Related Research Articles

Pacific Islanders, Pasifika, Pasefika, Pacificans or rarely Pacificers are the peoples of the Pacific Islands. As an ethnic/racial term, it is used to describe the original peoples—inhabitants and diasporas—of any of the three major subregions of Oceania or any other island located in the Pacific Ocean.
A violent crime, violent felony, crime of violence or crime of a violent nature is a crime in which an offender or perpetrator uses or threatens to use harmful force upon a victim. This entails both crimes in which the violent act is the objective, such as murder, assault, rape and assassination, as well as crimes in which violence is used as a method of coercion or show of force, such as robbery, extortion and terrorism. Violent crimes may, or may not, be committed with weapons. Depending on the jurisdiction, violent crimes may be regarded with varying severities from homicide to harassment. There have been many theories regarding heat being the cause of an increase in violent crime. Theorists claim that violent crime is persistent during the summer due to the heat, further causing people to become aggressive and commit more violent crime.

The Oceania Football Confederation (OFC) is one of the six continental confederations of international association football. The OFC has 13 members, 11 of which are full members and two which are associate members not affiliated with FIFA. It promotes the game in Oceania and allows the member nations to qualify for the FIFA World Cup.
Anglo-Celtic Australians is an ancestral grouping of Australians whose ancestors originate wholly or partially in the British Isles - predominantly in England, Ireland, Scotland and Wales, as well as the Isle of Man and Channel Islands.
Cultural assimilation is the process in which a minority group or culture comes to resemble a society's majority group or assimilates the values, behaviors, and beliefs of another group whether fully or partially.
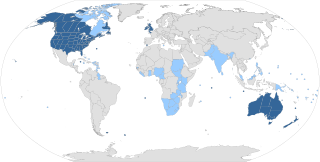
The English-speaking world comprises the 88 countries and territories in which English is an official, administrative, or cultural language. In the early 2000s, between one and two billion people spoke English, making it the largest language by number of speakers, the third largest language by number of native speakers and the most widespread language geographically. The countries in which English is the native language of most people are sometimes termed the Anglosphere. Speakers of English are called Anglophones.

European exploration and settlement of Oceania began in the 16th century, starting with the Spanish (Castilian) landings and shipwrecks in the Mariana Islands, east of the Philippines. This was followed by the Portuguese landing and settling temporarily in some of the Caroline Islands and Papua New Guinea. Several Spanish landings in the Caroline Islands and New Guinea came after. Subsequent rivalry between European colonial powers, trade opportunities and Christian missions drove further European exploration and eventual settlement. After the 17th century Dutch landings in New Zealand and Australia, with no settlement in these lands, the British became the dominant colonial power in the region, establishing settler colonies in what would become Australia and New Zealand, both of which now have majority European-descended populations. States including New Caledonia (Caldoche), Hawaii, French Polynesia, and Norfolk Island also have considerable European populations. Europeans remain a primary ethnic group in much of Oceania, both numerically and economically.

The Indigenous peoples of Oceania are Aboriginal Australians, Papuans, and Austronesians. These indigenous peoples have a historical continuity with pre-colonial societies that developed on their territories. With the notable exceptions of Australia, New Zealand, Hawaii, New Caledonia, Guam, and Northern Mariana Islands, indigenous peoples make up the majority of the populations of Oceania.
Australians, colloquially known as Aussies, are the citizens, nationals and individuals associated with the country of Australia. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or ethno-cultural. For most Australians, several of these connections exist and are collectively the source of their being Australian. Australian law does not provide for a racial or ethnic component of nationality, instead relying on citizenship as a legal status.

The term Other White, or White Other, is a classification of ethnicity in the United Kingdom, used in documents such as the 2021 United Kingdom Census, to describe people who identify as white persons who are not of the English, Welsh, Scottish, Roma, Irish or Irish Traveller ethnic groupings. In Scotland, the term Other White is also used to refer collectively to those not of Scottish or Other British ethnicity, in which case it also includes those of a Gypsy, Roma, Irish or Irish Traveller background.
On 11 April 2001, the Australian and American Samoan national association football teams played each other in an Oceanian qualifying match for the 2002 FIFA World Cup. The match was played at the International Sports Stadium in Coffs Harbour, Australia. Australia set a world record for the largest victory in an international football match, winning the game 31–0. Australia's Archie Thompson also broke the record for most goals scored by a player in an international match by scoring 13 goals. David Zdrilic, the scorer of eight goals in the match, scored the second-highest number of goals in an international match since World War I.
The British diaspora consists of people of English, Scottish, Welsh, Northern Irish, Cornish, Manx and Channel Islands ancestral descent who live outside of the United Kingdom and its Crown Dependencies.
The English diaspora consists of English people and their descendants who emigrated from England. The diaspora is concentrated in the English-speaking world in countries such as the United States, Canada, Australia, New Zealand, Scotland, Ireland, Wales, South Africa, India and to a lesser extent, Zimbabwe, Zambia and continental Europe.
Asian people are the people of the continent of Asia. The term may also refer to their descendants. According to the Merriam-Webster dictionary, an Asian is “a person of Asian descent”.
European Australians are citizens or residents of Australia whose ancestry originates from the peoples of Europe. They form the largest panethnic group in the country. At the 2021 census, the number of ancestry responses categorised within European ancestral groups as a proportion of the total population amounted to more than 57.2%. It is impossible to quantify the precise proportion of the population with European ancestry. For instance, many census recipients nominated two European ancestries, tending towards an overcount. Conversely, 29.9% of census recipients nominated "Australian" ancestry, tending towards an undercount.

Oceania is a region centered on the islands of the tropical Pacific Ocean. Conceptions of what constitutes Oceania vary, with it being defined in various ways, often geopolitically or geographically. In the geopolitical conception used by the United Nations, International Olympic Committee, and many atlases, the Oceanic region includes Australia and the nations of the Pacific from Papua New Guinea east, but not the Malay Archipelago or Indonesian New Guinea. The term is sometimes used more specifically to denote Australasia as a geographic continent, or biogeographically as a synonym for either the Australasian realm or the Oceanian realm.
Association football is one of the popular sports in Oceania, and 2 members of the Oceania Football Confederation (OFC) have competed at the sport's biggest event – the men's FIFA World Cup.
Oceanian Americans or Oceanic Americans are Americans whose ancestors came from Oceania, a region which is composed of the Australian continent and the Pacific Islands.
Norfolk Islanders, also referred to as just Islanders, are the inhabitants or residents of Norfolk Island, an external territory of Australia. The Islanders have their own unique identity and are predominantly people of Pitcairn and English descent and to a lesser extent of Scottish and Irish.
A majority-minority or minority-majority area is a term used to refer to a subdivision in which one or more racial, ethnic, and/or religious minorities make up a majority of the local population.
References
- ↑ Government of Canada, Statistics Canada (2022-10-26). "The Canadian census: A rich portrait of the country's religious and ethnocultural diversity". www12.statcan.gc.ca. Retrieved 2022-01-10.
In 2021, just over 25 million people reported being White in the census, representing close to 70% of the total Canadian population. The vast majority reported being White only, while 2.4% also reported one or more other racialized groups.