
Pamlico Sound in North Carolina in the US is the largest lagoon along the North American East Coast, extending 80 mi (130 km) long and 15 to 20 miles wide. It is part of a large, interconnected network of lagoon estuaries that includes Albemarle Sound, Currituck Sound, Croatan Sound, Pamlico Sound, Bogue Sound, Core Sound, and Roanoke Sound. Together, these sounds, known as the Albemarle-Pamlico sound system, comprise the second largest estuary in the United States, covering over 3,000 sq. mi. of open water.(Chesapeake Bay is the largest.) The Pamlico Sound is separated from the Atlantic Ocean by the Outer Banks, a row of low, sandy barrier islands that include Cape Hatteras National Seashore, Cape Lookout National Seashore, and Pea Island National Wildlife Refuge. The Albemarle-Pamlico Sound is one of nineteen great waters recognized by the America's Great Waters Coalition.
Rodanthe is an unincorporated community and census-designated place (CDP) located in Dare County, North Carolina, United States, on Hatteras Island, part of North Carolina's Outer Banks. As of the 2010 census it had a population of 261. Rodanthe, along with Waves and Salvo, are part of the settlement of Chicamacomico. Rodanthe includes the original Chicamacomico Life-Saving Station, decommissioned in 1954, but now a museum.

Hatteras is an unincorporated village and census-designated place (CDP) in Dare County, North Carolina, United States, on the Outer Banks island of Hatteras, at its extreme southwestern tip. As of the 2010 census it had a population of 504. Immediately to the west of the village of Hatteras is Hatteras Inlet which separates Hatteras Island from the neighboring Ocracoke Island. North Carolina Highway 12 passes through the community linking it to Frisco to the east and Ocracoke to the west.

The current Bodie Island Lighthouse is the third that has stood in this vicinity of Bodie Island on the Outer Banks in North Carolina and was built in 1872. It stands 156 feet (48 m) tall and is located on the Roanoke Sound side of the first island that is part of the Cape Hatteras National Seashore. The lighthouse is just south of Nags Head, a few miles before Oregon Inlet. It was renovated from August 2009 to March 2013, and was made climbable by the public. There are 214 steps that spiral to the top. The 170-foot structure is one of only a dozen remaining tall, brick tower lighthouses in the United States — and one of the few with an original first-order Fresnel lens to cast its light.

Hurricane Emily in 1993 caused record flooding in the Outer Banks of North Carolina while remaining just offshore. The fifth named storm and the first yet strongest hurricane of the year's hurricane season, Emily developed from a tropical wave northeast of the Lesser Antilles on August 22. It moved northwestward and strengthened into a tropical storm on August 25, after becoming nearly stationary southeast of Bermuda. Emily then curved to the southwest but quickly resumed its northwest trajectory while strengthening into a hurricane. Late on August 31, the hurricane reached peak winds of 115 mph (185 km/h) on its approach to North Carolina. Although part of the eye passed over Hatteras Island in the Outer Banks, its absolute center remained 23 mi (37 km/h) offshore. Gradually weakening, the hurricane swerved away from the coast toward the northeast and later east. Emily stalled again, this time northeast of Bermuda, and dissipated on September 6 to the southeast of Newfoundland.

Pea Island National Wildlife Refuge is a National Wildlife Refuge located on North Carolina's Pea Island, a coastal barrier island and part of a chain of islands known as the Outer Banks, adjacent to Cape Hatteras National Seashore. The sanctuary is located 10 miles (16 km) south of Nags Head, North Carolina on NC 12.
North Carolina Highway 12 (NC 12) is a 148.0-mile-long (238.2 km) primary state highway in the U.S. state of North Carolina, linking the peninsulas and islands of the northern Outer Banks. Most sections of NC 12 are two lanes wide, and there are also two North Carolina Ferry System routes which maintain continuity of the route as it traverses the Outer Banks region. NC 12 is part of the Outer Banks Scenic Byway, a National Scenic Byway. The first NC 12 appeared on the 1924 North Carolina Official Map and at its height ran from NC 30 in Pollocksville to NC 48 near Murfreesboro. Over time it was replaced by both US 258 and NC 58 and ceased to exist in 1958. The current NC 12 first appeared on the 1964 state highway map running from US 158 in Nags Head to Ocracoke. In 1976 NC 12 was extended to US 70 on the mainland and in 1987 was extended north to Corolla.

Currituck Sound is a protected inlet of the Atlantic Ocean, located in northeastern part of North Carolina and extreme southeastern Virginia. Thirty miles N-S and 3–8 miles wide, this shallow, island-filled sound is separated from the ocean by the Currituck Banks Peninsula, part of the Outer Banks. On the NE, it extends to Back Bay in Virginia Beach, Virginia. A fork on the northwest leads to the Albemarle and Chesapeake Canal, which is a part of the Atlantic Intracoastal Waterway that connects the sound to Hampton Roads and the Chesapeake Bay. Although several inlets connected it directly to the Atlantic at one time or another, they have all since closed and there is now no direct access to the Ocean from the Sound. This has caused the salinity levels to be significantly lower than they had been historically. Currently, the only access to the Ocean is through the Albemarle Sound, which joins the Currituck to the South. Currituck County's Mackay Island and Currituck National Wildlife Refuge as well as Back Bay National Wildlife Refuge and False Cape State Park in Virginia Beach border the sound and are winter habitats on the Atlantic Flyway. Many watersports activities occur in the sound, including parasailing, sea kayaking, and jet skiing. An area of barrier beaches, it is also noted for its duck and goose hunting.
The North Carolina Department of Transportation Ferry Division is a branch of NCDOT that is responsible for the operation of over two dozen ferry services that transport passengers and vehicles to several islands along the Outer Banks of North Carolina.

Hurricane Isabel of the 2003 Atlantic hurricane season produced moderate to heavy damage across eastern North Carolina, United States. Isabel formed from a tropical wave on September 6, 2003, in the tropical Atlantic Ocean. It moved northwestward, and within an environment of light wind shear and warm waters it steadily strengthened to reach peak winds of 165 mph (265 km/h) on September 11. After fluctuating in intensity for four days, Isabel gradually weakened and made landfall on the Outer Banks of North Carolina with winds of 105 mph (165 km/h) on September 18. It quickly weakened over land and became extratropical over western Pennsylvania the next day.
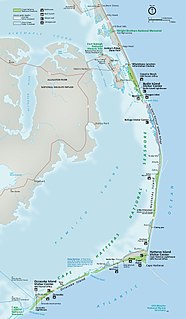
Hatteras Inlet is an estuary in North Carolina, located along the Outer Banks, separating Hatteras Island and Ocracoke Island. It connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Pamlico Sound. Hatteras Inlet is located entirely within Hyde County.

OcAcock Inlet is an estuary located in the Outer Banks, North Carolina, United States that separates Ocracoke Island and Portsmouth Island. It connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Pamlico Sound. It is the southern terminus of the Cape Hatteras National Seashore, and the northern terminus of the Cape Lookout National Seashore. The inlet is approximately two miles across, although it changes daily.
Drum Inlet and Ophelia Inlet are inlets of the Outer Banks in the U.S. state of North Carolina. They connect the Core Sound with the Atlantic Ocean and separate North Core Banks from South Core Banks. The exact inlet locations and names have changed with time, as new inlets open, merge, or close. Conversationally, the inlet or inlets between mile 19 and 23, as measured from Ocracoke Inlet, are typically called Drum Inlet even when, geologically, they have other names.

Pea Island is an island which is part of the Outer Banks of North Carolina. Because of the shifting nature of the barrier island system of which Pea Island is a part, and the way in which inlets open and close over time, Pea Island has, at times, been contiguous with the neighboring islands of Bodie Island or Hatteras Island. Pea Island was created when two inlets, the New Inlet in 1738, and Oregon Inlet in 1846, separated it from the neighboring islands. The island was rejoined to Hatteras Island intermittently from 1922 until 1945 as the narrow New Inlet opened and closed with shifting sands. Pea Island ceased to exist entirely from 1945 until 2011, when Hurricane Irene reopened the New Inlet, recreating Pea Island. From 1945 to 2011, Pea Island was merely the northern 11 miles or so of Hatteras Island. Pea Island was home to the Pea Island Life-Saving Station, the first U.S. Coast Guard life-saving station to have an all African-American crew. Since 1937, it has also been home to the Pea Island National Wildlife Refuge.
Carova Beach or Carova is an unincorporated community in Currituck County in the extreme northeast corner of North Carolina, United States. The community, begun in the 1960s, is found on Currituck Banks, north of Bodie Island, and can only be accessed by boat or by four-wheel drive vehicle. There are no paved roads connecting Carova to the town of Corolla, North Carolina. The neighboring settlement of Sandbridge in Virginia Beach, Virginia is not accessible by vehicle from Carova. In the 1960s when development began in Carova there were plans to construct a paved road from the Sandbridge south to Carova through the Back Bay National Wildlife Refuge but these never materialized. Today there is a permanent fence from ocean to sound to keep vehicles from crossing but, more importantly, to keep the wild horses from migrating to the Virginia side of the border. To reach Carova, four-wheel drive vehicles must drive north along the beach from Corolla into the community, as access from Virginia is limited to pedestrians and bicyclists.

The Core Banks are barrier islands in North Carolina, part of the Outer Banks and Cape Lookout National Seashore. Named after the Coree tribe, they extend from Ocracoke Inlet to Cape Lookout, and consist of two low-relief narrow islands, North Core Banks and South Core Banks, and, since September 2011, two smaller islands. New Drum Inlet, Old Drum Inlet and Ophelia Inlet now separate the islands. The Core Banks are now uninhabited. However, Portsmouth, at the north end of the North Core Banks, was once a substantial port, and Cape Lookout Village, about one and half miles south of the Cape Lookout Lighthouse, contains the historic Lookout Life-Saving Station, a U.S. Coast Guard Station, and several island homes.















