
Ticks are parasitic arachnids that are part of the mite superorder Parasitiformes. Adult ticks are approximately 3 to 5 mm in length depending on age, sex, species, and "fullness". Ticks are external parasites, living by feeding on the blood of mammals, birds, and sometimes reptiles and amphibians. The timing of the origin of ticks is uncertain, though the oldest known tick fossils are from the Cretaceous period, around 100 million years old. Ticks are widely distributed around the world, especially in warm, humid climates.
Tick-borne diseases, which afflict humans and other animals, are caused by infectious agents transmitted by tick bites. They are caused by infection with a variety of pathogens, including rickettsia and other types of bacteria, viruses, and protozoa. The economic impact of tick-borne diseases is considered to be substantial in humans, and tick-borne diseases are estimated to affect ~80 % of cattle worldwide.
Alkhurma virus (ALKV) is a zoonotic virus of the Flaviviridae virus family. ALKV causes Alkhurma hemorrhagic fever (AHF), or alternatively termed as Alkhurma hemorrhagic fever virus, and is mainly based in Saudi Arabia.
Relapsing fever is a vector-borne disease caused by infection with certain bacteria in the genus Borrelia, which is transmitted through the bites of lice or soft-bodied ticks.
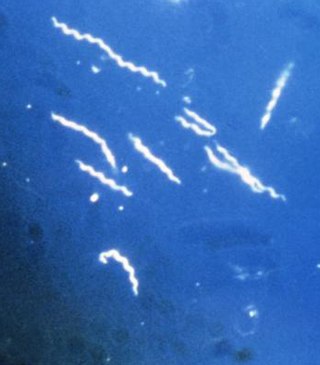
Borrelia is a genus of bacteria of the spirochete phylum. Several species cause Lyme disease, also called Lyme borreliosis, a zoonotic, vector-borne disease transmitted by ticks. Other species of Borrelia cause relapsing fever, and are transmitted by ticks or lice, depending on the species of bacteria. A few Borrelia species as Candidatus Borrelia mahuryensis harbor intermediate genetic features between Lyme disease and relapsing fever Borrelia. The genus is named after French biologist Amédée Borrel (1867–1936), who first documented the distinction between a species of Borrelia, B. anserina, and the other known type of spirochete at the time, Treponema pallidum. This bacterium must be viewed using dark-field microscopy, which make the cells appear white against a dark background. Borrelia species are grown in Barbour-Stoenner-Kelly medium. Of 52 known species of Borrelia, 20 are members of the Lyme disease group, 29 belong to the relapsing fever group, and two are members of a genetically distinct third group typically found in reptiles. A proposal has been made to split the Lyme disease group based on genetic diversity and move them to their own genus, Borelliella, but this change is not widely accepted. This bacterium uses hard and soft ticks and lice as vectors. Testing for the presence of the bacteria in a human includes two-tiered serological testing, including immunoassays and immunoblotting.

Lyme disease, or borreliosis, is caused by spirochetal bacteria from the genus Borrelia, which has 52 known species. Three main species are the main causative agents of the disease in humans, while a number of others have been implicated as possibly pathogenic. Borrelia species in the species complex known to cause Lyme disease are collectively called Borrelia burgdorferisensu lato (s.l.) not to be confused with the single species in that complex Borrelia burgdorferi sensu stricto which is responsible for nearly all cases of Lyme disease in North America.

Borrelia hermsii is a spirochete bacterium that has been implicated as a cause of tick-borne relapsing fever. It is spread by the soft-bodied tick Ornithodoros hermsi.
Carios erraticus, formerly called Ornithodoros erraticus, is a species of tick in the family Argasidae. The tick was described by Hippolyte Lucas in 1849.

Ornithodoros is a genus in the soft-bodied tick family, Argasidae.

Ornithodoros hermsi is a species of soft tick. It can be infected with Borrelia hermsii.
Borrelia duttoni, formerly known as Spirochaeta duttoni, is a species of Borrelia.

Ornithodoros moubata, commonly known as the African hut tampan or the eyeless tampan, is a species of tick in the family Argasidae. It is an ectoparasite and vector of relapsing fever in humans, and African swine fever in pigs.
Borrelia miyamotoi is a bacterium of the spirochete phylum in the genus Borrelia. A zoonotic organism, B. miyamotoi can infect humans through the bite of several species of hard-shell Ixodes ticks, the same kind of ticks that spread B. burgdorferi, the causative bacterium of Lyme disease. Ixodes ticks are also the primary vector in the spread of babesiosis and anaplasmosis.
Borrelia turicatae is a bacterial species of the spirochaete class of the genus Borrelia. It is one of the relapsing fever spirochaetes, which are globally distributed yet understudied agents of tick-borne relapsing fever. The tick vector Ornithodoros turicata transmits B. turicatae, which causes relapsing fever, an arthropod-borne infection of humans and other mammals caused by different Borrelia species. B. turicatae is long and spiral-shaped, as is typical for all spirochaetes. It is a Gram-negative bacterium and visible with light microscopy. Few epidemiological studies have been performed and few molecular data exist for B. turicatae and its arthropod vector O. turicata.
Borrelia coriaceae is a species of spirochete bacteria and member of the genus Borrelia. Strains of this species have been isolated from the soft tick Ornithodoros coriaceus and from mule deer.

Ornithodoros savignyi, known as sand tampan, African eyed tampan or Kalahari sand tampan, is one of some 37 species in the genus Ornithodoros and is a soft tick with a leathery, mammillated integument, causing paralysis and tampan toxicosis, two unrelated conditions. The sand tampan is an ectoparasite on humans, their livestock and wild animals, including birds and bats. Occurring in semi-desert areas of Africa, Saudi Arabia and other parts of the Persian Gulf, India, Sri Lanka and into Asia, it is able to survive for lengthy periods without feeding, spending most of its life burrowed under sand or loose soil, often in wait for animals that rest or sleep under trees or in the lee of rocks, but also in places where people or their animals congregate such as marketplaces, places of worship, cattle kraals and village squares. The timing of its activity is geared to coincide with that of potential hosts, but hot sunny conditions are usually avoided. Because of its habit of feeding and dropping from its host, adult dispersal is limited, whereas larvae may remain attached to their hosts for several days. During its life cycle it will feed on multiple hosts between moults.
Royal Farm virus, previously known as Karshi virus, was not viewed as pathogenic or harmful to humans. Although infected people suffer with fever-like symptoms, some people in Uzbekistan have reported with severe disease such as encephalitis and other large outbreaks of fever illness connected infection with the virus.
Ornithodoros alactagalis, the relapsing fever tick, is a species of soft tick in the family Argasidae.
Ornithodoros brasiliensis is a species of tick in the family Argasidae, or soft-bodied ticks, that occurs exclusively in Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. O. brasiliensis is a known parasite of humans, dogs, and smaller mammals such as armadillos and skunks.

Global climate change has increased the occurrence of some infectious diseases. Those infectious diseases whose transmission is impacted by climate change include for example the vector-borne diseases dengue fever, malaria, tick-borne diseases, leishmaniasis, zika fever, chikungunya and Ebola virus disease. One of the mechanisms for increased disease transmission is that climate change is altering the geographic range and seasonality of the insects that can carry the diseases. Scientists stated a clear observation in 2022: "the occurrence of climate-related food-borne and waterborne diseases has increased ."







