
European route E6 is the main north–south thoroughfare through Norway as well as the west coast of Sweden. It is 3,056 km (1,899 mi) long and runs from the southern tip of Sweden at Trelleborg, into Norway and through almost all of the country north to the Arctic Circle and Nordkapp. The route ends in Kirkenes close to the Russian border.
The signalling system used on the rail transport in Norway is regulated by the Regulations of December 4, 2001 no. 1336 about signals and signs on the state's railway network and connected private tracks.

The Nordland Line is a 729-kilometer (453 mi) railway line between Trondheim and Bodø, Norway. It is the longest in Norway and lacks electrification. The route runs through the counties of Trøndelag and Nordland, carrying a combination of commuter, long-haul passenger and freight trains. From Trondheim Central Station to Steinkjer Station the line is most heavily used, with hourly services by the Trøndelag Commuter Rail. There are three branch lines—the Stavne–Leangen Line at Leangen Station, the Meråker Line at Hell Station and the Namsos Line at Grong Station.

Nazi concentration camps in Norway were concentration camps or prisons in Norway established or taken over by the Quisling regime and Nazi German authorities during the German occupation of Norway that began on 9 April 1940 and used for internment of persons by the Nazi authorities. 709 prison camps or concentration camps, [including some death camps,] were counted by a project that had Randi Bratteli, as an advisor. Another source has claimed that there were around 620 prison camps.

The Ofoten Line is a 43-kilometre (27 mi) railway line in Narvik Municipality, Norway. It runs from the Port of Narvik to Riksgränsen on the Norway–Sweden border, where the line continues as the Ore Line via Kiruna and Gällivare to Luleå. The Ofoten Line is single track, electrified at 15 kV 16.7 Hz AC and has seven stations. The line only connects to the rest of the Norwegian railway network via Sweden. The main traffic is up to 12 daily freight trains operated by Malmtrafik that haul iron ore from Sweden to Narvik. In addition, CargoNet operates container trains, branded as the Arctic Rail Express (ARE), and Vy Tåg operates passenger trains, including a night train to Stockholm.

NSB Class 73 is a class of 22 electric multiple units built by Adtranz for the Norwegian State Railways. The four-car trains were modifications of Class 71, which was again based on the Swedish X2. The A-series consists of 16 intercity trains; they were delivered in 1999 and 2000 and are used on the Bergen, Dovre and Sørland Lines. The intercity service was branded as Signatur until 2003. The B-series consists of six regional trains delivered in 2002 and used on the Østfold Line. The regional trains were originally part of the Agenda concept. The trains have a power output of 2,646 kilowatts (3,548 hp) and a maximum speed of 210 km/h (130 mph). They have an overall length of 108 meters (354 ft) and have a capacity for 208 seated passengers in the A-series and 250 in the B-series. The trains have a tilting mechanism allowing for faster travel through curves.

Norske tog Class 92 is a class of 15 diesel multiple units built by Duewag for the Norwegian State Railways (NSB). The two-car trains were delivered in 1984 and 1985, and were put into service on the Røros Line and southern part of the Nordland Line—which later became the Trøndelag Commuter Rail. Later, they also entered service on the Meråker Line as part of the international Mittnabotåget service. Previously, the trains were also used on the Solør Line, further north on the Nordland Line and on the now electrified Arendal Line. In 2000, a unit was involved in the Åsta accident; which killed 19 people. The trains were refurbished in 2005 and 2006, and NSB plans to replace them by around 2019. Each twin unit seats 168 people, is 49.45 meters long and weighs 92 tonnes. The front car is powered with two electric motors, giving a power output of 714 kilowatts (957 hp) and a maximum speed of 140 kilometers per hour (87 mph).

The NSB Di 8 is a class of diesel-electric locomotives built by Maschinenbau Kiel (MaK), while it was part of Siemens Schienenfahrzeugtechnik, for the Norwegian State Railways (NSB). The locomotives are equipped with a Caterpillar 3516 DI-TA prime mover, which provides a power output of 1,570 kilowatts (2,110 hp) and a starting tractive effort of 270 kilonewtons (61,000 lbf).

The Norwegian language conflict is an ongoing controversy in Norwegian culture and politics about the different varieties of written Norwegian. From 1536/1537 until 1814, Danish was the standard written language of Norway due to the union of crowns with Denmark. As a result, the proximity of modern written Norwegian to Danish underpins controversies in anti-imperialistic nationalism, rural versus urban cultures, literary history, diglossia, spelling reform, and orthography.

The Polar Line is an incomplete and abandoned railway line in Norway, from Fauske to Narvik and, if finished, ultimately would have run 1,215 km (755 mi) to Kirkenes.

The Hell–Sunnan Line is a 105-kilometer-long (65 mi) railway line between Hell and Sunnan in Trøndelag county, Norway. The name is no longer in official use and the line is now considered part of the Nordland Line. The Hell–Sunnan Line branches from the Meråker Line at Hell and runs on the east shore of the Trondheimsfjord passing through Stjørdal Municipality, Levanger Municipality, Verdal Municipality, Inderøy Municipality, and Steinkjer Municipality.

Parliamentary elections were held in Norway on 13 and 14 September 2009. Elections in Norway are held on a Monday in September, usually the second or third Monday, as determined by the king. Early voting was possible between 10 August and 11 September 2009, while some municipalities also held open voting on 13 September. Voters elected 169 members for the Storting, each for a four-year term. Voter turn-out in the 2009 general elections was 76.4%.

The German occupation of Norway began on 9 April 1940. In 1942, there were at least 2,173 Jews in Norway. At least 775 of them were arrested, detained and/or deported. More than half of the Norwegians who died in camps in Germany were Jews. 742 Jews were murdered in the camps and 23 Jews died as a result of extrajudicial execution, murder and suicide during the war, bringing the total of Jewish Norwegian dead to at least 765, comprising 230 complete households.
Elisenberg station is an unfinished railway station within the Oslo Tunnel on the Drammen Line in Oslo, Norway. The ghost station was partially built during the construction of the tunnel between 1971 and 1980, but has never been put into use. It is located between Nationaltheatret Station and Skøyen Station, at Elisenberg in Frogner. A 220-meter (720 ft) long center platform and part of the access way has been built, but never completed. While the station initially was not put into use because of lack of funds to complete it, it is now unlikely that it will ever be completed, as the need for a station has disappeared and an opening would need a large investment of funds.

Jåttåvågen Station is a railway station located in the municipality of Stavanger in Rogaland county, Norway. The station is located at Jåtten in the city of Stavanger, about 7.2 kilometres (4.5 mi) from the main Stavanger Station. It is served by the Jæren Commuter Rail operated by Go-Ahead Norge by up to four hourly trains in each direction. The station is located along the double track section of the Sørland Line, and was opened on 8 January 2009, replacing Jåttå Station. The station is within a minute's walk of Viking Stadion and Jåttå Upper Secondary School. The station is co-located with a Kolumbus bus stop, allowing transfers to and from Line 11.
The Osvald Group was a Norwegian organisation that was the most active World War II resistance group in Norway from 1941 to the summer of 1944. Numbering more than 200 members, it committed at least 110 acts of sabotage against Nazi occupying forces and the collaborationist government of Vidkun Quisling. The organisation is perhaps best known for conducting the first act of resistance against the German occupation of Norway, when on 2 February 1942, it detonated a bomb at Oslo East Station in protest against Quisling's inauguration as Minister-President.

Bjørn Petter Westlie is a Norwegian journalist, historian, university college lecturer and non-fiction writer.

The Beisfjord massacre was a massacre on 18 July 1942 at Beisfjord Camp No. 1 in the village of Beisfjord in Narvik Municipality, Norway of 288 political prisoners. The massacre had been ordered a few days earlier by Josef Terboven, the Reichskommissar for Nazi-occupied Norway.
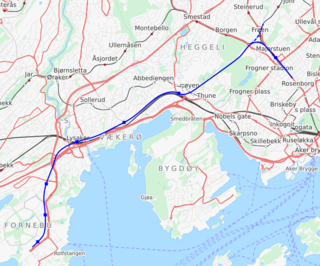
The Fornebu Line is an under construction rail line which will serve the peninsula of Fornebu in Bærum, Norway. The line is under construction and the transit agency Ruter is working towards connecting it to the Oslo Metro. The line has at various stages been proposed as an automated people mover, tram-train, tramway, light rail, stadtbahn, rapid transit, bus rapid transit and commuter rail, with the rapid transit option being selected as the final proposal. The metro line will start at Majorstuen Station and will run entirely in a tunnel for 8,150 meters (26,740 ft). The line will have six stations, at Skøyen, Vækerø, Lysaker, Telenor Arena, Flytårnet and Fornebu Senter. A depot will be built at Fornebu and the line will connect to the metro's Common Tunnel at Majorstuen.
Resett, also known as Resett.no, was a Norwegian online newspaper, which published news and op-ed content. The website was launched in 2017 with Helge Lurås as editor-in-chief. Resett aimed to "present cases from a different angle than established mass media, and to cover news that other media do not want to cover". The newspaper closed operations in December 2022.

















