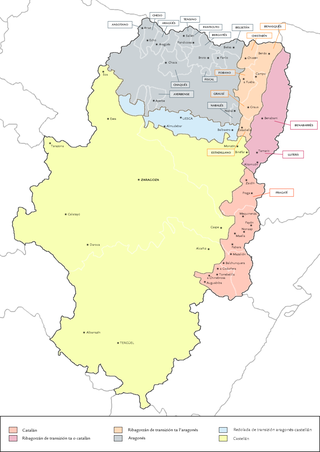
Aragonese is a Romance language spoken in several dialects by about 12,000 people as of 2011, in the Pyrenees valleys of Aragon, Spain, primarily in the comarcas of Somontano de Barbastro, Jacetania, Alto Gállego, Sobrarbe, and Ribagorza/Ribagorça. It is the only modern language which survived from medieval Navarro-Aragonese in a form distinct from Spanish.

Aragon is an autonomous community in Spain, coextensive with the medieval Kingdom of Aragon. In northeastern Spain, the Aragonese autonomous community comprises three provinces : Huesca, Zaragoza, and Teruel. Its capital is Zaragoza. The current Statute of Autonomy declares Aragon a historic nationality of Spain.

Zaragoza also known in English as Saragossa, is the capital city of the province of Zaragoza and of the autonomous community of Aragon, Spain. It lies by the Ebro river and its tributaries, the Huerva and the Gállego, roughly in the centre of both Aragon and the Ebro basin.

Moschidae is a family of pecoran even-toed ungulates, containing the musk deer (Moschus) and its extinct relatives. They are characterized by long 'saber teeth' instead of horns, antlers or ossicones, modest size and a lack of facial glands. While various Oligocene and Miocene pecorans were previously assigned to this family, recent studies find that most should be assigned to their own clades, although further research would need to confirm these traits. As a result, Micromeryx, Hispanomeryx, and Moschus are the only undisputed moschid members, making them known from at least 18 Ma. The group was abundant across Eurasia and North America during the Miocene, but afterwards declined to only the extant genus Moschus by the early Pleistocene.

The taifas were the independent Muslim principalities and kingdoms of the Iberian Peninsula, referred to by Muslims as al-Andalus, that emerged from the decline and fall of the Umayyad Caliphate of Córdoba between 1009 and 1031. They were a recurring feature of al-Andalus history.

The Crown of Aragon was a composite monarchy ruled by one king, originated by the dynastic union of the Kingdom of Aragon and the County of Barcelona and ended as a consequence of the War of the Spanish Succession. At the height of its power in the 14th and 15th centuries, the Crown of Aragon was a thalassocracy controlling a large portion of present-day eastern Spain, parts of what is now southern France, and a Mediterranean empire which included the Balearic Islands, Sicily, Corsica, Sardinia, Malta, Southern Italy, and parts of Greece.

Eleanor of Navarre,, was a Navarrese princess and monarch. She served as the regent of Navarre from 1455 to 1479, during the absence of her father, and then briefly as the queen regnant of Navarre in 1479. She was crowned on 28 January 1479 in Tudela.

Pecora is an infraorder of even-toed hoofed mammals with ruminant digestion. Most members of Pecora have cranial appendages projecting from their frontal bones; only two extant genera lack them, Hydropotes and Moschus. The name "Pecora" comes from the Latin word pecus, which means "cattle". Although most pecorans have cranial appendages, only some of these are properly called "horns", and many scientists agree that these appendages did not arise from a common ancestor, but instead evolved independently on at least two occasions. Likewise, while Pecora as a group is supported by both molecular and morphological studies, morphological support for interrelationships between pecoran families is disputed.

The Antilocapridae are a family of ruminant artiodactyls endemic to North America. Their closest extant relatives are the giraffids. Only one species, the pronghorn, is living today; all other members of the family are extinct. The living pronghorn is a small ruminant mammal resembling an antelope.

Hemicyon, also known as the "dog-bear", is an extinct genus of hemicyonine bear, which probably originated in Eurasia but was found in Europe, Asia and North America during the Miocene epoch, existing for approximately 16 to 13 mya. Hemicyon is the best-known genus in the Hemicyoninae, a subfamily intermediate between bears and their Caniform ancestors but most often classified as bears. Hemicyonid bears should not be confused with Amphicyonids (bear-dogs), which are their own separate family of carnivores.

Monzón is a small city and municipality in the autonomous community of Aragon, Spain. Its population was 17,176 as of 2014. It is in the northeast and adjoins the rivers Cinca and Sosa.
Marcelino Martínez Cao, known simply as Marcelino, is a Spanish former footballer who played as a striker.

Real Zaragoza Deportivo Aragón is the reserve team of Real Zaragoza, a Spanish football club based in Zaragoza, in the autonomous community of Aragon. Founded in 1958, currently plays in Segunda Federación – Group 2, holding home matches at Ciudad Deportiva del Real Zaragoza, with a capacity of 2,500 seats.

Cercanías Zaragoza is the name given to the Renfe operated commuter train service in and around the city of Zaragoza, in Aragon, Spain.

Joaquín Ascaso Budría was an Aragonese anarcho-syndicalist and President of the Regional Defence Council of Aragon between 1936 and 1937.

Triceromeryx is an extinct genus of Artiodactyla, of the family Palaeomerycidae, endemic to Europe from the middle Miocene epoch, 16.9—16.0 Ma, existing for approximately 0.9 million years.

Micromeryx is an extinct genus of musk deer that lived during the Miocene epoch. Fossil remains were found in Europe and Asia. The earliest record (MN4) of the genus comes from the Sibnica 4 paleontological site near Rekovac in Serbia.

Palaeomeryx is an extinct genus of Artiodactyla, of the family Palaeomerycidae, endemic to Europe and Asia from the Miocene epoch, 16.9 – 7.25 Ma, existing for approximately 9.65 million years.
Synthetoceratinae is an extinct subfamily of Protoceratidae, deer-like herbivorous mammals belonging to the order Artiodactyla. They were endemic to North America during the Miocene epoch, living 23.03—3.9 Ma, existing for approximately 19.13 million years.
Kyptoceratini is an extinct tribe of the subfamily Synthetoceratinae, deer-like mammals within the family Protoceratidae belonging to the order Artiodactyla, endemic to North America during the Miocene through Pliocene, living 23.03—3.6 Ma, existing for approximately 19.43 million years.

















