
Dare County is the easternmost county in the U.S. state of North Carolina. As of the 2020 census, the population was 36,915. Its county seat is Manteo.

Ocracoke is a census-designated place (CDP) and unincorporated town located at the southern end of Ocracoke Island, within Hyde County, North Carolina. The population was 948 at the 2010 census. In the 2020 census, the population had dropped to 797.

Pamlico Sound is a large estuarine lagoon in North Carolina. The largest lagoon along the North American East Coast, it extends 80 mi (130 km) long and 15 to 20 miles wide. It is part of a large, interconnected network of similar lagoons that includes Albemarle Sound, Currituck Sound, Croatan Sound, Roanoke Sound, Pamlico Sound, Bogue Sound, Back Sound, and Core Sound known collectively as the Albemarle-Pamlico sound system. With over 3,000 sq. mi. (7,800 km2) of open water the combined estuary is second only in size to 4,479 sq mi (11,600 km2) Chesapeake Bay in the United States.

Avon is an unincorporated community and census-designated place (CDP) in Dare County in the U.S. state of North Carolina. As of the 2020 census, it had a population of 832.

Rodanthe is an unincorporated community and census-designated place (CDP) located in Dare County, North Carolina, United States, on Hatteras Island, part of North Carolina's Outer Banks. As of the 2020 census it had a population of 213. Rodanthe, along with Waves and Salvo, are part of the settlement of Chicamacomico. Rodanthe includes the original Chicamacomico Life-Saving Station, decommissioned in 1954, but now a museum.

Hatteras Island is a barrier island located off the North Carolina coast. Dividing the Atlantic Ocean and the Pamlico Sound, it runs parallel to the coast, forming a bend at Cape Hatteras. It is part of North Carolina's Outer Banks and includes the communities of Rodanthe, Waves, Salvo, Avon, Buxton, Frisco, and Hatteras. It contains the largest part of the Cape Hatteras National Seashore. Prior to European settlement the island was inhabited by Croatoan Native Americans.

The current Bodie Island Lighthouse is the third that has stood in this vicinity of Bodie Island on the Outer Banks in North Carolina and was built in 1872. It stands 156 feet (48 m) tall and is located on the Roanoke Sound side of a portion of a peninsula that is the first part of the Cape Hatteras National Seashore. The lighthouse is just south of Nags Head, a few miles before Oregon Inlet. It was renovated from August 2009 to March 2013, and was made climbable by the public. There are 219 steps that spiral to the top. The 170-foot structure is one of only a dozen remaining tall, brick tower lighthouses in the United States — and one of the few with an original first-order Fresnel lens to cast its light.

Cape Hatteras National Seashore is a United States national seashore which preserves the portion of the Outer Banks of North Carolina from Bodie Island to Ocracoke Island, stretching over 70 miles (110 km), and is managed by the National Park Service. Included within this section of barrier islands along N.C. 12, but outside the national seashore boundaries, are Pea Island National Wildlife Refuge and several communities, such as Rodanthe, Buxton, and Ocracoke. Cape Hatteras is a combination of natural and cultural resources, and provides a wide variety of recreational opportunities.

The Outer Banks are a 200 mi (320 km) string of barrier islands and spits off the coast of North Carolina and southeastern Virginia, on the east coast of the United States. They line most of the North Carolina coastline, separating Currituck Sound, Albemarle Sound, and Pamlico Sound from the Atlantic Ocean. A major tourist destination, the Outer Banks are known for their wide expanse of open beachfront and Cape Hatteras National Seashore. The seashore and surrounding ecosystem are important biodiversity zones, including beach grasses and shrubland that help maintain the form of the land.

The Houses of Refuge in Florida were a series of stations operated by the United States Life Saving Service along the coast of Florida to rescue and shelter ship-wrecked sailors. Five houses were constructed on the east coast in 1876, with five more added in 1885 and 1886. There were also two life-saving stations built, one just south of the Jupiter Inlet, the other on the Gulf coast on Santa Rosa Island near Pensacola, Florida. A house of refuge was planned for the Marquesas Keys, but was never put into commission. The houses were staffed by civilian contractors who lived in the houses with their families. Most of these houses remained in service as life-saving stations until 1915 or later. Some of the locations became United States Coast Guard stations after the Life-Saving Service was merged with the United States Revenue Cutter Service to form the Coast Guard in 1915.

Pea Island National Wildlife Refuge is a national wildlife refuge located on North Carolina's Pea Island, a coastal barrier island and part of a chain of islands known as the Outer Banks, adjacent to Cape Hatteras National Seashore. The sanctuary is located 10 miles (16 km) south of Nags Head, North Carolina on NC 12.

North Carolina Highway 12 (NC 12) is a 148.0-mile-long (238.2 km) primary state highway in the U.S. state of North Carolina, linking the peninsulas and islands of the northern Outer Banks. Most sections of NC 12 are two lanes wide, and there are also two North Carolina Ferry System routes which maintain continuity of the route as it traverses the Outer Banks region. NC 12 is part of the Outer Banks Scenic Byway, a National Scenic Byway. The first NC 12 appeared on the 1924 North Carolina Official Map and at its greatest length ran from NC 30 in Pollocksville to NC 48 near Murfreesboro. Over time it was replaced by both U.S. Route 258 (US 258) and NC 58 and ceased to exist in 1958. The current NC 12 first appeared on the 1964 state highway map running from US 158 in Nags Head to Ocracoke. In 1976 NC 12 was extended to US 70 on the mainland and in 1987 was extended north to Corolla.
Oregon Inlet is an inlet along North Carolina's Outer Banks. It joins the Pamlico Sound with the Atlantic Ocean and separates Bodie Island from Pea Island, which are connected by the 2.8-mile (4.5 km) Marc Basnight Bridge that spans the inlet. As one of the few access points to the ocean along this stretch of coast, Oregon Inlet is a major departure point for charter fishing trips, with a nearby harbor serving as the base for many large boats that travel miles out towards the Gulf Stream almost every day. The inlet is also the location of a U.S. Coast Guard motor lifeboat station.
New Inlet was an inlet along the Outer Banks of North Carolina joining Pamlico Sound with the Atlantic Ocean. It had not existed since 1945 before Hurricane Irene temporarily re-opened the inlet in 2011.

Isabel Inlet was an informally named inlet along the Outer Banks of North Carolina. It was created by Hurricane Isabel when it swept ashore on September 18, 2003.
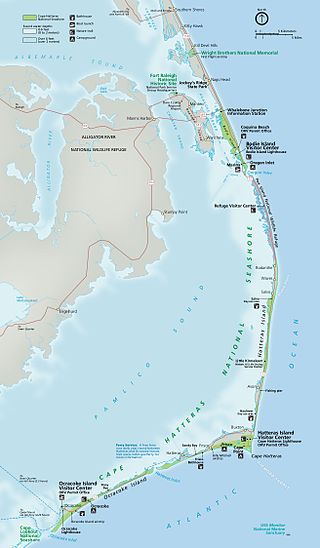
Hatteras Inlet is an estuary in North Carolina, located along the Outer Banks, separating Hatteras Island and Ocracoke Island. It connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Pamlico Sound. Hatteras Inlet is located entirely within Hyde County.

Ocracoke Inlet is an estuary located in the Outer Banks of North Carolina, United States that separates Ocracoke Island and Portsmouth Island. It connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Pamlico Sound. It is the southern terminus of the Cape Hatteras National Seashore, and the northern terminus of the Cape Lookout National Seashore. The inlet is approximately two miles across, although it changes daily.
Carova Beach or Carova is an unincorporated community in Currituck County in the extreme northeastern corner of North Carolina, United States. The community, begun in the 1960s, is found on Currituck Banks, north of Bodie Island, and can be accessed only by boat or by four-wheel drive vehicle. There are no paved roads connecting Carova to the town of Corolla, North Carolina. The neighboring settlement of Sandbridge in Virginia Beach, Virginia, is not accessible by vehicle from Carova. In the 1960s, when development began in Carova, there were plans to construct a paved road from Sandbridge south to Carova through the Back Bay National Wildlife Refuge, but these never materialized. Today, there is a permanent fence from ocean to sound to keep vehicles from crossing and, more importantly, to keep the feral horses from migrating to the Virginia side of the border. To reach Carova, four-wheel drive vehicles must drive north along the beach from Corolla into the community, as access from Virginia is limited to pedestrians and bicyclists.
Bodie Island is a long, narrow barrier peninsula that forms the northernmost portion of the Outer Banks. The land that is most commonly referred to as Bodie Island was at one time a true island, but in 1811 Roanoke Inlet, which had separated it from the Currituck Banks in the north, closed. As a result, the Currituck Banks and Bodie Island are now one contiguous peninsula, joined at the Nags Head area, where the inlet once flowed. Today, either name can be used to refer to the peninsula as a whole, but both portions colloquially retain their historical names.

Pea Island Life-Saving Station was a life-saving station on Pea Island, on the Outer Banks of North Carolina. It was the first life-saving station in the country to have an all-black crew, and it was the first in the nation to have a black man, Richard Etheridge, as commanding officer. On August 3, 2012, the second of the Coast Guard's 154-foot Sentinel-Class Cutters, USCGC Richard Etheridge (WPC-1102), was commissioned in his honor.

















