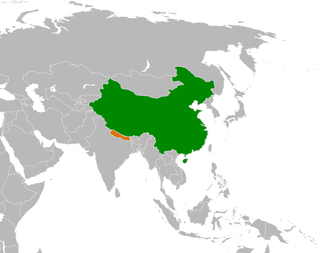
The Sino-Nepalese Treaty of Peace and Friendship was an official settlement between the governments of Nepal and China signed on 28 April 1960, which ratified an earlier agreement on the borders separating the neighboring nations from each other. Gerry Van Tronder has argued that this document fitted into an attempt to maintain the image that Beijing was a "powerful but essentially benevolent leader in Asia", following the 1959 Tibetan Uprising. Contemporary Nepali, Chinese and Indian commentators have stressed the importance of the treaty in determining Nepal's relationship with China in the past and present.

The Nicolaus Copernicus Astronomical Center is a Polish scientific research institute of the Polish Academy of Sciences headquartered in Warsaw, Poland. It is a leading institution in the country in the field of astronomy.